CHEM 1412 Exam #2 ... (Chapters 15,16, and 18) ...
advertisement

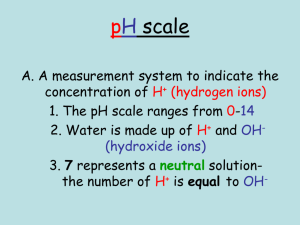
CHEM 1412 Exam #2 (Chapters 15,16, and 18) Name:___________________ Score: Part I - ( 3 points each) - please write your correct answer next to each question number. DO NOT CIRCLE 1. Calculate the pH of a solution if it's [OH] = 0.000700 M and indicate whether the solution is acidic, basic, or neutral. a. 3.15, acidic b. 17.2, basic c. 10.8, basic d. 11, basic 2. Which one of the conjugate bases of the following Brønsted-Lowry acids is incorrect? a. ClO- for HClO b. HS- for H2S c. H2SO4 for HSO4d. NH3 for NH4+ 3. At normal body temperature, 37°C, Kw = 2.4 x 10-14. Calculate [H+] if [OH-] = 1.3 x 10-9 M at this temperature. a. 1.3 x 10-9 M b. 1.0 x 10-7 M c.7.7 x 10-6 M d. 1.8 x 10-5 M 4. Calculate the pH of a 0.025 M solution of propanoic acid (Ka = 1.3 x 10-5). a. 5.7 x 10-4 b. 0.025 c. 1.6 d. 3.24 5. Predict whether aqueous solutions of the following compounds are acidic, basic, or neutral. Find the incorrect answer. a. KNO3 (neutral) b. NaC2H3O2 (basic) c. KClO (acidic) d. NaCN (basic) 6. Which of the following acids consider as a strong acid? a. HCN b. HClO4 c. HF d. HNO2 7. Does the pH increase, decrease, or remain the same on addition of each of the following? (i) NaNO2 to a solution of HNO2, (ii) HCl to a solution of NaC2H3O2 a. (i) decrease, (ii) increase c. (i) decrease, (ii) decrease b. (i) increase, (ii) increase d. (i) increase, (ii) decrease 8. Calculate the pH of a solution of 0.080 M H2SO4 . a. 1.10 b. 0.80 c. -1.10 d. 0.080 9. How many mL of 0.0350 M NaOH are required to titrate 65.0 mL of 0.0620 M HBr to the equivalence point? a. 8.69 x 10-3 mL b. 33.4 mL c. 36.7 mL d. 115 mL 10. Calculate the pH of a buffer that is 0.20 M in formic acid and 0.15 M in sodium formate (Ka = 1.8 x 10-4). a. 2.4 x 10-4 b. 3.63 c. 0.82 d. 8.33 11. Which of the following acid dissociation constants represents a stronger acid? a. Ka = 1.8x10-5 b. Ka = 7.4x10-4 c. Ka = 1.45x10-6 d. Ka = 6.67x1 0-10 12. If X is the solubility of a salt in moles per liter, which one of the following Ksp expressions is incorrect? a. Ag2S , Ksp = 4X3 c. BaSO4 , Ksp = 4 X2 b. AgCl , Ksp = X2 d. Cu(OH)2 , Ksp = 4X3 13. How does the entropy of the system change when each of the following occurs (i) a solid is melted, (ii) a liquid vaporizes, (iii) a gas liquefies? a. b. c. d. (i) increases, (ii) increases, (iii) decreases (i) increases, (ii) increases, (iii) increases (i) decreases, (ii) increases, (iii) increases (i) increases, (ii) decreases, (iii) increases 14. For each of the following processes, predict whether entropy, S , is positive or negative: (i) 2K(s) + Br2(l) 2KBr(s), a. (i) positive, (ii) positive c. (i) positive, (ii) negative (ii) 2MnO2(s) 2MnO(s) + O2(g) b. (i) negative, (ii) positive d. (i) negative, (ii) negative 15. Using the given values of S° ( J/mol.K) , calculate the value of S° for the reaction; C2H4(g) + H2(g) C2H6(g) S0 = 219.4 229.5 a. -120.5 J/ K b. 120.5 J/ K c. 10.1 J/ K d. -10.1 J/ K 16. For a certain reaction, H = 45 kJ and S = 125 J/K. Assume that H and S do not vary with temperature. At what temperature will the reaction have G = 0? a. 0.36 °C b. 0.36 K c. 360 °C d. 360 K 17. In which case does the entropy of the system decrease significantly? a. H2O(l) H2O(g) c. SnO2(s) + 4C(s) Sn(s) + 4CO2(g) b. C(s) + O2(g) CO2(g) d. N2(g) + 