WMM 3
advertisement

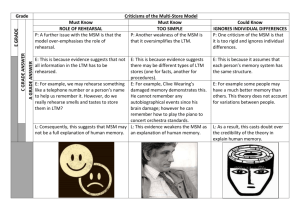
Instructions Individually, choose a component of working memory. Write a short paragraph describing the main features of this working memory component and outline a piece of research that supports the existence of this component. Use your notes and the research table from last week to help you. You have 15 minutes! Evaluation: Strengths and Weaknesses of the WMM Comparing the WMM and the MSM Specification Content What does this mean? The working memory model, including its strengths and limitations Describe and evaluate the working memory model. To outline case studies on brain-damaged patients to support the working memory model. To be able to evaluate the working memory model in terms of strengths and weaknesses. To compare the working memory model with the multi-store model of memory. Case studies on brain-damaged patients can provide support for the working memory model. What is a case study? A case study is a detailed study of one individual or event. KF suffered brain damage from a motorcycle accident that damaged his STM yet his LTM was normal. His performance on visual tests was better than his performance on auditory tests. This suggests that there are separate STM components for visual information (visuo-spatial sketchpad) and verbal information (phonological loop) and that KF’s brain damage was restricted to the phonological loop. LH suffered brain damage from a road accident. It was found that LH performed better on spatial tasks than those involving visual imagery. This case study suggests separate visual and spatial systems thus supporting the existence of the visuo-spatial sketchpad in working memory. Considerable amount of research to support the model. Continuing development of the model. Explains observations made by psychologists such as the wordlength effect and the partial short-term memory difficulties experienced by individuals with brain damage, such as KF and LH. An advance of STM as it is concerned with both active processing and the brief storage of information; relevant to activities such as mental arithmetic. Performance on almost any task of any complexity relies on some combination of the three major components in working memory, indicating that they are important parts of the human cognitive processing system. Little is known about the central executive, and it has been argued that it is probably more complex than it is currently represented. Most research has focused on the slave components rather than the central executive. The explanation and terminology used to describe the central executive is vague . The notion of a single central executive has been criticised. The three main components of the working memory model interact with each other in the performance of many tasks but it is not very clear how this happens in practice. How is the multi-store model of memory different to the working memory model in terms of the types of memory that it focuses on? Structural vs. functional models of memory: Which model is which? How does the concept of verbal rehearsal differ between the two models of memory? How does the concept of LTM differ between the two models of memory? How does the case study of KF support the WMM? Can it be used to support the MSM and if so, how? How do the two models differ in their explanation of STM?