Homogeneous vs Heterogeneous Review
advertisement

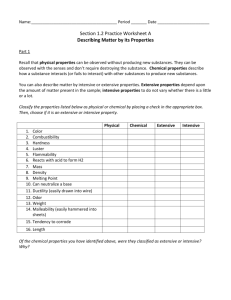
Name __________________________________________________ Date ___________________________________________________ HOMOGENEOUS VS. HETEROGENEOUS MATTER Classify the following as either homogeneous or heterogeneous. 1. flat soft drink (no bubbles) 9. air (with smog) 2. chocolate chip ice cream 10. paint 3. Italian salad dressing 11. alcohol 4. sugar 12. iron 5. soil 13. beach sand 6. aluminum foil 14. pure air 7. black coffee 15. chunky spaghetti sauce 8. sugar water -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------PURE SUBSTANCES VS. MIXTURES Classify the following as pure substances or mixtures. 1. sodium 2. water 3. soil 13. chocolate chip ice cream 4. coffee 14. nitrogen 5. oxygen 15. eggs 6. 70% isopropyl alcohol 7. carbon dioxide 17. table salt 8. cake batter 18. nail polish 9. air 19. milk 10. chicken noodle soup 11. iron 12. 16. 20. salt water blood soda CLASSIFICATION OF MATTER Check the appropriate categories for the substances listed below. All substances will have a check in more than one column. Substance lead metal table salt (NaCl) Kool-Aid drink vegetable soup oxygen gas distilled water concrete pure gold brass metal flat 7-Up soda raw egg (cracked open) air pure iron iron rust (Fe2O3) soil baking soda (NaHCO3) Heterogeneous Homogeneous Pure Solution Element Compound Mixture Matter Matter Substance PHYSICAL VS. CHEMICAL CHANGES 1 Classify the following as being a chemical or a physical change. 1. Sodium hydroxide dissolves in water. 2. Hydrochloric acid reacts with potassium hydroxide to produce a salt, water, and heat. 3. A pellet of sodium is sliced in two. 4. Water is heated and changed to steam. 5. Potassium chlorate decomposes to potassium chloride and oxygen gas. 6. Iron rusts. 7. When placed in water, a sodium pellet catches on fire as hydrogen gas is liberated and sodium hydroxide forms. 8. Evaporation. 9. Ice melting. 10. Milk sours. 11. Sugar dissolves in water. 12. Wood rotting. 13. Pancakes cooking on a griddle. 14. Grass growing in a lawn. 15. A tire is inflated with air. 16. Food is digested in the stomach. 17. Water is absorbed by a paper towel. PHYSICAL VS. CHEMICAL PROPERTIES & CHANGES 2 Part 1 - Indicate whether each of the following describes a chemical or a physical property. 1. Sulfur is a bright yellow solid. 2. Sulfur has a low melting point. 3. Sulfur causes silver to tarnish. 4. Aluminum is very malleable. 5. Monuments made of copper corrode in acid rain. 6. Copper is a good conductor of electricity. Part 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 2 - Classify the following as chemical or physical properties. color 14. solubility reactivity 15. expansion flammability 16. melting point odor 17. rusting porosity 18. reacts with oxygen stability 19. density ductility 20. conductivity Part 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 3 - Indicate whether these changes are chemical, physical, or nuclear. Lead reacts with acid in a car battery. 31. burning of gasoline Gasoline burns in a car engine. 32. liquefying oxygen Frost forms on a car window. 33. digestion of food Formation of plutonium from uranium. 34. tarnishing of silver Formation of clouds from water vapor. 35. magnetizing steel formation of dew on grass 36. reacting sodium and water melting of ice cream 37. dissolving sugar in water exploding of dynamite 38. burning sugar to produce carbon fission of uranium 39. decay of radon to lead sublimation of moth balls 40. fusion of hydrogen into helium