3 H2(g) 2NH3(g) 18. Calculate the equilibrium constant at 298 K for the reaction G0 = - 254.8 KJ CaCO3(s) CaO(s) + CO2(g) a. 4.61 b. 1.02x102 c. 4.61x1044 d. none of these 19. At equilibrium which of the following is zero? a. H b. G c. S d. All of these 20. Which of the following represents a spontaneous reaction ? a. K>1 b. G< 0 c. S >0 d. all of these PART II - ( 8 points each) Please show all your work. 21. If the pH of a solution is 6.30, what are the molar concentrations of H+(aq), OH-(aq) , and pOH in the solution? 22. Lactic acid, HC3H5O3, has one acidic hydrogen. A 0.10 M solution of lactic acid has a pH of 2.44. Calculate Ka. 23. Calculate the percent ionization of 0.10 M butanoic acid (Ka = 1.5 x 10-5) in a solution containing 0.050 M sodium butanoate. 24. A 50.0-mL sample of 0.50-M acetic acid, CH3COOH, is titrated with a 0.150 M NaOH solution. Calculate the pH after 25.0 mL of the base have been added (Ka = 1.8 x 10-5). 25. Given calcium hydroxide , Ca(OH)2, ( Ksp = 5.5x10-6) a) What is the molar solubility? b) What is the pH of this solution? BONUS QUESTION - (10 points) Given 20.0 ml , 0.05 M acetic acid ( Ka = 1.8x10-5) titrated with 0.05 M NaOH. Calculate the pH of the following solutions. a) b) c) d) e) initial solution mixture after adding 5.0 ml , 0.05 M NaOH solution mixture at one-half equivalent point mixture at equivalent point mixture after adding 25 ml , 0.05 M NaOH CHEM 1412 EXAM #2 (KEY) ( Chapters 16,17, and 18) PART - I 1. C 4. D 2. C 5. C 3. D 6. B 7. D 8. A 9. D 10. B 11. B 12. C 13. A 14. B 15. C 16. D 17. D 18. C 19. D 20. D PART - II 21. [ H + ] = 10 - pH = 10 - 6.30 = 5.0 x 10 -7 M 1.0 x 10 -14 [ OH - ] = = 2.0 x 10 -8 M ; 5.0 x 10 pOH = 14 - 6.30 = 7.7 -7 22. [ H + ] = 10 - pH = 10 - 2.44 = 3.63 x 10 -3 M [H +] ______ = MaKa ; 23. pka = 4.82 ; ( 3.63 x 10 -3 ) 2 ka = = 1.32 x 10 -4 ( 0.10 ) PH = 4.82 + log ( 0.050 / 0.10) = 4.82 - 0.30 = 4.52 [ H + ] = 10 - pH = 10 - 4.52 = 3.02 x 10 -5 M [ H + ] x 100 % ionization = = Ma 0R, ( 3.02 x 10 -5 ) ( 100 ) ( 0.10 ) = 3.02 x10 -2 % or .0302 % MaKa [H +] (0.10)(1.5 x 10 -5) = = = 3.0 x 10 - 5 M , % I = 0.0300% Ms ( 0.05 ) 24. (0.50)(50.0) [ H + ] = Ma = = 0.33 M (MORE ACIDIC), pKa = 4.75 (50.0 + 25.0) ( 0.150 ) ( 25.0 ) [ OH - ] = Mb = = 0.05 M ( 50.0 + 25.0 ) Mb 0.05 pH =4.75 +log = 4.75 + log = 4.75 - 0.748 = 4.00 Ma - Mb 0.33 - 0.05 25. (a) Ca(OH)2 (S) Ca 2+(aq) +2OH- (aq) ; Ksp=[Ca 2+ ] [OH- ]2 = (X)(2X)2=4X3 X = 3√ 5.5 x 10 -6 /4 = 1.11 x 10 - 2 M (b)[OH- ]= 2x = 2(1.11x10 -2) = 2.22 x10-2 M ; pOH =1.65 ; pH = 12.35 BONUS Kw ( 1.0 x 10 -14 ) Ka = 1.8 x 10 -5; Kb = = 5.56 X 10 -10 ; pKa = 4.75 10 -5 Ka ( 1.8 x ) __________________ ( 0.05 ) ( 1.8 x 10 -5 ) = 9.49 x 10 -4 M ; ______ + (a) [H ] = MaKa = (b) PH= 3.02 (0.05)(20.0) Ma = = 0.04 M ( WEAK ACID ) (20.0 + 5.0) (0.05) (5.0) Mb = = 0.01 M ( STRONG BASE) (20.0 + 5.0) Mb pH = 4.75 + log 0.01 = 4.75 + log Ma - Mb = 4.75 - 0.477 = 4.27 0.04 - 0.01 (c) At one-half equilibrium, pH = pKa = 3.75 (d) (0.05)(20.0) Mb = = 0.025 M; At equilibrium strong base dominates. (20.0 + 20.0) ______ ________________ [OH ]= MbKb = (0.025)(5.56x10-10) =3.72x10-6 M; pOH=5.42; pH = 8.57 (e) (0.05)(20.0) Ma = = 0.022 M ( WEAK ACID ) (20.0 +25.0) (0.05)(25.0) Mb = = 0.028 M ( STRONG BASE) (20.0 + 25.0) diff [OH-] = Mb – Ma = 0.028 – 0.022 = 0.006 M pH=14 + log (0.006) = 14 – 2.22 pH = 11.78