STM-WM

Summary: Iconic Memory
• Capacity: Very large
• Duration: Very short
• Transfer: Readout to STM
• Loss: Phenomenon of backward masking (and its necessity!)
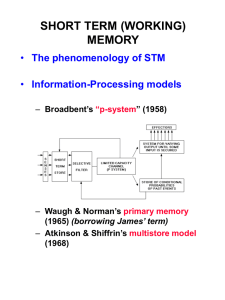
A Multi-store model of memory
• Benefits and limitations
• First memory: sensory store
• Next: Short term memory
Short term memory
• Current contents of memory
• Fundamental bottleneck in processing
• Multiple interpretations
• Capacity
• Duration
• Transfer
• Loss
Basic Operations of STM
• How things enter it
• How things stay in it.
• How we search for things within it.
• How things leave it
Peterson & Peterson: Decay
Waugh & Norman: Interference
Sternberg: Memory scanning
STM-WM (an alternative view)
• Another way of looking at it (STM vs Working
Memory) (Baddeley)
• The "bottleneck" issue and an example or two.
• Beating the limits--the work of Chase and
Ericcsson: chunks & retrieval structures.
• Finally, how do things move on--elaborative rehearsal
Baddeley: Model of
Working Memory
Chase, Ericcsson & Staszewski: Retrieval Structures
Moving on: LTM
• Issues include
– How things move on into LTM
– Size of LTM
– Is LTM “permanent”?
– Memory formation impairment
Permanence of LTM
• Work of Wilder Penfield
• Size of LTM (on assumption of permanence)
– 100,000,000,000 neurons x 10,000 connections =
10 15
– Input: time per percept 150 msec x 70 years x 10 4 bits per percept x 70 years = 10 14 bits
– Optic nerve capacity10 7 bits per second x 70 years =
10 16 bits.
– Pragmatic est. 100,000 words + 10,000 pictures +
75,000 chess patterns + 1000’s of episodes = 10 6
– But some argue that we forget most of what we input!
Long Term Memory Can be Long-term!
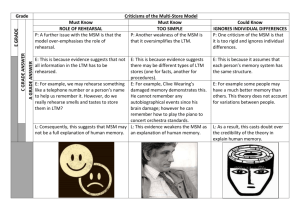
Earned an A grade- green, C grade- red (Study Hard!)
Most Famous Memory: HM
• Retrograde amnesia vs anterograde
• Declarative (semantic + episodic) vs procedural distinction in memory type
• How does this occur? –hippocampus and overlying cortical damage
Memory formation environmental effects
Memory operations in thinking:single/multiple codes?
*
Response->
Stimulus
Diagram
Pointing Vocal
28.2 11.3
Sentence 9.8 13.8
Collins & Quillien Experiment
John Anderson (CMU) ACT Model