Weather
advertisement

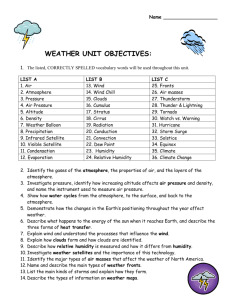
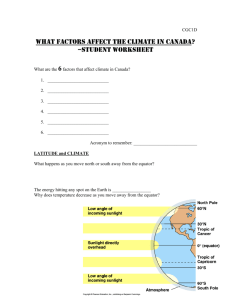
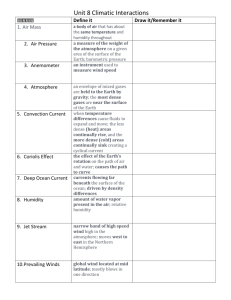
WEATHER PUTTING IT ALL TOGETHER FIRST, WHAT DID WE LEARN SO FAR? ON THE FOLLOWING SLIDES… There will be a 1 minute think session. Then, a 1 minute talk session. A group will be randomly selected. Each member of the group must answer a question. Correct answers are worth 1 point. THE ATMOSPHERE I will evaluate the effect humans have on the atmosphere. 1. The atmosphere is divided up … 2. The Earth is naturally warmed by … 3. Global warming is … 4. A question you could investigate is … EARTH’S MOTION AND SEASONS I will analyze the seasonal changes in each hemisphere. 1. The difference between rotation and revolution is … 2. Earth’s axis is tilted at … 3. Seasons on Earth occur because … 4. We would experience one extreme season if … WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE I will analyze the effects of humidity on the atmosphere, including cloud formation and precipitation. 1. Types of precipitation include … 2. Clouds form when … 3. A high relative humidity means … 4. Renovations at LV affect the water cycle by … THE WEATHER WATCH PROJECT TAUGHT YOU THAT… The type of cloud is an indicator of weather. Give an example. Rain and humidity meant a drop in air pressure. Why? Weather tends to move in the same direction across the USA. Which direction? Forecasting is tricky. Why? DRAW A STATION MODEL FOR CURRENT CONDITIONS IN P’VILLE. sample THE FACTORS THAT AFFECT WEATHER PROJECT TAUGHT US… Humidity vs. Pressure Pressure vs. Temperature Humidity vs. Temperature Wind speed vs. Pressure 100 32 31 80 30 60 29 humidity% 40 28 pressure (in) 27 20 26 0 25 1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 27 29 31 ON THE FOLLOWING SLIDES OF NEW STUFF… Sit with your teams and get your notebooks out. LEARNING TARGET I WILL ANALYZE THE EFFECTS THAT CHANGES IN AIR PRESSURE HAVE ON DIFFERENT LOCATIONS. AIR PRESSURE J S Miller Bill Nye 1. THE BASICS o What is air pressure? o The weight of the atmosphere as it pushes down on Earth’s surface o How is air pressure measured and what is standard? o A barometer measures air pressure in the following units: o o o o 14.7 pounds per square inch 29.92 inches or 760 mm of Mercury 1013.2 millibars or about 1 bar 1 atm At Sea Level 2. UNDERSTANDING o What makes air pressure change? o Humidity makes it decrease. o Temperature makes it decrease. o Wind makes it decrease. o What makes the wind blow? o The greater the pressure gradient, the stronger the wind. o In other words, the greater the change in air pressure between two locations the stronger the wind. o WIND – the movement of air from high to low pressure AIR PRESSURE IS SHOWN ON AN ISOBAR MAP. WIND TENDS TO Clockwise out C. Clockwise in 3. SO WHAT? o What are the purposes of isobars? o Isobars show areas of equal pressure. o High and low pressure systems can be identified. o Wind direction can likely be determined. o What can you conclude from the previous map? CHECK FOR UNDERSTANDING Answer me, these questions 3. TAKE YOUR TEAM TO A NEW TABLE 1 MINUTE LEARNING TARGET I WILL PREDICT THE WIND CONDITIONS FOR A GIVEN LOCATION. WIND 1. THE BASICS o What is the Coriolis Effect? o The tendency of an object moving freely over Earth’s surface to curve away from its path of travel. o What is the jet stream? o A large, fast band of swiftly moving air in the upper troposhere o Our jet stream moves from west to east. o Is the jet stream a result of a local wind or global wind? o Global wind Do you know when the jet stream was discovered? 2. UNDERSTANDING o Earth has different climates because… o The topography and locations of water are different. o The sun heats the Earth unevenly. o Put an X next to the correct statement(s). o ___ Air rises at the poles. o ___ Air rises at the equator. o ___ Air rises at our latitude (39 N). 3. SO WHAT? o What flight is more efficient? Why? o LA to DC or DC to LA or It doesn’t matter. o LA to DC is shorter and uses less fuel because it is with the Westerlies wind belt and the jet stream. o Explain how wind changes from day to night at the shore. In other words, draw a sea breeze, then a land breeze. o See next slides CHECK FOR UNDERSTANDING Answer me, these questions 3. TAKE YOUR TEAM TO A NEW TABLE 1 MINUTE LEARNING TARGET I WILL INFER THE TYPE OF WEATHER THAT PARTICULAR AIR MASSES CAN BRING. AIR MASSES 1. THE BASICS o What characteristics could an air mass have? o Temperature o Moisture 2. UNDERSTANDING o Describe the following air masses. o Continental polar (cP) o Dry and cold o Continental tropical (cT) o Dry and warm o Maritime polar (mP) o Moist and cold o Maritime tropical (mT) o Moist and warm o Continental arctic (cA) o Dry and really cold 3. SO WHAT? o How can a cP air mass bring clear weather to one region while causing heavy snow in another? o cP air is cold and dry and thus brings clear, cold weather to some regions. o If cP air travels over water, however, its moisture increases and it can cause snow. Do these result in high pressure or low pressure? LEARNING TARGET I WILL MAKE A WEATHER FORECAST BASED ON FRONT INFORMATION. FRONTS 1. THE BASICS o What is a front? o The boundary that separates opposing air masses o Name the types of fronts and include their map symbols. 2. UNDERSTANDING o What is the result of each of the front types? o See the next several slides 3. SO WHAT? o A mid-summer cold front is currently in Ohio and moving with the jet stream upper air flow in the upper troposphere. What type of weather will that likely bring us in a day or so? And would this be welcomed by farmers? o Thunderstorms are expected. o If they are currently in a dry spell, the thunderstorms might be welcomed, however, a warm front or stationary front that brings a prolonged, steady rain is best. OVERVIEW VIDEO CLICK HERE. Logon to Safari Montage with your ID and p’word.