1-4 ch2
advertisement

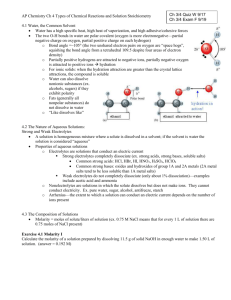
• • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Warm-up: (9-3-15) *Ch.2-1 video notes, Scientific method video notes, and rubric out for stamp! 1. What are the high seas? 2. What are 3 benefits of pole and line fishing? 3. What is per capita GDP? 4. What are benefits of marine reserves? 5. Why is it important for local people to benefit economically from ecotourism? *continue working on hw for next week. Be sure to initial your neighbor’s journal #4: Wild Pacific video Q’s from yesterday as well as their rubric If you were absent, write exempt on your rubric Q/A Law of conservation of matter Protons have what charge? Electrons? Neutrons? The volume of an atom is mostly made up of ____________. free space. Helium has how many protons? Electrons? Neutrons? a molecule, compound, or both? H2O O2 CO2 N2 You test the pH of 10 drops of coffee. Then you add two drops of HCl to it. Test and record the pH. Then you take 10 drops of coffee and add five drops of HCl to it. Test and record the pH. What is the independent variable? Dependent variable? Control? A __________ bond is made when an opposite charge created by the loss/gain of an electron between two atoms holds them together. A __________ bond is made when a pair of electrons is shared between two atoms. Carbon-14 and carbon-13 are examples of _____. Ch. 2-pt.1 Basic Chemistry and Scientific Method Mrs. Boyd Models of Systems Positive feedback: causes a system to continue further in the same direction – Ex. Compound interest in savings account Negative feedback: causes a system to go in the opposite direction – Ex. homeostasis: tendency to maintain a stable condition • maintain a certain temp., sweating Exponential growth of the human population is an example of (positive, negative) feedback. Your blood sugar rises after you eat. Then your pancreas secretes insulin and your blood sugar goes down. This is an example of (positive, negative) feedback. Ice caps are light in color and reflect light/heat. If the ice caps start to melt and reflect away less light, more heat is being absorbed by the dark ocean and more of the ice cap melts. This is (positive, negative) feedback. Time Delays: we may not know the effects of our actions today, it takes time for the effects of our actions to appear It takes time for negative feedback to occur. Processes and feedbacks in a system can (synergistically) interact to amplify the results. – E.g. smoking exacerbates the effect of asbestos exposure on lung cancer. If a system passes a tipping point, what does that mean? • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Tipping point Point at which the system shifts and it is irreversible. TYPES AND STRUCTURE OF MATTER Matter: anything that has mass and takes up space Earth is a CLOSED system for matter. The pH (potential of Hydrogen) is the concentration of hydrogen ions in one liter of solution relative to concentration of OH- ions. pH Scale for measuring relative concentrations of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions. Ranges from 0 – 14 0 is acidic; 7 is neutral; 14 is basic Acid or a base? High or low pH? Note that each decrease in pH by one pH unit means a tenfold increase in the concentration of hydrogen ions. (H+) So pure water (pH 7) has a concentration hydrogen ions of 1x10-7 moles per liter (0.0000001 moles per liter) pH 5 would have what concentration of hydrogen ions? (in moles per liter) 1x10-5 moles per liter Check for Understanding: 1. What does pH measure? 2. This solution is (acidic, basic) and has a (high, low) pH. 3. Give one example of positive feedback. 4. Give 1 example of a synergistic effect.