JDBC - Database Drivers - Computer Science
advertisement

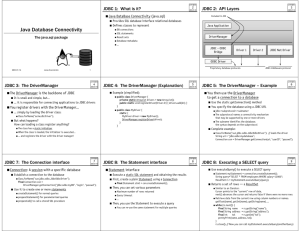
Java and Databases CS-328 Dick Steflik Database Drivers • Think of a database as just another device connected to your computer • like other devices it has a driver program to relieves you of having to do low level programming to use the database • the driver provides you with a high level api to the database ODBC • Open Data Base Connectivity • Developed by Microsoft for the Windows platform as the way for Windows applications to access Microsoft databases (SQL Server, FoxPro, Access) • Has become an industry standard • Most data base vendors supply native, odbc, and jdbc drivers for their data base products JDBC Architecture Java Application JDBC API Data Base Drivers Access SQL Server DB2 Informix MySQL Sybase JDBC Driver Types • Type 1 – JDBC-ODBC Bridge • Type 2 – Native API, partially java • Type 3 – JDBC Network Driver, partially java • Type 4 – 100% Java Type 1 Drivers • Translate JDBC into ODBC and use Windows ODBC built in drivers • ODBC must be set up on every client – driver must be physically on each machine for both java applications and applets – for server side servlets ODBC must be set up on web server • driver sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbc provided by JavaSoft with JDK Type 1 Driver (cont.) Client JDBCODBC Vendor Library ODBC DB Type 2 Drivers • Converts JDBC to data base vendors native SQL calls • like Type 1 drivers; requires installation of binaries on each client Type 2 Drivers (cont.) Client JDBC Vendor Library DB Type 3 Drivers • Translates JDBC to a DBMS independent network protocol • Typically talks directly with a middleware product which in turn talks to the RDBMS – Jaguar, DBAnywhere, SequeLink • Most flexible driver type • all java Type 3 Drivers (cont.) Client JDBC Tier 1 Vendor Middleware Tier 2 DB Tier 3 Type 4 Drivers • Converts JDBC directly to native API used by the RDBMS • compiles into the application , applet or servlet; doesn’t require anything to be installed on client machine, except JVM • handiest driver type Type 4 Drivers (cont.) Client JDBC DB Structured Query Language • Developed by C. Date for Relational Data Base Management Systems (RDBMS) • Simple Declarative Language – has no program control statements SQL • Two categories of commands – Data Manipulation Commands • deal with: – RETRIEVING DATA – MAINTAINING DATA (ADDING, UPDATING,DELETING – Data Definition Commands • DEAL WITH: – CREATING DATABASE OBJECTS (TABLES,VIEWS) – Object organization and attributes Referential Integrity • Rules to insure that table data stays accurate and accessible – rows in a table should be unique • one column should contain no duplicate data • primary key – column values cannot contain repeating groups or arrays – null is different than space and zero, 2 null values are not considered equal Data Manipulation Commands • Select - query and display data from a database • Insert - a new row into a table • Update - modify a column in a table • Delete a row from a table Select • • Select (column list) from (sources) where (conditions) order by (ocolumn list) column list - comma separated list of names of columns to be in output – Ex. ssn , lastname , firstname,gpa – can contain literals to be included in output • Ex. Ssn,”~”,lastname,”~”,firstname • • sources - name(s) of table(s) to retrieve data from conditions (optional) - conditions for selections – lastname like “S%” – (lastname = “Steflik) and (firstname like “R%”) • • ocolumn list (optional)- list of columns that output should be ordered by Ex – select * from student – select lastname,fristname from student where gpa > 3.0 – select lastname,firstname from student order by lastname,firstname Select - joined tables • Two tables may be joined and viewed as a single data source is the both have a common column • suppose we have 2 tables: Inventory and category and each has a column called catg_code • In category catg_code is unique and is the primary key Select - joined tables (cont.) join Inventory P_no Catg_code qty Category Catg_code descr Select - joined tables (cont.) • To retrieve all of the part numbers and the name of the category to which the part belongs: – select inventory.p_no category.descr from inventroy , category – select a.p_no,” “,b.descr from a inventory , b category Insert • Add a row to a table – insert into category values(“IGN”,”Ignition System”) • use jdbc execute Update method – ex. Stmt.executeUpdate(“insert into Category values(‘IGN’,’Ignition System’)”); Update • Modify an existing row in a table – update category set descr = “Ignition Subsystem” where catg_code = “IGN” • Use jdbc executeUpdate method – String s = “update category set descr = ‘Ignition Subsystem’ where catg_code = ‘IGN’ ”; – stmt.executeUpdate(s); Delete • Remove a row from a table – – delete from category where catg_code = “IGN” • remove the IGN category delete from category where catg_code like “I%” • remove all rows where catg_code starts with an “I” Data Definition Commands • Create table – add a table to a database • Drop Table – remove a table from a database • Alter Table – add or delete column(s)