Chapter 21 – Temperature, Heat, and Expansion We sense the
advertisement
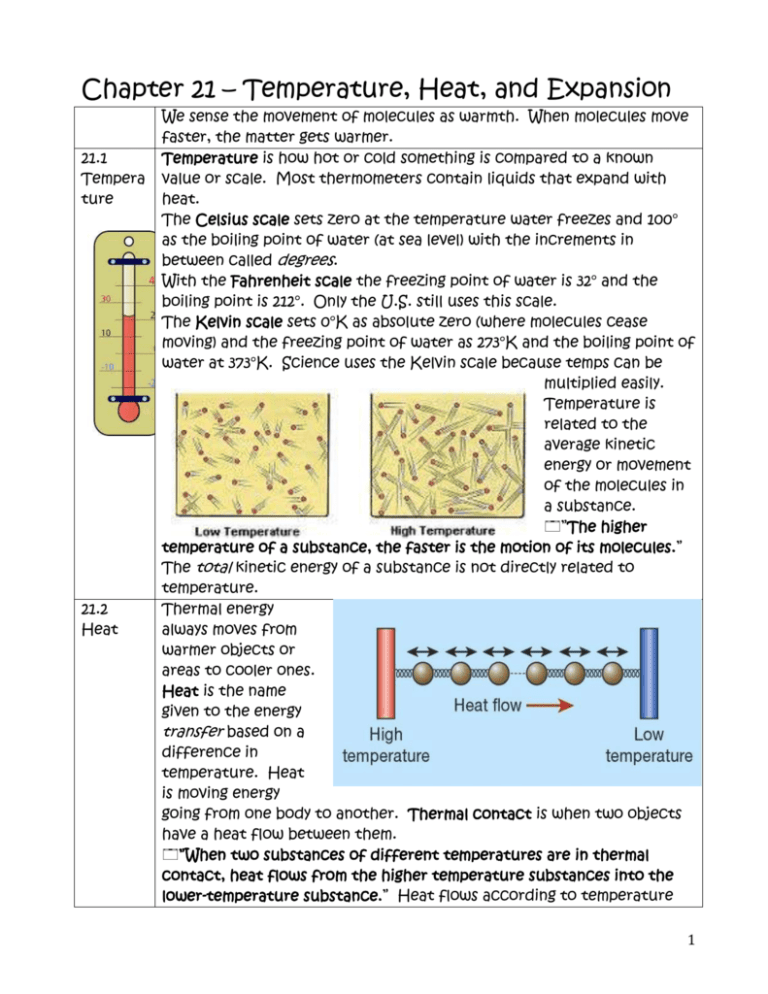
Chapter 21 – Temperature, Heat, and Expansion 21.1 Tempera ture 21.2 Heat We sense the movement of molecules as warmth. When molecules move faster, the matter gets warmer. Temperature is how hot or cold something is compared to a known value or scale. Most thermometers contain liquids that expand with heat. The Celsius scale sets zero at the temperature water freezes and 100° as the boiling point of water (at sea level) with the increments in between called degrees. With the Fahrenheit scale the freezing point of water is 32° and the boiling point is 212°. Only the U.S. still uses this scale. The Kelvin scale sets 0°K as absolute zero (where molecules cease moving) and the freezing point of water as 273°K and the boiling point of water at 373°K. Science uses the Kelvin scale because temps can be multiplied easily. Temperature is related to the average kinetic energy or movement of the molecules in a substance. ”The higher temperature of a substance, the faster is the motion of its molecules.” The total kinetic energy of a substance is not directly related to temperature. Thermal energy always moves from warmer objects or areas to cooler ones. Heat is the name given to the energy transfer based on a difference in temperature. Heat is moving energy going from one body to another. Thermal contact is when two objects have a heat flow between them. ”When two substances of different temperatures are in thermal contact, heat flows from the higher temperature substances into the lower-temperature substance.” Heat flows according to temperature 1 differences not total internal energy differences. **this is somewhat like a longitudinal wave or the flow of electricity. 21.3 Thermal Equilibri um* This is directly from the state standards & likely to be tested. 17.4 Evidenc e for Atoms 21.4 Internal Energy 21.5 Measure ment of Heat Thermal equilibrium is when objects in thermal contact reach the same temperature. There is no heat flow if the objects are in thermal equilibrium. ”When a thermometer is in contact with a substances, heat flows between them until they have the same temperature.” A thermometer reaches equilibrium with an object in thermal contact and then reads its own temperature. The idea of atoms goes back to Democritus and the ancient Greeks. John Dalton advocated that matter was made of atoms even though he had no direct evidence for their existence. In 1827 Robert Brown saw pollen grains floating on water through a microscope. Brown noticed that the grains were moving just a bit. The jiggling of small particle just large enough to be seen is called Brownian motion. Brownian motion is evidence not only for atoms, but also that atoms and molecules are in perpetual motion. Brown observed that the higher the temperature of the water, the more the particles moved. The kinetic energy of molecules displayed in Brownian motion proportional to temperature. This was evidence that temperature is related to the motion of molecules. http://3.bp.blogspot.com/_D8P4hByt4sc/TRriJx_WUuI/AAAAAAAAAc 0/p6EQnqIakPg/s1600/brownianmotion.gif Internal energy is the sum of all the different energies in a substance. Objects really have internal energy rather than heat. ”When a substance takes in or gives off heat, its internal energy changes.” ”The amount of heat transferred can be determined by measuring the temperature change of a known mass of a substance that absorbs the heat.” When energy is transferred in heat, the temperature