evolution_webquest 12-13
advertisement

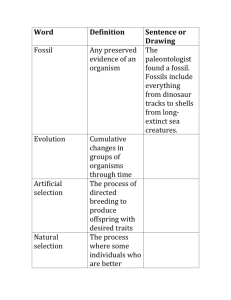
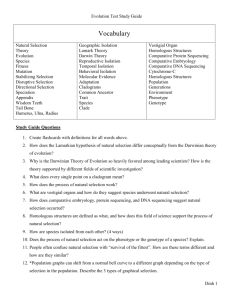
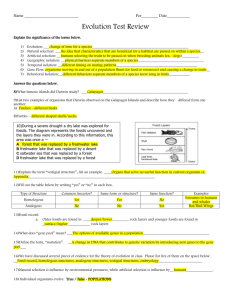
Webquest: Scientific Evidence for Evolution Shorecrest HS Biology 2013 Directions § As you proceed through this webquest, record all work on the graphic organizer § Remember to print and put the organizer in your lab notebook along with the coloring sheet by the due date Like all good scientific theories, evolution must have scientific evidence to support it This evidence falls into 8 or more important categories: 1. Fossil Record 2. Homologous structures 3. Analogous structures 4. Vestigial structures 5. Geographical distribution 6. Embryological studies 7. Genetic & biochemical comparisons 8. Resistance to antibiotics & pesticides Define the theory of evolution Go to the following site for information and then define the the theory in your own words: Interactive Site: http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/id/predictions.html Printable version: http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/id/pred-nf.html 1: Fossil Record A. Why are fossils considered part of the scientific data that supports Evolution? Watch the quick time video and read the text on this page: http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/library/04/3/l_043_01.html Visit this website to learn about transitional forms: http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/id/transitional.html 1: Fossil Record (cont.) B. What evidence did scientists use to determine the fossil they found was that of a whale? C. How do scientists use fossils to learn when whale ancestors were living on earth? Watch the 10 minute video (Video # 3: “How Do We Know Evolution Happens”) answer the Questions above in your notebook: http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/educators/teachstuds/svideos.html 2: Homologous structures A. Color-code the homologous structural parts on the sheet "Adaptive Radiation: Mammalian Forelimbs." B. What are homologous structures? C. Why are these considered evidence for Adaptive Radiation or Divergent Evolution? http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/darwin/origin/index.html http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/article/similarity_hs_01 3: Analogous structures A. What are analogous structures? B. How is this evidence for Convergent Evolution? http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/article/similarity_hs_01 4: Vestigial structures A. What are vestigial structures? § Give an example of a vestigial structure in humans. § Give an example of a vestigial structure in some other organism. B. Why are vestigial structures considered evidence for evolution? http://www.livescience.com/animals/top10_vestigial_organs.html 5: Geographical Distribution A. What did Wallace and Wegener discover? B. How does their evidence support the theory of evolution? http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/article/0_0_0/history_16 6: Embryology A. What is embryology? § Compare the stages of development illustrated on the sheet "Comparative Embryology" and in the diagrams in the Glencoe textbook (Page 433, Figure 18.11) § Create a branching diagram (like a family tree) which shows the degree of relationship between the animals listed in these pictures (Pg. 433, fig. 18.11) (6 total). Relationships are based on the similarity of their embryos. B. How do embryological studies provide evidence for evolution? 7. Genetic & Biochemical AND 8. Resistance to antibiotics & pesticides § We will study these two types of evidence later this year, so leave #7 and #8 blank for now More Connections: Lucy A. Where was Lucy found? B. How old is she? C. What does Lucy tell us about evolution? http://iho.asu.edu/lucy More Connections: Hydrothermal Vents A. How are Hydrothermal vent ecosystems similar to what it may have been like on the Early Earth? http://www.divediscover.whoi.edu/ expedition1/