toxaemiapregnancy - Dr. Mehdi Hasan Mumtaz
advertisement

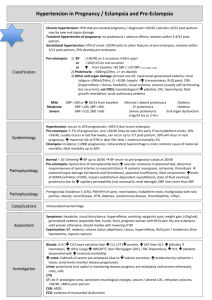
HYPERTENSIVE DISEASE OF PREGNANCY Prof. Mehdi Hasan Mumtaz 1 MATERNAL PHYSIOLOGY Anaemia. Hyperventilation. Hypovolaemia. Hyper-coagubility. 2 HYPERTENSIVE DISEASE OF PREGNANCY Pre-eclampsia. Eclampsia. HELLP syndrome. 3 PRE-ECLAMPTIC TOXEMIA (PET) TRIAD Hypertension. Proteinurea. Oedema. 4 SEVERE-PRE-ECLAMPSIA Definitions BP> 140/90. Proteinurea >0.5 G/24h or >2+ urine analysis + Epigastric pain. Haedache. Visual disturbances. Clonus> 3beats. Platelet count <100x109. ALT>50IU/L. SPB = DBP = PROTEINUREA OR > 170 > 110 >0.5 G/24h OR > 2+ URINE ANALYSIS. 5 HAEMODYNAMIC FINDINGS Severe Pre-eclampsia Low plasma volume. Low /Normal CO. Low/ Normal CVP/PCWP. myocardial contractility. Low COP. 6 ECLAMPSIA Hypertension. Protein urea. Oedema. Convulsion. 7 HELLP SYNDROME “Mos severe end of pre-eclamptic condition” H – Haemolysis. EL - Liver enzyme. LP - Platelet count. “Additional: Haemopoietic system” “Liver involvement” 8 PATHOLOGICAL FEATURES Hypertension. Renal functions. Hypovolaemia. Hypoproteinaemia. Coagulation/fibrinolytic imbalance. Cerebral irritability. Placental perfusion. 9 NORMAL PREGNANCY Vasoconstriction Vasoconstriction Platelet aggregations Platelet aggregations Uterine activity Uterine activity Utero-placental blood flow Utero-placental blood flow Prostacyclin Thromboxane 10 PRE-ECLAMPSIA Vasoconstriction Platelet aggregations Uterine activity Utero-placental blood flow Prostacyclin Vasoconstriction Platelet aggregations Uterine activity Utero-placental blood flow Thromboxane 11 FLUID MANAGEMENT “Important” Relatively Low PV Low PAWP CO Endothelial damage. Low COP Excessive fluid therapy fetal distress oligurea risk pulmonary oedema 12 MANAGEMENT Definitive Delivery of baby Delivery of plaenta Symptometic Control Blood pressure. Convulsions. Fluid balance 13 MANAGEMENT SYMPTOMATIC HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE Dangers: Cerebral haemorrhage. Pul oedema Objective: DBP 90-100mmHg <90 uteroplacentl perfusion 14 BLOOD PRESSURE CAUTION. 4.5% HES 500ml preload. Before IV anti-hypertensive. EXCEPTION. Patient post delivery. Who has 4.5% HES already. DBP >120. 15 BLOOD PRESSURE HYDRALLAZINE 5mg/5min in 20 min. If BP 90-100 40mg/N-saline, 1-5mg/h. IF AT 20min DBP >100 5mg/min in 20 min. If BP 100 40mg/N-saline, 1-5mg/h. IF AT 20min DBP >100 LABETALOL 10-20mg IV/10min If DBP 90-100 or Total 220mg given 16 BLOOD PRESSURE Labetalol. 10-20mg boluses/15min. If DBP 90-100. Infusion 5mg/ml (0-160mg/hr). Ca+ channel blockers. Nitrates. Adrenergic neuron blockers. 17 ECLAMPSIA ROOM Indications. 1. Eclampsia. 2. Hypertension > 170/110 + Proteinurea > 2+ 3. Hypertension > 140/90 Proteinurea 2+ + One of the symptom/signs 18 SYMPTOM/SIGNS Headaches. Visual disturbances. Hyper-reflexia. Clonus (>3beats). Nausea & vomiting. Epigastric pain. Raised liver enzymes. Thrombocytopenia<100x10/L. 19 “MONITORING” Eclampsia Room ECG. NIBP. SPO2. Fluid balance. Urine output. CTG. CVP. 20 INTRACELLULAR INTERSTITIAL VASCULAR CAPILLARY EG CELL OSMOLALITY Na+ COP 21 FLUID BALANCE Restrict fluids. (2000ml/24hrs) Urine output <25ml/hr. Pass CVP catheter. CVP Group A: CVP <4mmHg- underfilled. Group B: CVP 4-8mmHg- optimialy filled. Group C: CVP >8mmHg- over filled. 