1.4: Isotopes
advertisement

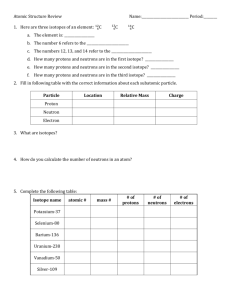
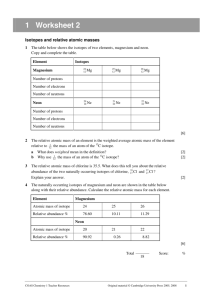
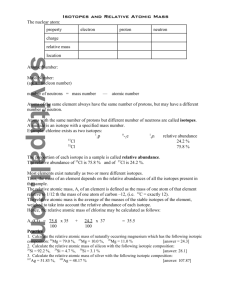
1.4: Isotopes Isotopes • Atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons (protons and electrons remain unchanged) • Example: Carbon-12 and Carbon-14 are two isotopes of carbon. • They both have 6 protons and 6 electrons. • Carbon-12 has 6 neutrons, • Carbon-14 has 8 neutrons. Isotopes • Isotopic Abundance – The percentage of a given isotope in a sample of an element • For example, natural magnesium is a mixture of three isotopes: • Magnesium-24 (78.7% abundance), • Magnesium-25 (10.1%), and • Magnesium-26 (11.2%). • Every single atom of Mg does not have the exact same mass!! • The atomic mass of an element on the periodic table is actually an average! Isotopes • Mass Spectrometer – an instrument used to determine the mass and abundance of Isotopes • Atomic Mass Unit (amu) – approximately the mass of one proton or neutron, which is 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom. • Unit symbol = µ Isotopes Application: Carbon-14 Dating • C-14 loses those extra neutrons and becomes C-12. This is called radioactive decay. It happens regularly, like a clock. For carbon, this decay is relatively short (a few thousand years). • Some elements take longer and others have a decay that happens over a period of minutes. Isotopes Calculations Determining the Atomic Mass of Elements Atomic mass = % abundance of isotope 1 (mass of isotope 1) + % abundance of isotope 2 (mass of isotope 2) … ** convert percentages into decimals!! Isotopes Calculations Example: Calculate the atomic mass of magnesium. The isotopic abundances are: Magnesium-24 78.7% Magnesium-25 10.1% Magnesium-26 11.2% It was found that an element was composed of isotopes with atomic masses 29.0μ, 30.0μ and 31.0μ. Isotope-29 has a 15% abundance and isotope-31 has a 58% abundance. What is the average atomic mass of the element? An element is composed of 30% of an isotope with an atomic mass of 57.0μ. If the other isotope contains 3 more neutrons per atom, what is the average atomic mass of the element? Two isotopes have masses of 120μ and 124μ. If the relative abundance of the more massive isotope is 5 times that of the less massive, determine the average atomic mass of the element. Read pages 23 – 29 and answer questions1-9 on page 29.