Chapters 4-6 Study Guide
advertisement
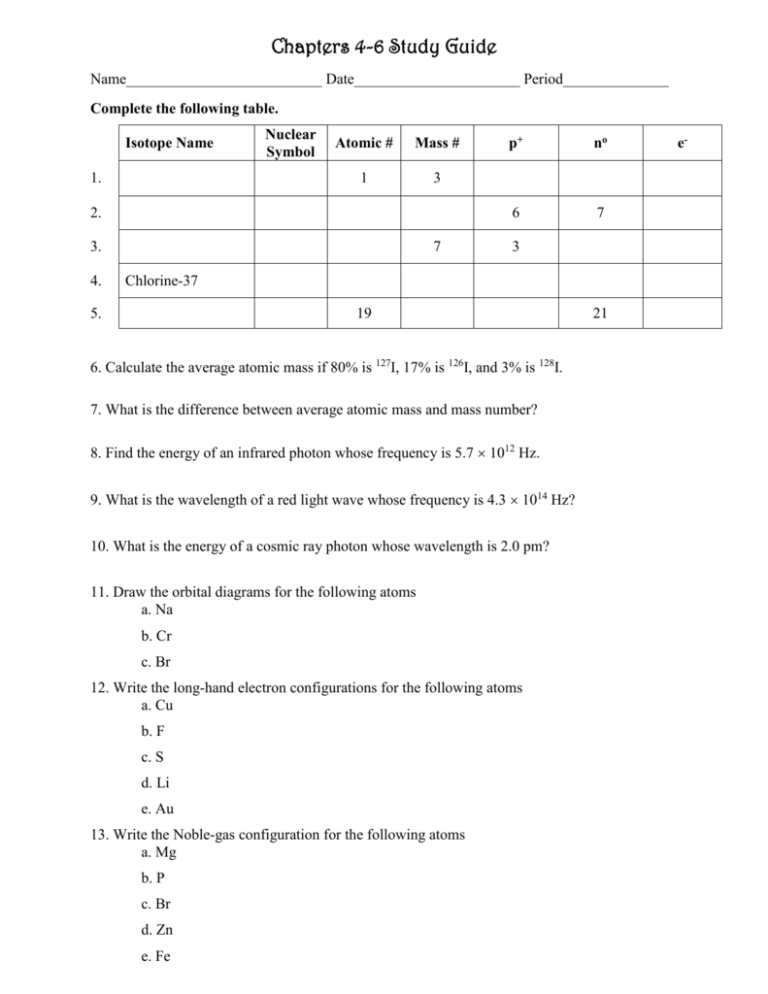
Chapters 4-6 Study Guide Name__________________________ Date______________________ Period______________ Complete the following table. Isotope Name 1. Nuclear Symbol Atomic # Mass # 1 3 2. 3. 4. 7 p+ no 6 7 3 Chlorine-37 5. 19 6. Calculate the average atomic mass if 80% is 127I, 17% is 126I, and 3% is 128I. 7. What is the difference between average atomic mass and mass number? 8. Find the energy of an infrared photon whose frequency is 5.7 1012 Hz. 9. What is the wavelength of a red light wave whose frequency is 4.3 1014 Hz? 10. What is the energy of a cosmic ray photon whose wavelength is 2.0 pm? 11. Draw the orbital diagrams for the following atoms a. Na b. Cr c. Br 12. Write the long-hand electron configurations for the following atoms a. Cu b. F c. S d. Li e. Au 13. Write the Noble-gas configuration for the following atoms a. Mg b. P c. Br d. Zn e. Fe 21 e- 14. Explain what each of the following quantum numbers tells us a. Principle Quantum Number b. Angular Momentum Quantum Number c. Magnetic Quantum Number d. Spin Quantum Number 15. Describe how each of the following scientists contributed to the atomic theory a. Bohr b. Dalton c. Rutherford d. Schrodinger 16. Draw a picture of a wave and label the follow in the picture: wavelength, frequency, amplitude, crest, and trough 17. Explain the relationship between energy, wavelength, and frequency. 18. Compare the periodic trends for ionization energy, atomic radius, metallic character, electron affinity, and electronegativity. 19. Order the following according to wavelength, frequency, and energy: IR, UV, visible light, X-rays, microwaves, gamma rays, and radio waves 20. Which element is in the second period is best represented by the six successive ionization energies below? Explain your reasoning. 1st IE 2nd IE 3rd IE 4th IE 5th IE 6th IE 775 1975 3250 12850 16000 19510 21. Explain how shielding contributes to the atomic radius trend within a group. 22. Why do magnesium, phosphorus, and zinc exhibit slightly higher first ionization energies than the general trend within each of their periods. 23. Explain the significance of Hund’s Rule, Pauli Exclusion Principle, and the Aufbau Principle in electron configurations and orbital diagrams. 24. Which atom has the larger atomic radius? Why? a. C or Sn b. Sr or In 25. Which of these atoms has the larger 1st ionization energy? a. Fr or Ne b. Na or Si 26. Which of these has the highest electronegativity? a. Ca or O b. Mg or Al ANSWERS Complete the following table. Nuclear Symbol Isotope Name Atomic # Mass # p+ no e- 1 3 1 2 1 1. Hydrogen – 1 3 1 2. Carbon – 13 13 6 C 6 13 6 7 6 3. Lithium – 7 7 3 Li 3 7 3 4 3 4. Chlorine-37 37 17 Cl 17 37 17 20 17 5. Potassium – 40 40 19 19 40 19 21 19 H K 6. Calculate the average atomic mass if 80% is 127I, 17% is 126I, and 3% is 128I. 126.86 amu 7. What is the difference between average atomic mass and mass number? 