22 CVP GROUP - A. Fluid challenge. HES 4.5% 100ml. Bring CVP 4-8. GROUP - B. Fluid challenge careful. CVP 4-8. Urine O/P <25ml give dopamine.. GROUP - C. No pul oedema. Dopamine 1-3g/kg/min. Pulmonary oedema present. Frusemide 20mg. Refer to ICU. 23 SEIZURE PROPHYLAXIS “Severe pre-eclampsia” “Controversial” Magnesium sulphate. Loading dose 4G. Infusion 2G/hr. Optimum level 2-4mmol/L. 24 MAGNESIUM SULPHATE Blood Levels Mgnesium (mmol/L) 0.7-1 2-4 >5 >7.5 >10 Effect Normal Therapeutic range. Loss of reflexes. Respiratory depression Cardiac arrest 25 MAGNESIUM SULPHATE Magnesium level >4 = dose (.5-1G/h) Magnesium level <1.7=give 2G bolus. dose 2.5G/h. Magnesium level 1.7-2 continue 2G/h. 26 MONITORING DURING MAGNESIUM INFUSION Patellar reflex. ECG. SPO2. Mgnesium level. 27 MANAGEMENT MAGNESIUM TOXICITY Loss of patellar reflex. Stop infusion. Measure level. Withold till reflex returns. Once reflex return – 1G/h. Give O2. Stop maintenance dose. Measure level. Inform anaesthetist. Stop infusion. CPR. Calcium gluconate. Intubation/ventilation. SPO2 <90%. Cardio-respiratory arrest. 28 MAGNESIUM THERAPY Considerations Tocolytic effect. Interaction – muscle relaxants. Interaction – calcium antagonists. 29 “INDICATIONS” ICU – ADMISSION Severe coagulopathy or DIC. Recurrent seizures. Hypertension – poor control. Persistant oligurea. Pulmonary oedema + oligurea. Compromised myocardial function. 30 MANAGEMENT Definitive Delivery of baby Delivery of plaenta 31 MANAGEMENT Severe Cases Arrest & prevention of convulsion. Barbituates. Benzodiazepines. Megnesium SO4. Paralyse & IPPV. Blood pressure. Hypertension – vasodilatation. Hypotension – inotropics. 32 MANAGEMENT Severe Cases Restoration of blood volume. Low proteins. Colloids. Colloid substitutes. Progressive dehydration. Replace out put. Keep BV normal. 33 ECLAMPSIA “Labour Room” S.B.P. > 160 Torr. DBP > 110 Torr. Protein urea >5G/24h. Oligurea 500ml or less. Epigastric pain. Cyanosis. Pulmonary oedema. Convulsions. 34 IN ICU B. P. < 80 Torr. Urine output – nil. Convulsions. Pulmonary oedema. Cyanosis. 35 ROUTINE CVP Monitoring. Urinary catheter. Nasogastric catheter. Heavy sed with: Valium. Pheno. IPPV. Aemocel 500ml daily Blood 500ml/day. Digitalise. Inotropes if needed. Balance. Negative 7-10day=10-14L Ventilator off 3-4 day. 36 IDEAL MANAGEMENT Pass CVP catheter. Pass urinary catheter. Pass nasogastric tube. Replace obvious loss by crystaloids. Normalise blood volume by colloids. Remove excess fluids. From ext vascular comp. By forced diuresis. Keep the body in electrolyte balance. 37 IDEAL MANAGEMENT Routine investigations. Hb. HCT. Plasma proteins. Serum Na+ K+. Monitoring. Urine output. ECG. BP. Pulse CVP. 38 HELLP SYNDROME H – Haemolysis. EL – elevated Liver enzyme activity. LP - Platelet count. “most sevre end of pre-eclamptic condition” 39 CLINICAL FEATURES Epigastric pain. Upper abdominal tenderness. Proteinurea. Hypertension. Jaundice. Nausea & vomiting. Haematuria. Oligurea. A T necrosis. Cortical necrosis. Pan-hypopituitarism. Actue liver rupture RDS. 40 MANAGEMENT Early diagnosis. Stbilization. Prompt delivery if. Pre-eclampsia worsens. Worsening of hepatic renal functions. Severe thrombocytopenia. Gestational age at or beyond 32-34wks. Evidence of foetal distess. Evidence of foetal maturity. 41 MANAGEMENT Pre-op investigations. Platelet count. PCV. Hb. PTT. Fibrinogen concentration. FDP. LFTs. Creatinine. Urea. Uric acid. X-ray chest. 42 Platelet infusion if. <50000mm-3 cs. <20000mm-3 vag.D. Blood transfusion if. B <10.0G/dl. Hb. PPF. FFP. CVP. Urine output. Maternal blood glucose control. IPPV. 43