Ionic Compounds
advertisement

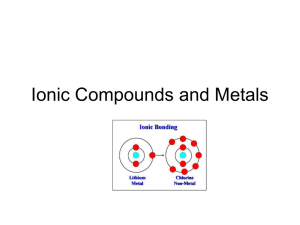
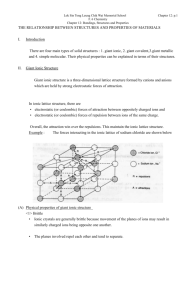
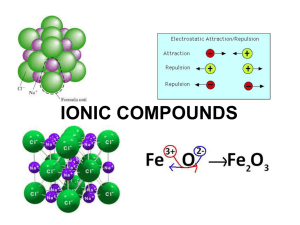
Ionic Bonds A Closer Look Ionic Bonds Are formed when atoms lose or gain electrons (forming ions) to become stable. Metals tend to lose electrons Nonmetals tend to gain electrons Ionic compounds are formed when metals and nonmetals react together Are formed from the electrostatic attractions of oppositely charged ions. Ionic Compounds When ionic bonds form ionic compounds they produce a repeating arrangement of the ions into a crystal structure called a lattice. The formula for an ionic compound is called the formula unit. The formula unit is represented in the crystal lattice. KF (potassium fluoride) is the formula unit for the solid crystal formed when K+1 ions and F-1 ions are bonded ionicly Sketch a simple crystal pattern Ionic Solids Ionic solids exist in a lattice (crystal) structure. Ionic compounds can form different kinds of lattice structures. Lattice structures depend on the number of ions involved the charge of the ions involved the sizes of the ions. Lattice Energy (Bond Energy for Ionic Compounds) The strength of an ionic bond depends on the size of the ions and the amount of charge each ion carries. Bigger ions will have weaker ionic bonds (lower lattice energy) Greater ionic charges will have stronger ionic bonds. (higher lattice energy)