Lecture 11 Class: Cellular Respiration Starter: Which of the following
Lecture 11 Class: Cellular Respiration
Starter:
Which of the following generates the most ATP?
A.
oxidative phosphorylation
B.
glycolysis
C.
citric acid cycle
D.
cellular respiration
E.
fermentation
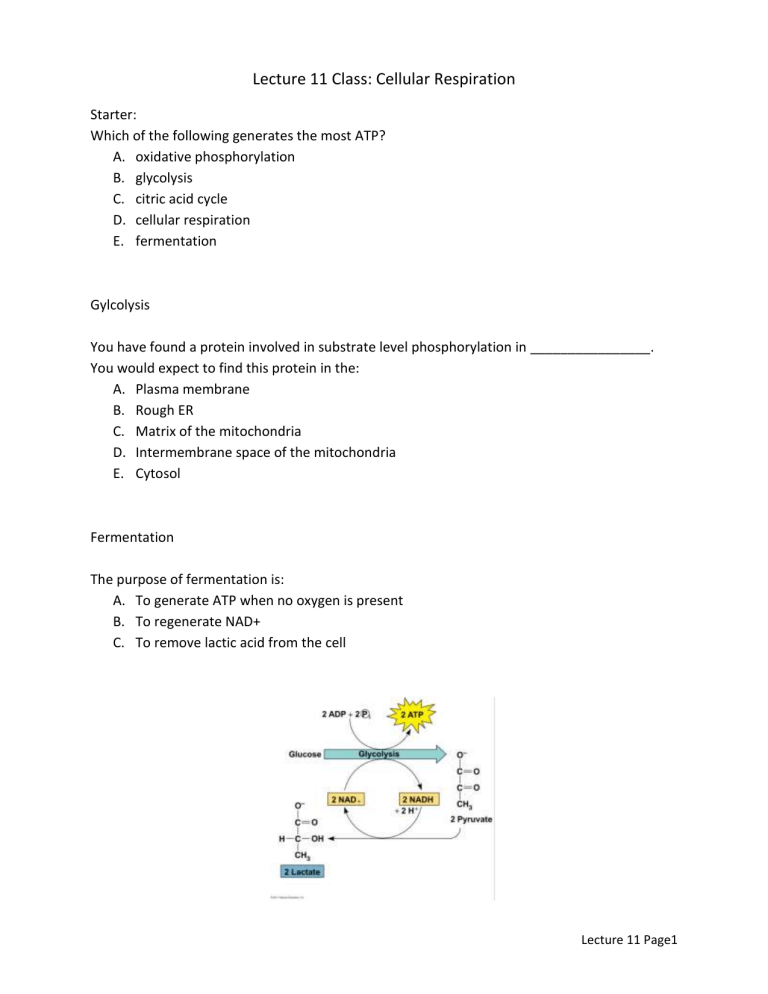
Gylcolysis
You have found a protein involved in substrate level phosphorylation in ________________.
You would expect to find this protein in the:
A.
Plasma membrane
B.
Rough ER
C.
Matrix of the mitochondria
D.
Intermembrane space of the mitochondria
E.
Cytosol
Fermentation
The purpose of fermentation is:
A.
To generate ATP when no oxygen is present
B.
To regenerate NAD+
C.
To remove lactic acid from the cell
Lecture 11 Page1
Chlamydia is an intracellular bacterium that relies on the host cell to provide energy. When a researcher tried to infect host cells that had a defective pyruvate transport protein, the
Chlamydia infection didn’t last long. How did the defective pyruvate transport protein prevent the host cells from making enough energy to support the Chlamydia?
A.
The intermembrane space was acidic compared to the mitochondrial matrix
B.
NAD+ became oxidized in the cytosol
C.
The electron transport chain stopped because it lacked a final electron acceptor
D.
Host cells had to use lactic acid fermentation to make ATP
E.
Substrate level phosphorylation was inhibited
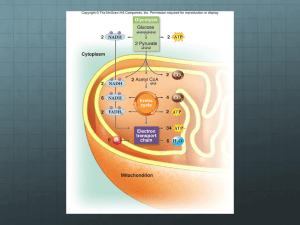
Oxidative Phosphorylation
When the electron transport chain in a mitochondrion is ______________________, which of the following occurs?
A.
Electrons are pumped into the intermembrane space
B.
NADH is oxidized to NAD+
C.
Oxygen is produced in the mitochondrial matrix
D.
pH of the mitochondrial matrix decreases
E.
ATP synthase actively pumps protons
Lecture 11 Page2
Three Experiments:
Mix together in a test tube these basic ingredients:
1.
Isotonic saline and intact mitochondria
2.
Succinate (an electron donor)
3.
ADP and Pi
Experiment 1: Basic ingredients only
Experiment 2: Basic ingredients plus cyanide (blocks Complex IV, prevents electrons from binding to O2)
Experiment 3: Basic ingredients plus dinitrophenol (creates hole in inner mitochondrial membrane)
Lecture 11 Page3
Triglycerides, a type of fat, are found in high concentrations in the blood after eating starchy and fatty foods. What process will cells use to generate ATP from triglycerides?
A.
oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria
B.
glycolysis in the mitochondria
C.
digestion in the stomach
D.
cellular respiration in the blood
A small amount of _________________ is produced by the enzyme pyruvate kinase during glycolysis. In this exergonic reaction:
A.
The enzyme is a carbohydrate
B.
The potential energy of the reactants is higher than the products
C.
There is no activation energy
D.
An inhibitor of this enzyme would decrease the amount of ADP
E.
ATP is needed to drive the reaction forward.
Piazza Question
Which of the following statements about enzymes is TRUE?
A.
Enzymes can be synthesized on free or bound ribosomes
B.
Enzymes speed up reaction rate by increasing the energy available
C.
All biological enzymes are most effective at pH 7
D.
Enzymes can use energy from ATP to become macromolecules
E.
Enzymes can turn an endergonic reaction into an exergonic reaction
Lecture 11 Page4