Vocabulary
advertisement

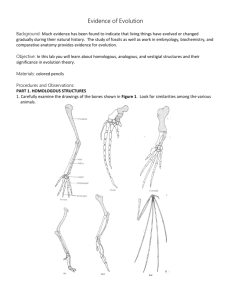
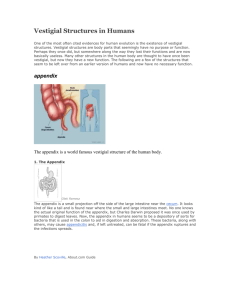
Evolution Test Study Guide Vocabulary Natural Selection Theory Evolution Species Fitness Mutation Stabilizing Selection Disruptive Selection Directional Selection Speciation Appendix Wisdom Teeth Tail Bone Humerus, Ulna, Radius Geographic Isolation Lamark Theory Darwin Theory Reproductive Isolation Temporal Isolation Behavioral Isolation Molecular Evidence Adaptation Cladograms Common Ancestor Trait Species Clade Vestigial Organ Homologous Structures Comparative Protein Sequencing Comparative Embryology Comparative DNA Sequencing Cytochrome-C Homologous Structures Population Generations Environment Phenotype Genotype Study Guide Questions 1. Create flashcards with definitions for all words above. 2. How does the Lamarkian hypothesis of natural selection differ conceptually from the Darwinian theory of evolution? 3. Why is the Darwinian Theory of Evolution so heavily favored among leading scientists? How is the theory supported by different fields of scientific investigation? 4. What does every single point on a cladogram mean? 5. How does the process of natural selection work? 6. What are vestigial organs and how do they suggest species underwent natural selection? 7. How does comparative embryology, protein sequencing, and DNA sequencing suggest natural selection occurred? 8. Homologous structures are defined as what, and how does this field of science support the process of natural selection? 9. How are species isolated from each other? (4 ways) 10. Does the process of natural selection act on the phenotype or the genotype of a species? Explain. 11. People often confuse natural selection with “survival of the fittest”. How are these terms different and how are they similar? 12. *Population graphs can shift from a normal bell curve to a different graph depending on the type of selection in the population. Describe the 3 types of graphical selection. Dinh 1 Evolution Test Study Guide 13. What is an adaptation? 14. How does a population change over time? 15. Similarities between species can be seen using the Cytochrome-C protein. How are these species similar and how do we know? 16. Darwin observed 14 different species of finches on the Galapagos Islands. How did these 14 different species arise from one common ancestor? 17. Why would certain traits (long tail, black fur, etc.) develop and some other traits die off? 18. The Appendix in the human body is vestigial. What does vestigial mean and how does it support the theory of evolution? Dinh 2