2014 Fall Semester Final Study Guide
advertisement

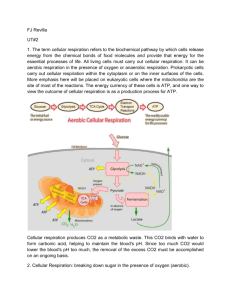
2014 Fall Semester Final Study Guide - Wolfe Chapter 1 – pp. 2 – 28 1. What is a hypothesis? 2. What is a very important aspect of a hypothesis that makes it different from an inference? 3. In Redi’s experiment, he kept many variables the same. What was his manipulated variable? 4. If a plant is dying, what might be a good hypothesis? (List at least 2) 5. When does a hypothesis become a theory? 6. How many variables are tested in a controlled experiment? 7. What are the characteristics of living things? (List all 8.) 8. Most birds fly south for the winter. What characteristic of livings things explains this? 9. What is homeostasis? 10. What are the metric units of length, mass, and volume? Chapter 2 – pp. 34 – 53 11. What are the 3 particles in an atom? 12. In a chemical reaction, what are the reactants? 13. What is a catalyst? 14. What is a chemical reaction? 15. What is an enzyme? 16. List 3 functions of proteins. 17. Which macromolecule is the main source of energy for living things? Chapter 3 – pp. 62 – 80 18. What is the main source of energy for most organisms/ecosystems? 19. What is the smallest level of organization within the biosphere that includes living and nonliving things? 20. The combined portions of Earth in which all living things exist is the ______________________. 21. Are organisms at the beginning of the food chain producers or consumers? 22. What are 2 names for organisms that cannot make their own food? 23. Why can matter be recycled through the biosphere? 24. What is a food web? 25. What is a trophic level? 26. Very little energy gets passed from one tropic level to another because organisms use the energy for basic processes like _______________, __________________, and __________________ 27. How is carbon stored in the biosphere? (List at least 3 ways) Chapter 4 – pp. 86 – 112 28. What is climate? 29. What effect helps keep Earth within a suitable temperature range for life? 30. What does the rising and falling of different air masses cause? 31. List at least 3 examples of abiotic factors in the environment. 32. What is a niche? 33. What is predation? 34. What is mutualism? 35. What is ecological succession? 36. What kind of aquatic ecosystems are ponds and lakes, standing or flowing? 37. What is the photic zone? Chapter 5 – pp. 118 – 132 38. List three factors that affect a population’s growth rate. 39. What is population density? 40. What is immigration? 41. What is emigration? 42. What is exponential growth? 43. What is a limiting factor? 44. List 3 examples of a density-dependent limiting factor. 45. List 3 examples of a density-independent limiting factor. 46. What is demography? 47. What must happen to the birth and death rates for a population to grow? Chapter 6 – pp. 138 – 160 48. What is a big source of environmental change on Earth? 49. Why are fossil fuels nonrenewable? 50. What is sustainable development? 51. What is an endangered species? 52. What is global warming? 53. What was DDT used for? . 54. As DDT moves up the trophic levels in food chains, or food webs, its concentration ______________. 55. What is an ecological hotspot? Chapter 7 – pp. 168 – 193 56. Which scientist came up with the term cell by looking at cork under a microscope? 57. What 3 things does the cell theory state? 58. What type of microscope can produce 3D images of cells? 59. Prokaryotes do not contain a _________________. (important cell part that controls functions) 60. What is an example of a prokaryote? 61. Which organelle converts chemical energy from foods into a usable form for cells? 62. Name 2 organelles you can find in plant cells but not animal cells. 63. What are the channels/pumps in the cell membrane made of? 64. What is diffusion? 65. List the levels of organization in a multicellular organism from least complex to most complex. 66. What is osmosis? 67. What is cell specialization? Chapter 8 – pp. 200 – 214 68. What are the 3 parts of an ATP molecule? 69. When a phosphate group is removed from ATP, is energy released or stored? 70. What are 2 products of photosynthesis? 71. What are pigments? 72. Why do plants appear green? 73. What is the Calvin cycle another name for? Chapter 9 – pp. 220 – 232 74. What are the 3 stages of cellular respiration, in order? 75. What is the equation for cellular respiration? 76. How many ATP molecules are made during cellular respiration? 77. What is the starting molecule of glycolysis? 78. Cellular respiration is called an aerobic process because it requires _____________________. 79. What are the products of cellular respiration? 80. What is gas released during cellular respiration? 81. How are the products of photosynthesis related to cellular respiration? (Hint: Look at the comparison chart at the end of chapter 9) Chapter 10 – pp. 240 – 252 82. The rate at which wastes are produced by a cell depends on the cell’s _____________________. 83. What is cell division? 84. What happens during interphase? 85. What are the 4 phases of mitosis, in order? 86. What structure of the chromosome does A represent? (hint: look at p. 244) 87. What structure of the chromosome does B represent? 88. During which phase of mitosis do chromosomes line up along the middle of the cell? 89. What are 3 problems that growth can cause for cells? 90. What are the 4 phases of the cell cycle? 91. What is the role of the spindle during mitosis? Chapter 11 – pp. 262 - 280 92. What does the principle of dominance state? 93. What is the probability you will flip tails when you flip a coin? 94. What can the principles of probability be used to predict in genetics? 95. What is a homozygous individual? 96. Create a punnett square using the letter A and cross a homozygous dominant individual with a heterozygous individual. 97. What does the principle of independent assortment state? 98. What types of organisms do Mendel’s principles apply to? 99. How are gametes produced? 100. Compare the end results of mitosis and meiosis.