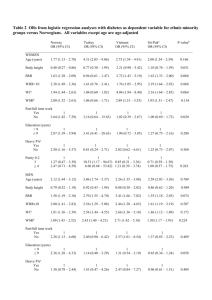
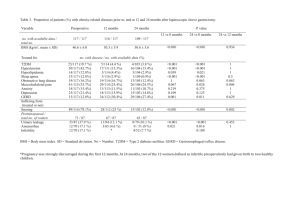
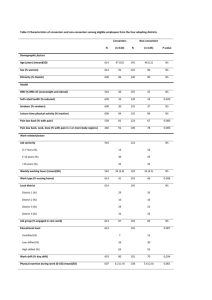
Table 1: Summary of clinical studies examining the impact of obesity
advertisement

Table 1: Summary of clinical studies examining the impact of obesity on mortality in Trauma Intensive care Units Studies Choban et al.1991 (36) Study design Retrospective Single center Neville et al. 2004 (40) Prospective Case-control Single center Brown et al. 2005 (93) Retrospective Single center Byrnes et al 2005 (38) Retrospective Single center Bochicchio et al. 2006 (41) Prospective Single center Ryb et al. 2008 (39) Retrospective Multicenter Duchesne et al. 2009 (96) Retrospective Single center Nelson et al, 2012 (74) Retrospective Single center Ditillo et al. 2014 (28) Retrospective Single center Glance et al. 2014 (37) Retrospective Multicenter Number of groups, BMI in kg/m2 (number of patients) Type of ICU Conclusions 3 groups: BMI > 27(140) BMI: 27-31(25) BMI >31 (31) Trauma Mortality rate was higher in obese than normalweight and overweight patients 2 groups: BMI < 30 (63) BMI > 30 (179) Trauma 2 groups: BMI < 30 (870) BMI > 30 (283) Trauma Obesity was independently associated with mortality rate, LOS and days of mechanical ventilation 5 groups BMI <25 (488) BMI:25-29.9 (401) BMI: 30-34.9 (168) BMI: 35-39.9 (65), BMI> 40 (57) Trauma Obesity increased mortality and ICU complications. Mortality rate for obese patient increased with the severity of injuries (ISS > 15) 2 groups: BMI < 30–49 (1105) BMI ≥ 49 (62) Trauma Obesity increased mortality and in-hospital complications including LOS 3 groups: BMI: 18.5-25 (n = 619) BMI 25-30 (n = 561), >30 (n = 437) Patients from the CIREN database Trauma Mortality rate was 2 fold higher in obese patients compared to lean patients 3 groups: BMI<29 (51) BMI 30-39 (38) BMI >40 (15) Trauma Morbid obesity is associated with higher mortality rate and increased complications including LOS, postoperative infection, length of ventilation support and multiple organ failure 4 groups: BMI < 18.5 (30) BMI:18.5–24.9 (603) BMI: 25.0–29.9 (361) BMI: > 30 (90) Trauma Obesity increased mortality rate and incidence of multiple organ failure, but did not affect LOS in patients with ISS ≥ 16 2 groups: BMI < 40 (16,390) BMI > 40 (16,390) Patient from NTDB database with blunt trauma and matched-injury scores Trauma Morbid obesity increased mortality, in-hospital complications and LOS 6 groups classified in percentile using the empiric weight distributions. Underweight (1248) Reference (109582) Grade 1 obesity (20970) Grade 2 obesity (8131) Grade 3 obesity (6084) Grade 4 obesity (1665) Exclusion of non trauma patients Trauma Severe obesity increased mortality rate, organ failure and wound-related complications Obesity increased mortality and incidence of multiple organ failure Abbreviations: The number of patients in each weight category is listed in parenthesis. BMI, body mass index in kg/m2; ISS; injury severity, LOS, length of stay. NTDB, National Trauma Data Bank. CIREN, Crash Injury Research and Engineering Network database.