Option C: A
advertisement

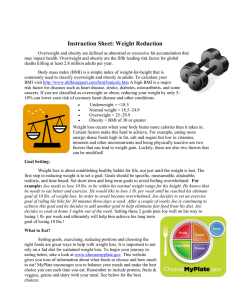
Option C: A.2 Energy in human diets Energy content is different in all nutrients. Carbohydrates 1760 kJ per 100g Protein 1720 kJ per 100g Lipids 4000 kJ per 100g Why is this so?? High energy storing bonds occur between ____________ This is more than C-O. Since Lipids have a high ratio of C-H, they store more energy. (You don’t have to consume a lot of fat because of the amount of energy it contains. Sources of Energy in Different Ethnic Groups. Rice: Main source for 1 in 5 people on Earth. Type of grass native to southeast Asia, Africa Rice production and consumption Countries are China, Japan, India, Indonesia, Bangladesh, Vietnam and Thailand. Energy in rice comes from ____________________________________________. Wheat: Widespread and popular in bread, cake, pasta, semolina for couscous. Thought to originate from the ‘fertile crescent, a region running from the Nile river delta to Mesopotamia. Many cultures use wheat. Countries such as Russia, Australia, Turkey, Canada and Iran. Cassava or Manioc: Shrub originated in South America. Grown in many tropical countries The root provides an excellent _______________________ Can be eaten like a potato or used to produce flour for tapioca. Maize: Originated in Central America. Mexico is one of the leading producers of corn today. ___________________________________ Uses: Flour for tortillas, directly eaten as kernels Fish and Meat Source of energy comes from _________________________. Fish mainly used in the Seychelles population (off the coast of Africa), Inuit people of Greenland World’s largest per capita consumer of meat is the US. (90kg/person/year vs. 37 kg/person/year globally) See p. 222 for a table summary of above. 1 Can we have too much?? ~Health consequences of diets rich in carbohydrates, fats and proteins ~ Excess Carbohydrate in the Diet Too much energy entering the body. If not burned/used, excess energy is stored Sugar is converted into either _________________________ Health Consequences: Weight gain (possible obesity), possible tendency for diabetes Type II Excess Fat in the Diet Contains more than double the amount of energy than carbohydrates. Storing energy is ____________________________ **Don’t forget about the consequences of saturated and trans fats** Health consequences: Weight gain (possible obesity), possible increase in cardiovascular disease Excess Protein in the Diet 2-3 servings of protein per day are generally required for a healthy diet. Many people over do their consumption because of portion size. We cannot store excess protein Digestive system, liver and kidneys become overworked trying to eliminate excess protein which leads to hypertrophy (oversized) Kidneys need calcium in order to excrete protein. Excess protein _________________________ Health consequences: Decalcified bones, hypertrophied and overworked kidneys and liver Appetite Control System Appetite is the desire to eat. Hunger is the body’s way of alerting you that it needs food Mechanisms of satiety and appetite control are complex and involve feed back loops from the ________________________________________________________ system. (ie. when you finish eating the pancreas releases hormones to reduce appetite) Hypothalamus plays an important role in regulating appetite. (Appetite Control Centre) After a meal your stomach fills & expandsstimulates nerve cells of the vagus nervehypothalamus Intestines also produce hormones to send signals to the brain about __________________ Fat cells produce leptin (hormone)hypothalamus to suppress appetite. More fat that is stored , the more leptin is produced to indicate to the brain that enough energy is stored. Note: Compulsive eating and persuasive advertising can override leptin’s effects. 2 Body Mass Index (BMI) BMI = (Mass kg) (Height in m)2 Calculate your BMI below… Where do you fall in the BMI status… BMI Below 18.5 18.5-24.9 Status Underweight Normal weight Overweight Obese 25.0 – 29.9 30.0 and above Note: BMI does not tell you how mass is distributed!! BMI should only be used as a guide! Why are so many people Obese?? Over the past number of years, obesity has increased and are still increasing. (750 million-1.6 billion overweight worldwide from 2002 - 2005) Reasons include: o Type and quantity of food o Less amount of daily physical activity (Migration from farm to urban centres contributed to this) Lifestyle changes contribute to obesity! Ex. Heating the home Ex. Farming Ex. Availability of high-energy affordable food all year Ex. Fast-food was not available in the past and portion size is very large!! 3 To avoid obesity… o More physical activity o Fresh fruit and vegetables o Less processed high-fat food o Smaller quantities of food. Anorexia Nervosa Eating disorder with firm conviction that they are overweight despite being normal or underweight Unhealthy self image caused by: o Cultural pressure mass media dictating what is beautiful o Traumatic experiences in a person’s life o Physiological causes from the person’s genetic makeup or brain chemistry. Fear of gaining weight Will refuse food Force Vomiting Exercise excessively to burn off energy from food Affects mainly females (9/10), however, males can get be affected by this as well Consequences of Anorexia Nervosa… Endocrine system malfunctions Hormones responsible for regulating menstrual cycles are not produced and most often stop menstruating Loss of head hair Dehydration Fainting Anaemia Low blood pressure Kidney stones or kidney failure. Yellowing of skin Fine hair growth all over the body Weakened immune system Osteoporosis Psychological and emotional problems affecting family relationships, friendships and romantic relationships. Most serious consequence is death. If left untreated, patients can starve themselves to death. Early diagnosis and treatment are important o Treatment involves changing the person’s ____________________ o Medical, psychiatric help and emotional support from friends and family Homework p. 229 # 7-15 4