CHAPTER 15
advertisement

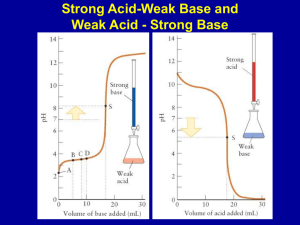
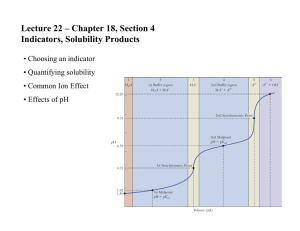
CHAPTER 15 AP CHEMISTRY COMMON ION EFFECT • If you have HC2H3O2(aq) <=> H+ (aq) + C2H3O2-(aq) • • • What would happen if you added the salt NaC2H3O2? Addition of C2H3O2- would cause the system to shift to the left This is called the COMMON-ION EFFECT Page 682 example BUFFER • Prepared by adding both the weak acid HB and its • • • • • • • • conjugate base B- to water [H+] = ka[HB] = ka nHB [B-] nBEffect of adding strong acids or bases to a buffer HB(aq) + OH-(aq) ---> H2O(l) + B-(aq) B-(aq) + H+(aq) ---> HB(aq) H+ and OH- ions are consumed so the pH is not affected Buffered solutions are most effective when concentrations of H+ and base B- are about the same Read chapters 19 and 20 notes are due the first day of fourth term CONTINUED • Henderson-Hasselbach equation is used in biology to calculate the pH of the buffer • pH = pka+ log [base] • [acid] ACID-BASE TITRATION • Read and study pages 699-711 • Titration curve – Graph of pH to concentration • strong acid - strong base page 697 • H+(aq) + OH-(aq) <=> H2O(l) k = 1/kw = 1/(1 X 10-14) – pH = 7, change rapidly as you near the end point CONTINUED • Weak acid-strong base • HA(aq) + OH-(aq) <=> A-(aq) + H2O(l) k =1/kb • pH > 7 at end point, change occurs slowly at end • • • • • point Strong acid-weak base H+ (aq) + A-(aq) <=> HA(aq) k = 1/ka pH < 7, at end point, change occurs slowly at end point Titration of polyproptic acids When neutralization steps are separated the substance will show a titration curve with multiple equivalence points INDICATORS • HIn(aq) <=> H+(aq) + In-(aq) In = indicator • HIn and In- have different colors, the wavelengths that • • • • • • bounce back are different when hydrogen is attached Color of a solution depends on the concentration ratio [HIn] = [H+] [In- ] ka Endpoint occurs when [H+] = ka About pH 5 for methyl red, pH 7 for bromothymol blue, and pH 9 for phenolphthalein Read pages 711-716 SOLUBILITY EQUILIBRIA • If Q(ion product) is compared with the ksp, the following can be said • Q > ksp ppt occurs until Q = ksp • Q = ksp equilibrium (saturation has occured) • Q < ksp solid dissolves until Q = ksp • AgCl(s) <=> Ag+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) • Slightly soluble ksp found on page 718 • ksp = [Ag+][Cl-] CONTINUED • the solubility of slightly soluble salts containing basic anions will increase as the [H+] increases • Looking at the solubility of a salt • In pure water it is the same as the reaction • CONTINUED • Complex ions – Metal ions with Lewis bases bonded to it page 958, 731-737 • Amphoterism – Behavior of water molecules around a metal ion • Read pages 724-730