A&P Basic Biological Topics to Review Basic Chemistry
advertisement

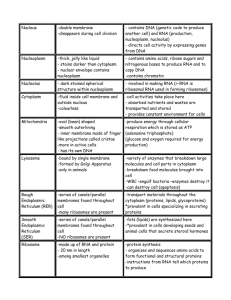
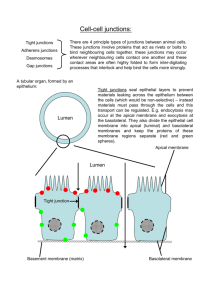
A&P Basic Biological Topics to Review Basic Chemistry & Biochemistry (Chp 2, Part 2: pgs 41-60) Inorganic compounds: o Water Unique characteristics Importance of these characteristics for the human body o Salts ions as electrolytes importance of salts (ionized form) for the human body o acids & bases Proton donor v. Proton acceptor Ions released when dissolved in water Biologically important acids & bases & their role in the human body Neutralization reactions Buffers – biological significance; general understanding of how they work Organic compounds: o Carbohydrates Examples Relation of size to solubility Mono v. di v. polysaccharides – structural description & identify key examples & their biological importance What is an isomer? Hydrolysis v. dehydration synthesis Carbohydrate function o Lipids Solubility Neutral fats v. phospholipids v. steroids: description, examples & biological importance of each o Proteins Examples & description of biological functions (there are many) Structural levels Fibrous v. Globular proteins Denaturing Enzymes Biological significance Activation energy Induced fit model Enzyme-Substrate complex o Nucleic Acids DNA v. RNA (structure & function) Nucleotides Base-pairing Relationship between DNA, RNA & protein o ATP Biological significance ATP v. ADP How is energy stored/released? Review Cellular Basis of Life (Chp 3) The Plasma Membrane: Structure o Fluid Mosaic Model Basic Features Phospholipid bilyaer Integral proteins - role Peripheral proteins - role Glycocalyx – role Cholesterol - role o Specializations of the Plasma Membrane Microvilli – What are they for? What type of cells are they found in? Membrane Junctions Basic Characteristics Tight Junctions (impermeable junctions) Desmosomes (anchoring junctions) Gap Junctions The Plasma Membrane: Function o Membrane Transport Basic characteristics Passive processes (general description of passive transport) Simple diffusion Osmosis Facilitated diffusion (proteins as passive carrier molecules, “channels”) Filtration Active processes (general description) Active transport (proteins as active carrier molecules, “pumps”) Vesicular transport Endocytosis o Phagocytosis o Receptor-mediated Exocytosis Generating & Maintaining a Resting Membrane Potential o Basic characteristics o Membrane potentials (Be able to explain with respect to Na/K pump) Resting membrane potentials Concentration gradients Active transport pumps The Cytoplasm o Basic characteristics (What are the three components of the cytoplasm?) o Organelles (How does organelle structure reflect function?) Mitochondria Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough Smooth Golgi apparatus Lysosomes Peroxisomes Cytoskeleton Microtubules Microfilaments Centrosome and Centrioles Cilia and Flagella The Nucleus o Basic characteristics o Nuclear envelope o Nucleoli o Chromatin Cell Growth & Reproduction o Cell Life Cycle Interphase G1 S (DNA Replication) o Summarize the steps of DNA replication o Complementary base-pairing G2 M-Phase (cell division) Mitosis (nuclear division) o General description of the four stages Cytokinesis (cell division) Why do cells divide? o Be able to calculate SA:V ratios o Protein Synthesis RNA v. DNA (structural & functional differences) The role of each type of RNA mRNA rRNA tRNA Transcription Summarize key events Translation Summarize key events