Store energy by adding a phosphate to ADP (forming ATP).
advertisement

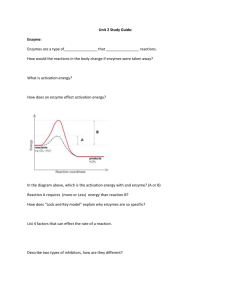
Biology --Unit 1-Review Flashcards •Store energy by adding a phosphate to ADP (forming ATP). What can ATP be used •Release energy by removing a for in cells? phosphate from ATP. •CHONPS •Carbon, ListHydrogen, out all ofOxygen, the Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sulfur biological elements: •Able to maintain homeostasis. •Able to grow/develop. •Able to respond/adapt/evolve. What characteristics are •Able to reproduce. required to be living? •Able to metabolize and excrete. •Basic Units of Matter = Atoms •Basic Units of Life = Cells What are the basic units of matter? Of life? •Chemical Potential Energy: Energy in the bonds of Whatstored is the difference molecules. between chemical potential •Kinetic Energy: and kinetic Energy being used right now in a energy? chemical reaction. •They cannot do any of the following on their own (or without a host cell): Why are viruses NOT •Maintain homeostasis considered •Grow / Developto be •Metabolize / Excrete •Reproduce living? •Carbohydrate Monomers = Monosaccharides •Lipid Monomers = Fatty Acids + Glycerol •Protein Monomers = Amino Acids •Nucleic Acid Monomers = List out the Monomers for: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins and Nucleic Nucleotides Acids •Carbohydrate Polymers = Polysaccharides •Lipid Polymers = Phospholipids, Fats, Oils •Protein Polymers = Polypeptides, Enzymes •Nucleic Acid Polymers = DNA & RNA List out the Polymers for: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids •Provide cells with: Immediate energy …and… What are the functions Intermediate energy of carbohydrates? •Provide cells with long term energy storage. What are the functions •Form cell membranes. of lipids? •Catalyze chemical reactions. •Express instructions in DNA. What are the functions of proteins? •Provide cells with genetic instructions to make protein. What are the functions of nucleic acids? •There is an uneven distribution of charge across the surface of a molecule. (One end of the molecule is more What does polar mean? positively charged, and the other end is more negatively charged.) •The structure of the active site on the ENZYME changes. •The enzyme can no longer What happens when an function in the reaction. enzyme is denatured? •The enzyme can no longer INCREASE the speed of the reaction. 1) Dehydration Synthesis 2) Water is being removed. 3) The monomers are being bonded For this diagram: together to form a polymer. 1) What is the name of the process? 4) Cells use this to store energy in 2)What is happening with water? newly formed bonds. 3) What is happening with the molecules? 4) What is this process used for? 1) Hydrolysis 2) Water is being added. 3) The polymer is being broken apart into individual monomers. For this 4) Cells use this todiagram: release energy 1) What is the name of the process? from2)What the broken is happeningbonds. with water? 3) What is happening with the molecules? 4) What is this process used for? •Speed up the rate (make it go faster). What do enzymes do to chemical reactions? •Carbohydrates What type of biomolecule are starches and sugars? •Carbon What is the most common and important biological element? •To make/build cell membranes. What is the function of phospholipids? •Dehydration Synthesis What reaction bonds together monomers to form larger polymers? •Hydrolysis Which reaction breaks apart polymers to form smaller monomers? •Hydrolysis Which reaction is used to release energy? •Dehydration Synthesis Which reaction is used to store energy? •A protein in our blood that allows oxygen to bind to our red blood cells. What is hemoglobin? •By removing a phosphate. How is energy released from ATP? •A phosphate is added. How is energy stored in ADP? •Since Benedict tests for Monosaccharides: A•The solution reactsmonosaccharides. with Benedict solution contains •The solution provides short term energy. and Iodine (which test for monosaccharides and •Since Iodine tests for Polysaccharides: •The solution contains polysaccharides. polysaccharides). •The solution provides intermediate energy. List out everything you know about this solution: •Since Sudan tests for Lipids: • It contains lipids. • It is made of fatty acids and glycerol. • It could form cell membranes or provide long term energy storage. A solution reacts with Sudan (which test for lipids). List out everything you know about this solution: •Since Biuret tests for Proteins: • It contains proteins. • It is made of amino acids. • It could catalyze chemical reactions. A solution reacts with Biuret (which test for proteins). List out everything you know about this solution: Draw 2 graphs to compare monosaccharides and polysaccharides. •The monosaccharide line shows a quick spike and Energy Monosaccharide Time Energy Polysaccharide Time drop in energy, because monosaccharides provide a short burst of energy. •The polysaccharide line shows longer lasting energy, because polysaccharides provide intermediate energy. Explain why you drew them like this… Draw 2 graphs to compare a reaction happening WITH an enzyme, and one WITHOUT an •The “with” line is shorter, because enzymes allow enzyme. reactions to happen with less (or decreased) Activ. Energy “WITH” Time Activ. Energy “WITHOUT” Time activation energy required. •The “without” line is taller, because without an enzyme, more activation energy is required to get the reaction going. Explain why you drew them like this… • Enzymes denature at high temperatures (like what you have when you have a fever). • When an enzyme denatures, the structure of its active site changes… • This prevents the substrate from binding to it… • Which means the enzyme can’t function in that reaction anymore. • Living things rely on chemical reactions and enzymes to stay alive, so without enzymes, the living thing can die. Explain why fevers are dangerous to enzymes and living organisms: • A living thing should: • Be made of cells. • Be made of water. • Be made of 6 biological elements (CHONPS). • Be made of 4 biomolecules (Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids, Nucleic Acids). • Be able to do the following on its own: Explain what scientists can use to identify if something is living: • Grow • Reproduce • Adapt/Evolve • Metabolize / Excrete • Maintain Homeostasis