cellular respiration, gulf coast 2013
advertisement

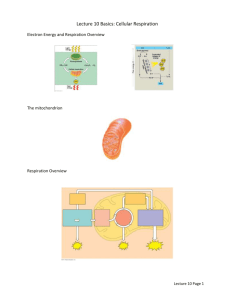
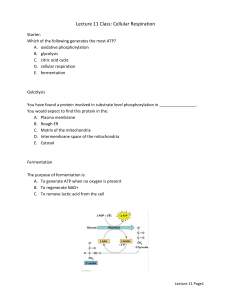
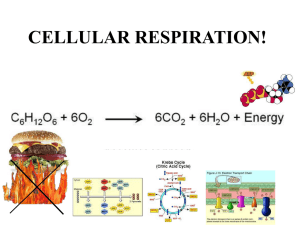
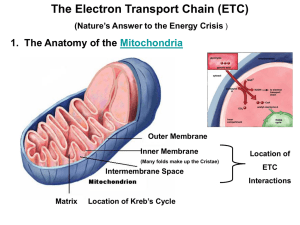
GSCI 2013: Group 2-Cell and Developmental Biology Seth Jones, University of Kentucky Karen Maruska, Louisiana State University Joy Davis, Baton Rouge Community College Sabrice Guerrier, Millsaps College Naila Mamoon, Millsaps College Facilitator: Peter Cavnar, University of West Florida CELLULAR RESPIRATION Context What kind of course is unit designed for? mid-level How long is unit? 1 week When will the unit be used in the course? After students have learned basic chemistry, energetics, redox rxn, protein structure, cell membrane, transport, and organelles Class size? Should be fine for all ranges Learning goal • Understand how the energy from electrons in glucose is converted to chemical energy in ATP during oxidative phosphorylation. Learning outcomes • Explain the role of oxygen in cellular respiration • Explain how the H+ gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane is generated and how it drives ATP synthesis • Predict the effects of various drugs on oxidative phosphorylation How long can you hold your breath? Brainstorm: So why do you think we need oxygen? Loss of hydrogen atoms (becomes oxidized) C6H12O6 6 O2 6 CO2 6 H2O Glucose Gain of hydrogen atoms (becomes reduced) ATP + Heat CYTOPLASM NADH Electrons carried by NADH NADH Glycolysis Pyruvate Glucose Pyruvate Oxidation Citric Acid Cycle FADH2 Oxidative Phosphorylation (electron transport and chemiosmosis) Mitochondrion ATP ATP ATP Substrate-level phosphorylation Substrate-level phosphorylation Oxidative phosphorylation Figure 6.10 H+ Intermembrane space H+ H+ H+ H+ Mobile electron carriers Protein complex of electron carriers H+ ATP synthase IV I II FADH2 Electron flow NADH Mitochondrial matrix H+ H+ III Inner mitochondrial membrane H+ NAD+ FAD 2 H+ 1 2 O2 H2O H+ ADP P ATP H+ Electron Transport Chain Oxidative Phosphorylation Chemiosmosis Welcome to Club Mitochondria • Instructions: Pair with a partner then identify the characters within the analogy that correspond to the following: • 1. Electrons • 2. Protons • 3. Electron transport chain (ETC) • 4. ATP synthase • 5. Mitochondrial Matrix • 6. Intermembrane space What is the layout in Club Mitochondria? Main entrance Female Patron Foyer Dance Floor Male Patron Consider a scenario where the electron transport chain ("dance line") is disrupted in the mitochondria. What is most likely to happen to the H+ concentration ([H+]) in the intermembrane space? • A. Decrease in [H+] • B. Increase in [H+] • C. No change • D. I don't know Consider a scenario where the electron transport chain ("dance line") is disrupted in the mitochondria. What change would you expect in ATP concentration in the cell? • A. Decrease in [ATP] • B. Increase in [ATP] • C. No change • D. I don't know Figure 6.11 Inhibitors of cellular respiration Rotenone Cyanide, carbon monoxide H+ H+ H+ Oligomycin ATP synthase H+ H+ H+ H+ DNP FADH2 FAD NAD+ NADH 1 O 2 2 2 H+ H+ Your homework: List the signs and symptoms in victims with acute cyanide poisoning AND we would like you to extend the analogy to include oxygen and ATP H2O ADP P ATP