Lewis Structures - The University of Texas at San Antonio
advertisement

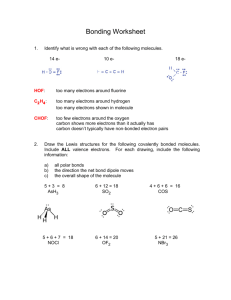
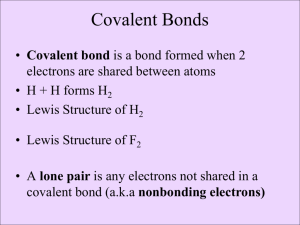
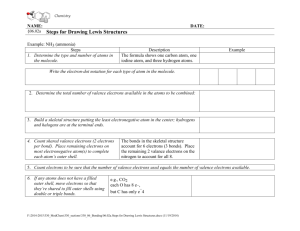
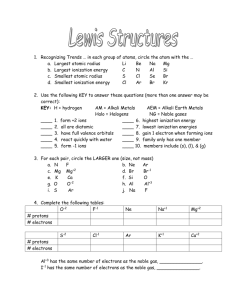
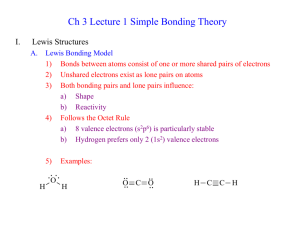
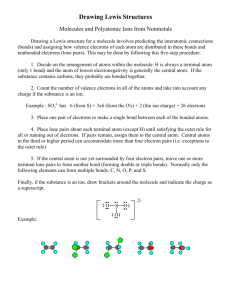
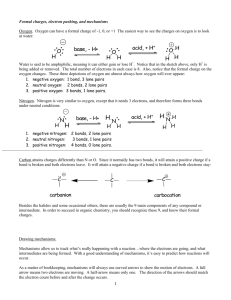
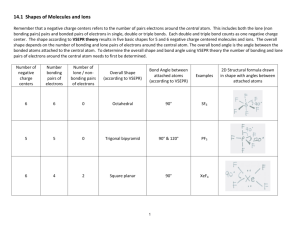
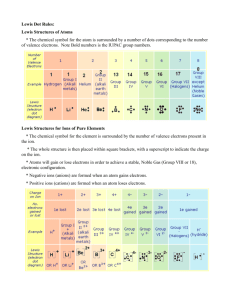
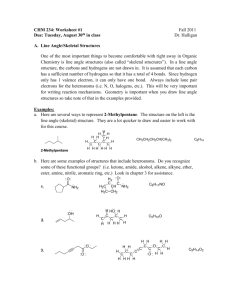
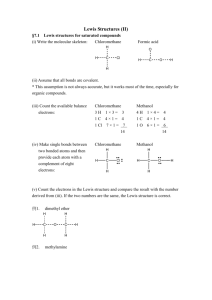
Org. Chem I Handout #1 DRAWING LEWIS STRUCTURES General rules to follow: 1. 2. 3. Draw only the valence electrons Assign no more than 8 electrons to second‐row elements Each hydrogen only gets two electrons The number of bonds in most covalent molecules or polyatomic ions may be calculated using the equation: # of covalent bonds = # of electrons shared / 2 (electrons per bond) In neutral species: Element need ‐ available = # e‐ shared carbon 8 ‐ 4 = 4 hydrogen 2 ‐ 1 = 1 nitrogen 8 ‐ 5 = 3 oxygen 8 ‐ 6 = 2 How to draw Lewis structures: Step 1: Arrange the atoms next to each other with hydrogen and halogen atoms on the periphery (since they can only form one bond). Example: H For CH4: H H C put H's on the periphery H H For CH3OH: H O C H H Step 2: Count the electrons. Examples: CH4 CH3OH 1 C x 4 e‐ = 4 e‐ 4 H x 1 e‐ = 4 e‐ TOTAL = 8 e‐ 1 C x 4 e‐ 1 O x 6 e‐ 4 H x 1 e‐ TOTAL= 14 e‐ Copyright © Doug E. Frantz The University of Texas at San Antonio Org. Chem I Handout #1 Step 3: Add the bonds and lone pairs. H For CH4: H 8 e- total (2 per bond) all e- accounted for correct Lewis structure H C H H H add lone pairs For CH3OH: H O C H H H C O H H 14 e- total correct Lewis structure does not satisfy octect rule only 10 eaccounted for so far Formal Charges You can determine the formal charge of each atom using the following equation: Formal charge = # of valence e­ ­ # of e­ an atom “owns” For simplicity, an atom “owns” all of its unshared e‐ and half of its shared electrons. The formal charge of a molecule is the sum of the formal charges of all of its constituent atoms. Example: Calculate the formal charge on oxygen. H3C O CH3 CH3 1. 2. # of e‐ owned by O = 2 (lone pair) + ½(6) = 5 formal charge on O = 6 – 5 = +1 Formal charges are always indicated with a + or – sign to indicate the charge as positive or negative. Resonance Structures Many times it is more realistic (based on physical data) to represent a molecule or ion as a composite of a number of classical structures. Example: The nitrate anion. O O O O O O N N N O O O ! O O N The ! symbol is used to indicate "partial" charge (either positive or negative) O ! classical, localize contributing structures ! non-classical, delocalized hybrid resonance structure dashed lines are using to indicate "partial" bonding character Copyright © Doug E. Frantz The University of Texas at San Antonio