Ch. 22: Organic Chemistry
advertisement

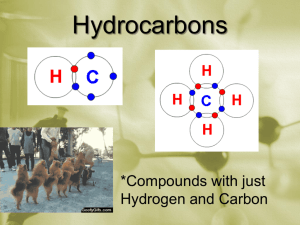
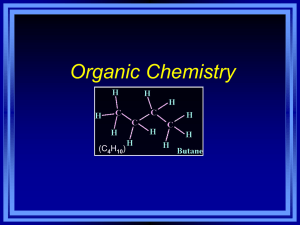
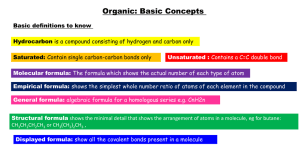
Ch. 22: Organic Chemistry 22.1 Alkanes Alkanes saturated hydrocarbons only single bonds each C has 4 atoms bonded to it all C have tetrahedral arrangement sp3 hybridization straight-chained, normal, unbranched hydrocarbons with no substituent groups are long chain alkanes Alkanes really a zigzag shape because of 109.5° in C-C-C bond structural isomers different molecules with same atoms (formula) different bonding have different properties C4H10 C4H10 Naming Find the longest chain of carbons If there are substituent groups, number the carbons in the chain from one end to the other count the number and find the prefix name is prefix and –ane ending for alkanes make the #s for groups as small as can Name the groups by taking the prefix for the number of carbons in the group and add -yl Naming the positions of each group are given by the #s of the carbon they are attached to put hyphen between # and group and a comma between #s For more than 1 group, list then in alphabetical order add prefix (di, tri, etc) if there are more than one of the same type Practice Naming longest 1 chain is 3 name: propane C group: methyl group off of #2 carbon 2-methylpropane longest chain is 3 2- methyl groups 2,2-dimethylpropane Practice Naming Reactions with Alkanes fairly unreactive combustion always added to O2 always makes CO2 and H2O substitution when a halogen is added to it, one halogen may replace one hydrogen CH4 + Cl2 CH3Cl + HCl dehydrogenation 2H atom are removed to form unsaturated CH3CH3 CH2=CH2 + H2 cyclopropane planar unstable cyclobutane planar and unstable cyclopentane planar and stable cyclohexane puckered and stable Cyclic Alkanes Unsaturated: Alkenes and Alkynes alkenes: contain at least one double bond alkynes: contain at least one triple bond change the ending of name to –ene or –yne add a # telling the starting position of the special bond Unsaturated: Alkenes and Alkynes can also have unsaturated rings cyclohexene double bonds prevent rotation cis-trans isomerism: cis- identical groups on same side of bond trans – identical groups on opp side of bond Reactions: Alkenes and Alkynes Addition Reactions Hydrogenation: add hydrogen pair to remove special bond CH2=CHCH3 + H2 CH3-CH2-CH3 Halogenation: add halogen pair to remove special bond CH2=CHCH3 + Br2 CH2Br-CHBr-CH3 Aromatic Hydrocarbons cyclic unsaturated hydrocarbons benzene phenyl group: when attached to a chain functional groups