change between the objects depends on the kind of substances and how much of each substance is involved in the thermal contact. Heat is commonly measured in calories. One calorie is the amount of heat needed to raise one gram of water one degree Celsius. The Calories that we use to rate the energy in food are actually kilocalories. One calorie is equal to 2 21.6 Specific Heat Capacity 4.186J. Calorie ratings of food are determined by burning the foods and measuring how much energy is released. Different substances can hold more or less heat. ”The capacity of a substance to store heat depends on its chemical composition.” The amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a substance 1°C is called its specific heat capacity. Specific heat capacity is a substance’s resistance to changing temperature – like a thermal version of inertia. Not all internal energy is temperature or kinetic energy of translational motion. Energy that is absorbed could be in rotational motion of the molecules, internal vibrations, or potential energy as chemical bonds. Water molecules absorb energy in these other forms in addition to temperature (kinetic energy) increases. Because of this, water ‘holds’ more energy. 21.7 The Small amounts of water can store lots of energy with only small changes High in temperature. Water is used to cool engines because of its high Specific specific heat capacity. Heat Capacity of Water ”The property of water to resist changes in temperature improves the climate in many places.” Places near the ocean or with predominantly on-shore winds have more moderate climates. Northern Europe is considerably warmer because of the Gulf Stream. On the west coast of 3 North America the temperature is warmer in the winter and cooler in the summer. East coast regions of America have a wider range of temperatures. Areas in the center of the continent have extreme lows in the winter and extreme highs in summer. 21.8 With increased temperatures and molecular movement objects expand. Thermal ”Most forms of matter—solids, liquids, and gases—expand when they Expansio are heated and contract when they are cooled.” n Typically, gases expand the most, then liquids then solids the least. Expansion rates of various materials must be considered in engineering and construction. Expansion joints are seen in sidewalks and bridges. Since different materials expand at different rates, this can be used to cause bimetallic strips to arc. Bimetallic strips can be used in thermostats or pointer thermometers. When the temperature causes a bimetallic strip to bend a set amount, it may close a circuit and cause a furnace to turn on. Borosilicate glass does not expand much when heated and is used in test tubes and cookware designed for heating. When heated a metal lid can expand making it easier to open. 21.9 Liquid water at 0°C will contract until it reaches 4°C – its densest Expansio point. From 4°C upward, water expands as heated. Ice is water n of arranged open crystal structures so the density is 0.9167 g/cm3 whereas Water water at 4°C is 1.0 g/cm3. ”At 0°C, ice is less dense than water, and so floats on water.” The fact that liquid water is more dense than ice is important for life on earth (and ice fishing). In order for a body of water to freeze, it must all reach 4°C. Mr. Collom sanitized an 8-gallon bucket by filling it to the top with boiling water. He left it in his garage overnight and found the water 2 cm below the rim in the morning. What happened? What is wrong with goblet on the left? can ice sink below the How water? 4 5