Water
advertisement

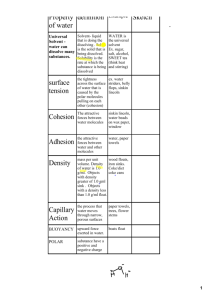
Properties of Water What molecule supports all of life? Water Cycle What is a polar molecule? • Has polar bonds: • Water has polar covalent bonds • Oxygen is more electronegative than H • Electrons of covalent bonds spend more time closer to Oxygen than to H • Creates a polar molecule • O region is partially negative • H regions are partially positive • Causes the properties of water POLAR MOLECULE – O H + H H2O + – HYDROGEN BONDS + Water (H2O) + Hydrogen bond – Ammonia (NH3) + + + States of Water How does this change when water is in different states? • Slightly positive H of 1 molecule is attracted to slightly negative O of nearby molecule creating a H bond that holds those molecules together Water and Polarity Hydrogen bonds What are the Properties of Water? • • • • • • Adhesion Cohesion Surface Tension High specific heat Expands when frozen Universal solvent 1. Cohesion • Cohesion – water “sticking” to itself 1. Cohesion • Cohesion contributes to transport of water and dissolved nutrients against gravity in plants 2. Adhesion Adhesion is water “sticking” to something else • Cohesion is supported by Adhesion • What is Adhesion? • clinging of one substance to another • Adhesion of water to cell walls by those same hydrogen bonds Adhesion vs. Cohesion 3. Surface Tension • How is this related to Surface Tension? • Surface tension= how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid Examples of surface tension Benefits of properties 1-3: • Bugs that walk on water • Bugs that use air bubble to breathe underwater • Leads to transport of water and its dissolved nutrients against gravity in plants • Water molecules leaving plants by evaporation cause H bonds to tug on water molecules, creating an upward force of water in the plant Water and Temperature Hydrogen bonds 4. High Heat Capacity a.k.a. High Specific Heat •Water’s temperature does not change easily •Water can absorb or release a good deal of heat before its overall temperature changes. What is specific heat? • the amount of heat that must be absorbed or lost for 1 g of that substance to change its temperature by 1 °C Evaporative Cooling Benefits of having a high heat capacity: • Keeps temperatures more constant in bodies of water so animals can survive better • Keeps water warm on a cool day and cool on a hot day, and in turn, cools the air around it on a hot day and heats air around it on a cool day • Keeps temperature from fluctuating greatly due to the fact that oceans cover the earth • Helps moderate Earth’s climate • Contributes to stability of temperature in lakes and ponds • Prevents land organisms for overheating What happens to the ice? 5. Expansion Upon Freezing • Water is less dense as a solid than as a liquid • Ice Floats • Begins freezing when its molecules are no longer moving vigorously enough to break their hydrogen bonds • Becomes about 10% less dense Hydrogen Bond angles Benefits of water expanding upon freezing: •Fish get to survive in cold temperatures •We get cold drinks 6. Universal Solvent A few terms regarding solutions… • Solution• Liquid that is completely homogeneous mixture of two or more substances • Solvent• Dissolving agent of a solution • Solute• Substance that is dissolved • Aqueous solution• Solution in which water is the solvent Solution Suspension Colloid (This is why you should shake milk first!) Why is water a versatile solvent? • Due to polarity of the ions • Ions have mutual affinity through electrical attraction of the opposite charges • Compounds don’t have to be ionic to dissolve water • Dissolve when water molecules surround each of the solute molecules, forming hydrogen bonds with them •Hydrophilic – any substance that “loves” water and dissolves easily into it •Hydrophobic – any substance that “hates” or repels water and will not mix with it Benefits of water’s solubility: •Allows the movement of solvents through cohesion •Makes the solvent hydrophilic, benefitting cellular processes QUIZ TIME! • The model illustrates hydrogen bonding found in water. This attraction between water molecules is the result of water’s • A ionic bonding. • B polar covalent bonding. • C positively charged atoms. • D negatively charged atoms. Which property of water is displayed here? Which property of water is displayed here? Which property of water is displayed here? Which property of water is displayed here? Which property of water is displayed here? Which property of water is displayed here?