Unit 2 Study Guide:
advertisement
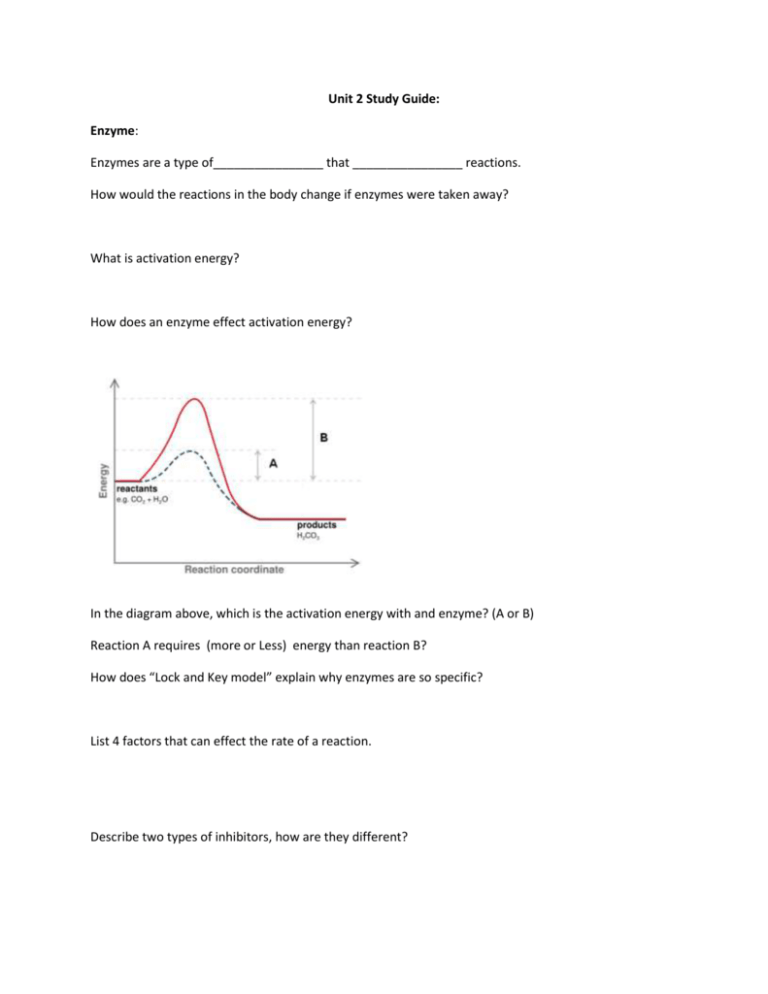
Unit 2 Study Guide: Enzyme: Enzymes are a type of________________ that ________________ reactions. How would the reactions in the body change if enzymes were taken away? What is activation energy? How does an enzyme effect activation energy? In the diagram above, which is the activation energy with and enzyme? (A or B) Reaction A requires (more or Less) energy than reaction B? How does “Lock and Key model” explain why enzymes are so specific? List 4 factors that can effect the rate of a reaction. Describe two types of inhibitors, how are they different? Explain what this diagram above is showing. r How is an enzyme affected by being outside its “range”(such as pH or temperature range)? What does it mean when an enzyme is denatured? Acids / Bases: Draw and label the range of the pH scale, label the acidic, neutral, and basic regions? Water: What is surface tension, and what makes it possible? How does soap effect surface tension? What is cohesion? What is adhesion? What is capillary action? Organic compounds: What element do ALL organic compounds contain? List 2 examples of monosaccharides, and where they are found in life. List 2 examples of disaccharides, and where they are found in life. List 3 examples of polysaccharides, and where they are found in life. Draw the structures of the following 2 monosaccharides, 1 disaccharide. glucose: fructose: Which polysaccharide is un-digestible by humans? Proteins: What are the building blocks of proteins? Name an 3 examples of a protein's function in life. Sucrose: Lactose: Lipids: List 2 examples of lipids, and explain their function in life. What parts make up a lipid (triglyceride)? What are the 3 main difference between a saturated fat and an unsaturated fat? Which one is saturated: Nucleic Acids: What are the building blocks of nucleic acids? Name 2 examples of nucleic acids, and explain their function.