16S rRNA gene sequence analysis
advertisement

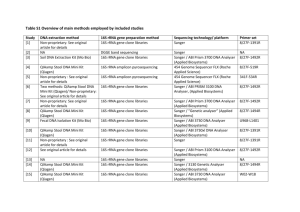
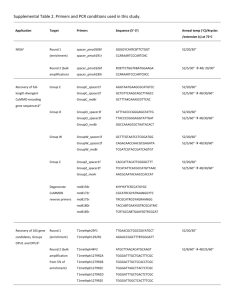
Supplementary File 1 Material and methods Whole-Genomic DNA Extraction from vaginal swab samples Vaginal swabs were thawed on ice prior to extraction and briefly homogenized by vortexing. A 0.5 ml aliquot of each sample was transferred to a sterile 2.0 ml FastPrep Lysing Matrix B tube (MP Bio, Santa Ana, CA, USA) containing 0.1 mm silica beads, and 0.5 ml of PBS (Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA) was added. Cells were lysed by addition of 5 µl of lysozyme (10 mg/ml; Millipore Corp., Billerica, MA, USA), 13 μl of mutanolysin (13.7 U/µL; Sigma-Aldrich corp., St. Louis, Mo, USA), and 3.2 μL of lysostaphin (4,243 U/mL in sodium acetate, Sigma-Aldrich corp., St. Louis, MO, USA). After incubation at 37°C for 30 min, 10 µl proteinase K (20 mg/ml; Invitrogen Corp., Carlsbad, CA, USA), 50 µl of 10% sodium dodecyl sulphate (BioRad, Hercules, CA, USA) in distilled, deionized water, and 2 µl of DNase-free RNase A (10 mg/ml, Fermentas Inc., Glen Burnie, MD, USA) were added and the tubes were incubated for 45 min at 55°C. The cells were then disrupted by bead beating, which was performed in a FastPrep®24 Instrument (MP Bio) for 40 sec at room temperature, 6.0 m/s and then placed on ice. The lysate was processed using the ZR Fecal DNA extraction kit (ZYMO Research, Irvine, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s recommendations, omitting the lysis steps (steps 1-3). The DNA was eluted into 100 µl of sterile deionized water. Each set of extractions included a PBS control that was processed along the biological samples to test for potential reagent contamination. DNA concentrations were measured using the Quant-iT PicoGreen dsDNA assay kit (Invitrogen). 16S rRNA genes amplification and sequencing The V1-V3 hypervariable regions of the 16S rRNA gene were PCR amplified using the following barcoded universal primer pair 27F*-534R: 27F* -5’-CCATCTCATCCCTGCGTGTCTCCGACTCAGTCAGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3’ 534R-5’-CCTATCCCCTGTGTGCCTTGGCAGTCTCAGNNNNNNNNCATTACCGCGGCTGCTGGCA-3’, where the sequences in bold characters are the 454 Life Sciences® Titanium sequencing primers – B in 27F* and A in 534R – and the underlined characters denote the universal 16S rRNA gene primers 27F* and 534R. The variable length barcode (6-8 bp) within primer 534R is represented as 8 Ns. The 27F* primer was a formulation previously shown to better maintain the original rRNA gene ratio of Lactobacillus spp. to Gardnerella spp. in quantitative PCR assays, particularly under stringent amplification conditions (75). The 16S rRNA gene fragments were amplified in 96-well microtiter plates using the following conditions: 2.5 µl 10X PCR buffer II (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA), 2.0 µl MgCl2 (25 mM; Applied Biosystems), 0.5 µl deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate (10 mM), 0.75 µl each of primer 27F* (10 µM) and 5.0 µl 534R (1.5 µM/µl each), 0.125 µl AmpliTaq DNA polymerase (5 U/µl; Applied Biosystems), 10 µl of template DNA (5 ng/µl), and 4.125 µl of H 2O, in a total reaction volume of 25 µl. Reactions were run in a PTC-100 thermal controller (MJ Research, St Bruno, Quebec, Canada) using the following cycling parameters: 5 min denaturation at 95°C, followed by 30 cycles of 30 sec at 95°C, 30 sec at 52°C, and 60 sec at 72°C, with a final extension at 72°C for 7 minutes. Negative controls (10 µl dH2O) for each primer pair used and extraction PBS controls (10 µl) were included. The presence of amplicons was confirmed by gel electrophoresis on a 2% agarose E-gel-96 (Invitrogen). PCR products were quantified using Quant-iT PicoGreen® dsDNA Kit (Invitrogen) and 50 ng of each amplicon were pooled into a single tube. Amplification mixture was gel purified and processed with the AMPure XP Kit (Beckman Coulter, Indianapolis, IN, USA). The purified amplicon mixture was sequenced by 454 FLX Titanium pyrosequencing using 454 Life Sciences® primer A (76) by the Genomics Resource Center at the Institute for Genome Sciences, University of Maryland School of Medicine, using protocols recommended by the manufacturer (SRA accession number pending). 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis All sequences were trimmed before the first ambiguous base pair. The QIIME software package (version 1.7.0) (77) was used for quality control and demultiplexing, using the following criteria: 1) minimum and maximum length of 300 bp and 600 bp; 2) an average of q25 over a sliding window of 25 bp. If the read quality dropped below q25, it was trimmed at the first base pair of the window then reassessed for length criteria; 3) a perfect match to a barcode sequence; and 4) presence of the 534R 16S rRNA gene primer sequence used for amplification. Sequences were binned based on sample-specific barcodes then trimmed by removal of the barcode and primer sequences (forward, if present, and reverse). High-quality sequence reads were first de-replicated (99% similarity) using the UCLUST software package (78). Chimera detection was performed using the UCHIME component of UCLUST (79) with the de novo algorithm. Chimeric sequences were removed prior to taxonomic assignments. Operational taxonomic units (OTU) were