Chapter 2 - Environmental Systems
advertisement

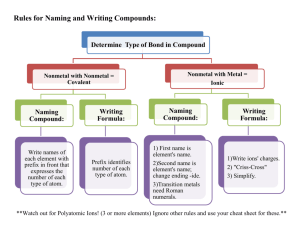
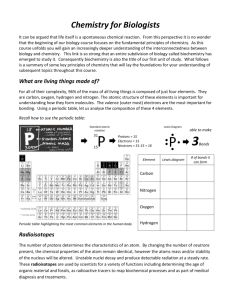
Chapter 2 Matter – mass + space Atoms – elements; periodic table; symbols o Atomic number, mass number, isotope o Radioactivity • Radioactive decay, half-life Compounds – formulas o Covalent bonds – molecules (very strong) o Ionic bonds – ions (slightly less strong) Additional types of bonds o Hydrogen bonds – polarity (fairly weak) Strong covalent bonds hold oxygen and hydrogen together Oxygen is much more electronegative than hydrogen it is an electron ‘hog’ the electrons spend more time around it than hydrogen water is a polar molecule The slight – charge on the oxygen side of the molecule is attracted to the slight + charge on the hydrogen side of another molecule (hydrogen bonding) This polarity and hydrogen bonding of water causes all its other properties: o o o o o Surface tension Capillary action Specific heat Density of ice Solubility Acids o Excess H+ ions in solution o NNO3 (nitric acid) and H2SO4 (sulfuric acid) o pH < 7 Bases o Excess OH- ions in solution o NaOH (sodium hydroxide) and Ca(OH)2 (calcium hydroxide) o pH > 7 The law of conservation of matter o It’s a LAW! Chemical reactions must obey! How does this impact the environment? o There is no ‘away’… Compounds o Inorganic – no carbon or no carbon bound to hydrogen o Organic – have carbon-carbon and carbon-hydrogen bonds o Four important ones: • • • • Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic acids (DNA & RNA) Energy - the ability to do work; power – the rate of work Forms of energy: o Kinetic – energy of motion o Potential – stored energy Temperature o Kinetic energy of the molecules within a substance Energy has laws too! First law of thermodynamics o Not created or destroyed, just changed Second law of thermodynamics o Changes in energy result in a decrease in usable energy and an increase in entropy Open system: exchanges of matter or energy o Example – a lake: water flows in as well as out Closed system: no exchanges of matter or energy o Example – not as common; some underground cave systems Which is Earth with respect to matter? How about energy? Steady state systems o Input = output system is not changing over time o Most natural systems are in a steady state due to feedback • Negative feedback loop – system returns to original state by decreasing its rate of change (resists) • Positive feedback loop – system accelerates by increasing its rate of change (amplifies)