218.Atomic and Lewis Model Practice
advertisement
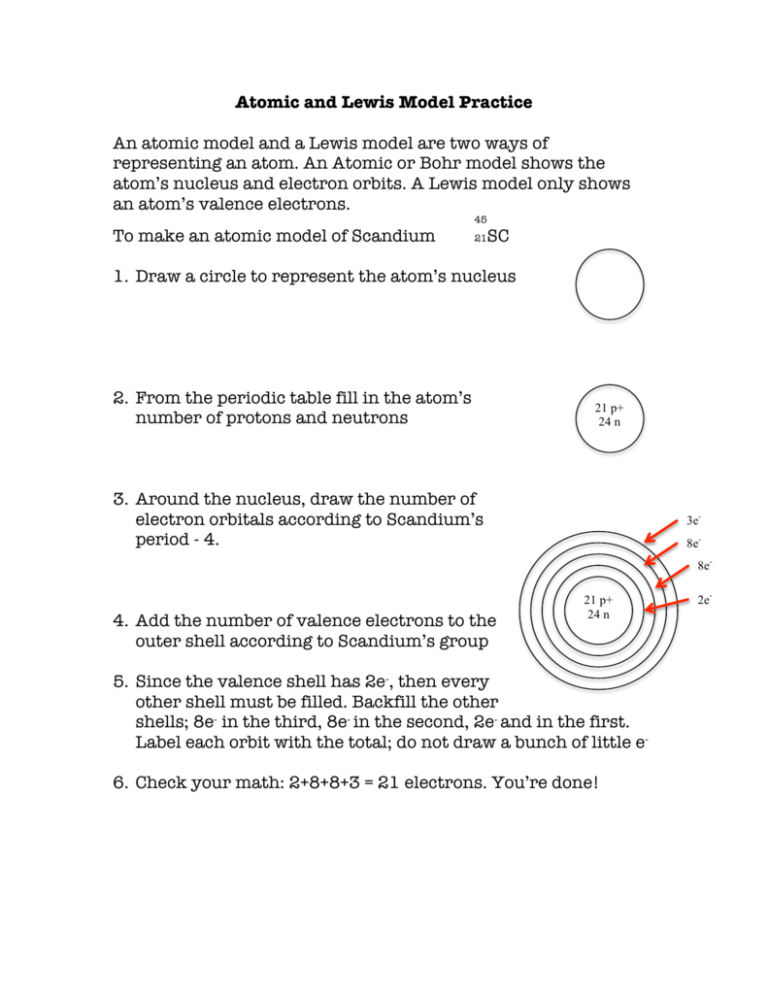
Atomic and Lewis Model Practice An atomic model and a Lewis model are two ways of representing an atom. An Atomic or Bohr model shows the atom’s nucleus and electron orbits. A Lewis model only shows an atom’s valence electrons. 45 To make an atomic model of Scandium 21 SC 1. Draw a circle to represent the atom’s nucleus 2. From the periodic table fill in the atom’s number of protons and neutrons 21 p+ 24 n 3. Around the nucleus, draw the number of electron orbitals according to Scandium’s period - 4. 3e8e8e- 4. Add the number of valence electrons to the outer shell according to Scandium’s group 21 p+ 24 n 5. Since the valence shell has 2e-, then every other shell must be filled. Backfill the other shells; 8e- in the third, 8e- in the second, 2e- and in the first. Label each orbit with the total; do not draw a bunch of little e6. Check your math: 2+8+8+3 = 21 electrons. You’re done! 2e- For a Lewis model, Gilbert Lewis was only Lewis was only concerned with valence electrons. 1. In large letters, write the element’s symbol Sc 2. Lewis used dots to indicate valence electrons. Determine the number of Scandium’s valence electrons according to its group – 3. Starting at 3:00, draw a dot slightly higher than center. Sc 3. Add further electrons, one at a time, at 6, 9, and 12:00. If an element has more than 4 valence electrons, start again at 3:00, finishing with up to 8 back at 12:00 and aligning the electrons as shown below. Remember, a Lewis model is limited to the maximum number of valence electrons - 8 4. 4 8 3 7 1 5 2 6 5. and done! Sc







