hon-chem-ch-22-notes-2
advertisement

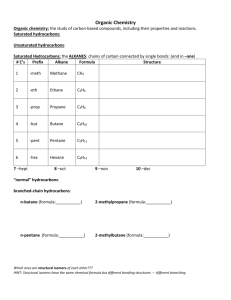
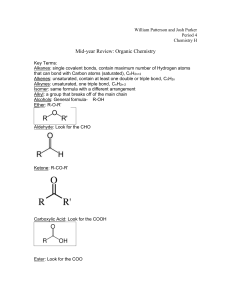
Hon Chem Ch 22 Notes, Organic Chem Names ______________________ Pg 669 1. Organic compounds contain what main element? Pg 671 2. Draw the structural formula for butane. 3. Write the chemical formula for butane. Pg 674 4. Hydrocarbons contain what 2 main elements? 5. Define what it means to be a saturated hydrocarbon. 6. Hydrocarbons that contain only single bonds are called _____________ . 7. What is the formula used to calculate the chemical formula of hydrocarbons that have only single bonds after knowing how many carbons are in the molecule? Pg 676 8. List the prefixes for the hydrocarbons that have the following number of carbon atoms in their structure: one carbon – six - two – seven - three – eight - four - nine - five - ten – Pg 674 9. What suffix is used as the ending of all the names of all the hydrocarbons that contain only single bonds? Pg 681 10. How does fractional distillation change petroleum into all the different fuels we use? Pg 682 11. What does it mean to be an unsaturated hydrocarbon? 12. Hydrocarbons that contain double covalent bonds between one or more of the carbons in their structure are called ___________________. (remember covalent is weaker than ionic) 13. What suffix is used as the ending of all the names of all the hydrocarbons that contain double bonds? 14. What is the general formula for calculating the chemical formula of a hydrocarbon with double bonds once the number of carbons is known? Pg 685 15. What is the most common hydrocarbon with double bonds? (proper name and common name) 16. Explain 3 things this most common double-bonded hydrocarbon can be used for. 17. Hydrocarbons that contain triple covalent bonds between one or more of the carbons in their structure are called ___________________. 18. What suffix is used as the ending of all the names of all the hydrocarbons that contain triple bonds? 19. What is the general formula for calculating the chemical formula of a hydrocarbon with triple bonds once the number of carbons is known? 20. What is the most common hydrocarbon with triple bonds? (proper name and common name) Pg 686 21. What is the most common hydrocarbon with triple bonds used for? Pg 687 22. Define aromatic hydrocarbons. 23. Draw a diagram of the basic structure of an aromatic hydrocarbon. 24. What is the most common aromatic hydrocarbon? Pg 689 25. How is a normal hydrocarbon changed into an alcohol? Pg 681 26. How is a normal hydrocarbon changed into an alkyl halide? 27. What are two DIFFERENT well known alkyl halides? 28. Explain how tetrafluoroethene gets its name. (the first part of the word as well as the last part) Pg 691 29. What are aldehydes and ketones used for? Pg 692 30. How is a normal hydrocarbon turned into a carboxylic acid? 31. What are 2 common carboxylic acids that may be in our pantry or refrigerator at home? Pg 693 32. How is hydrogenation of an oil done? 33. What does hydrogenation of an oil do? Pg 694 34. When water is removed from amino acids in a condensation reaction, what is formed? Pg 695-7 35. Explain the relationship between a monomer and a polymer. 36. What is the name of the polymer in plastic which is made from oil? 37. What is the name of the polymer in some permanent press fabrics that is also made from oil? Pg R35-40 38. Complete the following information regarding the 4 organic biological natural polymers. Name of Polymer Name of Monomer Examples 1. 2. 3. 4. 39. Explain the difference between monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides AND an example of each. Use Pg R35-40 and Pg 707-09 MonoDi – Poly -