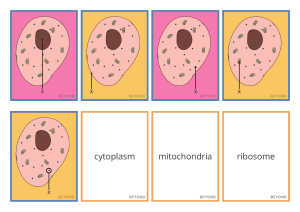
Cell structure and function animal and plant cells
advertisement

National 4/5 Biology Unit 1: Cell Biology Section a: Cell Structure and Function What do you remember? A B C D What are we learning today? • We are learning to: recognise the difference between a plant and an animal cell • Success criteria: – I can name the structures of plant and animal cells – I can state the functions of the structures of a plant and animal cell – I can recognise diagrams and explain the differences between a plant and animal cell Some starter information • • • • • Cells are the basic units of life All living organisms contain cells There are many different types of cells Unicellular organisms are made up of just one cell Multicellular organisms are made up of many cells • Cells can be stained to see cell structures more clearly Animal cell structure 1. Cytoplasm 2. Ribosome 3. Nucleus 4. Mitochondria 5. Cell membrane Structure and function 1. Cytoplasm Site of biochemical reactions 2. Ribosome Site of protein synthesis 3. Nucleus Contains genetic information. Control centre of the cell 4. Mitochondria Site of aerobic respiration 5. Cell membrane Controls what enters and exits the cell Cheek epithelial cells: Example of animal cell Plant cell structure 1. Mitochondria 2. Vacuole 3. Chloroplast 4. Ribosome 5. Nucleus 6. Cytoplasm 7. Cell membrane 8. Cell wall Structure and function 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Mitochondria Site of aerobic respiration Vacuole Contains watery cell sap Chloroplast Site of photosynthesis Ribosome Site of protein synthesis Nucleus Contains genetic information. Control centre of the cell Cytoplasm Site of biochemical reactions Cell membrane Controls what enters and exits the cell Cell wall Boundary round plant cell, maintains cell shape. Freely permeable Examples of plant cells Onion Rhubarb Elodea What do all these cells appear to have in common?