8. Find the energy of an infrared photon whose frequency is 5.7 1012 Hz. 3.8 x 10-21 J 9. What is the wavelength of a red light wave whose frequency is 4.3 1014 Hz? 7.0 x 10-7 m 10. What is the energy of a cosmic ray photon whose wavelength is 2.0 pm? 9.9 x 10-14 J 11. Draw the orbital diagrams for the following atoms a. Na _ 1s 2s 2p 3s b. Cr _ _ 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d c. Br _ 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 12. Write the long-hand electron configurations for the following atoms a. Cu 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 b. F 1s2 2s2 2p5 c. S 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4 d. Li 1s2 2s1 e. Au 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s2 4d10 5p6 6s1 4f14 5d10 13. Write the short-hand (Noble-gas) configuration for the following atoms a. Mg [Ne] 3s2 b. P [Ne] 3s2 3p3 c. Br [Ar] 4s2 3d10 4p5 d. Zn [Ar] 4s2 3d10 e. Fe [Ar] 4s2 3d6 4p 14. Explain what each of the following quantum numbers tells us a. Principle Quantum Number b. Angular Momentum Quantum Number c. Magnetic Quantum Number d. Spin Quantum Number 15. Describe how each of the following scientists contributed to the atomic theory a. Bohr b. Dalton c. Rutherford d. Schrodinger 16. Draw a picture of a wave and label the follow in the picture: A: wavelength, frequency = 2 Hz, B: amplitude, D: crest, and C: trough 17. Explain the relationship between energy, wavelength, and frequency. 18. Compare the periodic trends for ionization energy, atomic radius, metallic character, electron affinity, and electronegativity. 19. Order the following according to wavelength, frequency, and energy: IR, UV, visible light, X-rays, microwaves, gamma rays, and radio waves Decreasing wavelength (), Increasing frequency (), Increasing energy (E) Radio waves → Microwaves → IR → Visible (ROY G. BIV) → Ultraviolet → X-ray → Gamma 20. Which element is in the second period is best represented by the six successive ionization energies below? Explain your reasoning. Boron 1st IE 2nd IE 3rd IE 4th IE 5th IE 6th IE 775 1975 3250 12850 16000 19510 21. Explain how shielding contributes to the atomic radius trend within a group. 22. Why do magnesium, phosphorus, and zinc exhibit slightly higher first ionization energies than the general trend within each of their periods. 23. Explain the significance of Hund’s Rule, Pauli Exclusion Principle, and the Aufbau Principle in electron configurations and orbital diagrams. 24. Which atom has the larger atomic radius? Why? a. C or Sn b. Sr or In 25. Which of these atoms has the larger 1st ionization energy? a. Fr or Ne b. Na or Si 26. Which of these has the highest electronegativity? a. Ca or O b. Mg or Al








