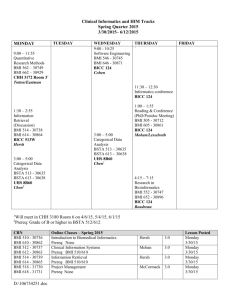
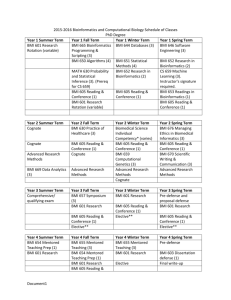
View - aoahyderabad2015
advertisement
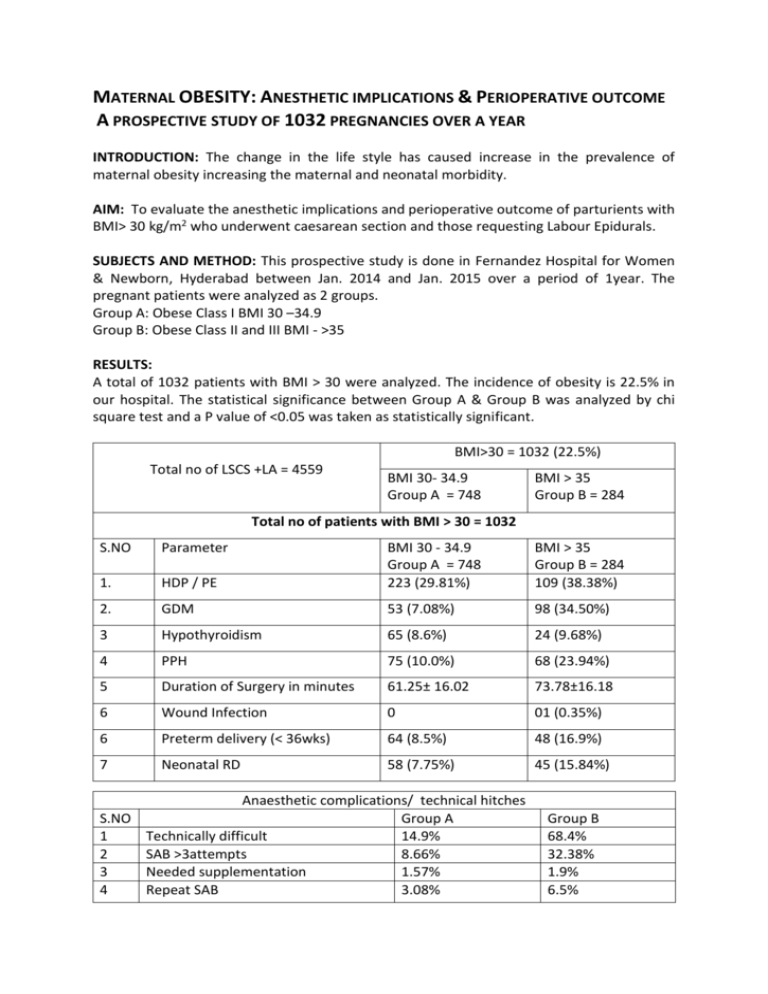
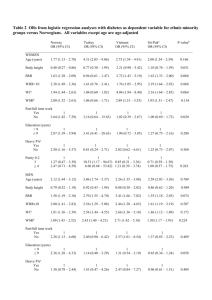
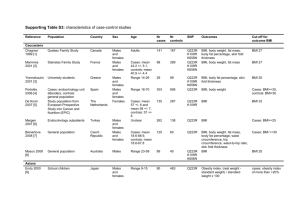
MATERNAL OBESITY: ANESTHETIC IMPLICATIONS & PERIOPERATIVE OUTCOME A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF 1032 PREGNANCIES OVER A YEAR INTRODUCTION: The change in the life style has caused increase in the prevalence of maternal obesity increasing the maternal and neonatal morbidity. AIM: To evaluate the anesthetic implications and perioperative outcome of parturients with BMI> 30 kg/m2 who underwent caesarean section and those requesting Labour Epidurals. SUBJECTS AND METHOD: This prospective study is done in Fernandez Hospital for Women & Newborn, Hyderabad between Jan. 2014 and Jan. 2015 over a period of 1year. The pregnant patients were analyzed as 2 groups. Group A: Obese Class I BMI 30 –34.9 Group B: Obese Class II and III BMI - >35 RESULTS: A total of 1032 patients with BMI > 30 were analyzed. The incidence of obesity is 22.5% in our hospital. The statistical significance between Group A & Group B was analyzed by chi square test and a P value of <0.05 was taken as statistically significant. BMI>30 = 1032 (22.5%) Total no of LSCS +LA = 4559 BMI 30- 34.9 Group A = 748 BMI > 35 Group B = 284 Total no of patients with BMI > 30 = 1032 S.NO Parameter HDP / PE BMI 30 - 34.9 Group A = 748 223 (29.81%) BMI > 35 Group B = 284 109 (38.38%) 1. 2. GDM 53 (7.08%) 98 (34.50%) 3 Hypothyroidism 65 (8.6%) 24 (9.68%) 4 PPH 75 (10.0%) 68 (23.94%) 5 Duration of Surgery in minutes 61.25± 16.02 73.78±16.18 6 Wound Infection 0 01 (0.35%) 6 Preterm delivery (< 36wks) 64 (8.5%) 48 (16.9%) 7 Neonatal RD 58 (7.75%) 45 (15.84%) Anaesthetic complications/ technical hitches S.NO Group A 1 Technically difficult 14.9% 2 SAB >3attempts 8.66% 3 Needed supplementation 1.57% 4 Repeat SAB 3.08% Group B 68.4% 32.38% 1.9% 6.5% 5 6 7 8 9 10 High spinal Hypotension Fall in saturation <94% Failed regional - GA GA with antecedent problems Mean Hospital Stay NIL 18.1% NIL 2.36% NIL 3.48days 1.08% 32.3% 0. 8% 1.3% NIL 6.5days CONCLUSION: Maternal obesity is associated with increased materno fetal morbidity, anaesthetic and peri operative risks. The magnitude of risk increases with the degree of obesity.