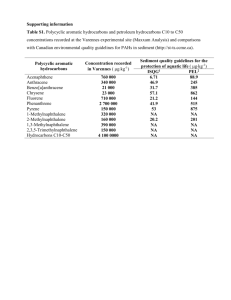
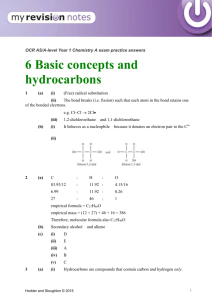
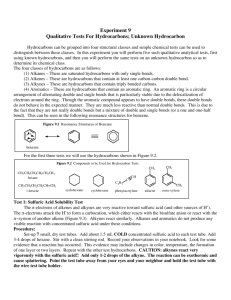
Nomenclature
advertisement

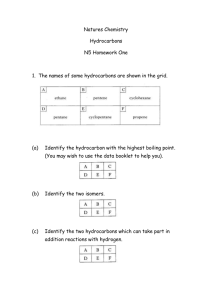
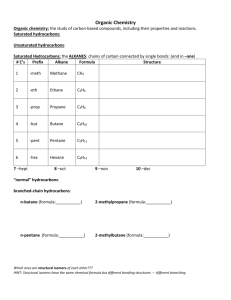
Activity #2 Name :_______________ The Hydrocarbons and Their Derivatives: Nomenclature, Physical/Chemical Properties, and Synthesis. Background Hydrocarbons are compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen. Hydrocarbons are usually divided into different types, depending on the actual functional group. For example, saturated hydrocarbons include the alkanes, unsaturated hydrocarbons include the alkenes and alkynes, while aromatic hydrocarbons include benzene and its many derivatives. Substituting any alkyl group (methyl, ethyl, etc.) for one or more hydrogen atoms within these families does not affect their “hydrocarbon” status, through you have produced an alkyl derivative of these families. But substituting a halogen (F, Cl, Br, I) for one or more hydrogen atoms within these families results in a “halo derivative” being formed which, by inspection, is no longer just a hydrocarbon. The general formula for an alkane is CnH2n +2, while the general formula for an alkene is CnH2n, while that for an alkyne is CnH2n-2. Objectives To practice writing names and formulas for the hydrocarbons and their derivatives To experience some chemical tests that will differentiate between the different types of hydrocarbons To practice completing reactions for the hydrocarbons 141 Directions Part 1. Nomenclature of the Hydrocarbons and Their Derivatives Give names or structures for the following: 1. CH 3CH3 9. CH3CHBrCH2CH2Br 2. CH3CH2CHCH3 Br 10. CH3CH=CHCH2CH 3. BrCH2CH2CH2Br 11. CH3CCCH2CH3 12. Benzene 13. Methylbenzene 4. 5. 1-Chlorocyclohexene 1, 3- dimethyl 1-cyclopentene 142 6. CH2C(CH3)2 14. CH3CH2CH2CHCH2CH2CH3 CH3 7. Aminobenzene 15. CH3CH2CHCHCH2CH3 8. Br CH3 CH3-CH-CH-C-CH3 Br CH3 16. ethylbenzene 143 Give a structure for the following names: 1. propane 8. 2,2-dichloropentane 2. octane 9. 4-ethyl-2-methylhexane 3. 3-ethyloctane 10. 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene 4. trans-1,2-difluoropropene 11. cis-2-pentene 5. 3-hexyne 12. 2-bromo-propane 6. chlorobenzene 13. cyclobutane 7. benzoic acid 14. ethyl benzene 144 The following names are incorrect. State why they are incorrect and then give their correct names. 1-chloroethane: 3-bromobutane: 2-chloro-3-bromo-4-methylhexane trans-1-propene 1-bromo-3-pentyne 145 Part 2. Chemical Tests Used to Differentiate Between the Hydrocarbons. A Demonstration. As your instructor demonstrates these reactions, respond to the following questions. Combustion What type of flame is produced when an alkane is burned? What type of flame is produced when an alkene is burned? What type of flame is produced when an alkyne is burned? What type of flame is produced when an aromatic compound is burned? Halogenation: Iodination. What color results when iodine is added to an alkane? What color results when iodine is added to an alkene? What color results when iodine is added to an alkyne? What color results when iodine is added to an aromatic compound? 146 Halogenation. Bromination. Record what happens when a solution of bromine in acetic acid is added to hexane: Record what happens when a solution of bromine in acetic acid is added to hexene: Record what happens when a solution of bromine in acetic acid is added to hexyne: Record what happens when a solution of bromine in acetic acid is added to toluene: Based on these two chemical tests, state how can you chemically differentiate between a) a saturated hydrocarbon and an unsaturated hydrocarbon? b) a saturated hydrocarbon and an aromatic hydrocarbon? 147 c) an unsaturated hydrocarbon and an aromatic hydrocarbon? Part III. Reactions of Hydrocarbons Complete the following reactions: 1. Cl2 CH3CH3------------------_________________________ light 2. -------------------- ___________________________ Br2, light 3. CH2=CH2 + H2O---------------------- 4. HCCCH2CH3 --------------------- Excess H2, Pt 148