defined at 97% sequence similarity (80) and taxonomic assignments were performed using the Ribosomal Database Project (RDP) Naive Bayesian Classifier in QIIME (77) software (version 1.7.0) on the longest sequence read representative of each OTU. Taxa present in at least 25% of all samples were used for the analysis. Depth of sequencing coverage was analyzed using rarefaction curves of Good’s coverage indices, as implemented in QIIME (version 1.7.0) (81). Weighted Unifrac indices (41) were used to generate PCoA plot using QIIME (version 1.7.0) (81). Relative abundances were calculated using the number of sequence reads for each taxon divided by the total number of sequence reads for each sample. Evenness was calculated as the ratio of the Shannon diversity index, 𝐻 = ∑𝑛𝑖=1 𝑝𝑖 ln(𝑝𝑖 ), where, 𝑝𝑖 is the relative abundance of the i-th phylotype, by ln(𝑛), where n is the species richness (the number of taxons). 16S rRNA gene quantitative PCR The total number of 16S rRNA gene copies per swab, an estimate of total bacterial carriage, was quantified using a broad-coverage qPCR assay for each sample as described previously (40). 16S rRNA gene copies were normalized to the total amount of DNA extracted per swab using the following procedure. First, a linear regression was used to generate a calibration curve (10 2-108 16S rRNA gene copies vs Ct value). The regression line was used to generate estimates of total 16S rRNA gene abundance for each of the three qPCR replicates. Student t-distribution was fitted to the differences between the logs of estimated total 16S rRNA gene copies. The resulting scale and degrees of freedom estimated from the Student t-distribution were used to assign to each sample estimated total 16S rRNA abundance as the mean of the Student t regression. Phylotype absolute abundance was defined as the product of the total 16S rRNA count and the phylotype relative abundance (calculated after excluding chlamydial sequence reads) in a given sample. Chlamydial reads were excluded because the PanBacterial total 16S rRNA gene qPCR assay performs poorly in detecting Chlamydia species as reported by Liu et al. (40). Clustering communities The number of clusters displayed in Figure 4 was first evaluated using the Cindex and the plots for both infected and non-infected animals are provided below. 100 60 20 Value C-index 140 Infected humans and guinea pig samples 1 2 3 4 5 6 Number of Clusters 7 8 C. caviae-specific ompA qPCR To quantify the amount of C. caviae cells in each sample, we designed a TaqMan qPCR assay targeting C. caviae outer membrane protein A gene (ompA), which is used to serotype Chlamydia spp. (82). Primers were designed using the Primer-Blast program (83) and C. caviae ompA gene sequence (10). The top 5 primer sets were tested using a modified SYBR green qPCR assay (84) and TaqMan primers were selected that produced: 1) the highest Ct value in the non-template controls, samples known to be C. caviae negative (including DNA isolated from non-infected guinea pig and human vaginal swabs); and 2) the lowest Ct values with C. caviae DNA, DNA isolated from C. caviae-infected guinea pig vaginal swabs, and DNA isolated from Chlamydia-negative human vaginal swabs that were spiked with 25 ng of C. caviae DNA. The selected primers include segments VDIII and VDIV of the ompA gene; ompA-F: 5’and GCGCAGTCTAATCCTAAGATCG-3’; 5’- ompA-R: TCAGTAGCGCTCTCTGTTCC-3’. The internal probe sequence was also designed using the primer-blast program and is complimentary to 18 bp of ompA encoding the VDIV segment. Its sequence is ompA-P: GGCAGAGGGAAGTTGGCCGCTGTCCCTTTA-3’–MGBNFQ. The 6FAM-5’139 bp resulting PCR product was cloned into pCR 2.1 TOPO vector using TOPO TA cloning kit (Invitrogen) following the manufacturer’s instructions. The propagated plasmid was purified using QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit (Qiagen Inc., Valencia, CA, USA). The sequence was verified using Sanger sequencing. The resulting plasmid DNA was quantified using Quant-iT PicoGreen dsDNA Kit (Invitrogen) and used as control in all experiments. Each sample was assayed in triplicate using the following conditions: 1 µl of DNA template, 5 µl of 2X Platinum Quantitative PCR SuperMix-UDG w/ROX (Invitrogen), 0.45 µl of each primer (40 µM), 0.11 µl of the TaqMan probe (20 µM), and 2.99 µl of molecular-grade water. Each experiment included an in-run standard curve of the target sequence cloned into the pCR 2.1 TOPO vector (Invitrogen) using 101 to 108 ompA gene copies and a three no template controls. Amplification and real-time fluorescence detection were performed on a 7900HT Real-time PCR system (Applied Biosystems) using the following conditions: 3 min at 50°C, 5 min at 95°C, then 45 cycles of 15 sec at 95°C, and 1 min at 60°C. Cycle threshold values for each qPCR reaction were obtained using the automatic baseline tool in the Sequence Detection systems v2.3 software (Applied Biosystems). For each assay, DNA extracted from guinea pig vaginal swabs and plasmid standards were run in triplicate. The standard curve and calculations of the number of ompA gene copies were generated using the approach described above for total 16S rRNA gene copies analysis. Assay results were normalized to total volume (200 µl) DNA extracted from a swab and expressed as C. caviae ompA gene copies per swab.