Ch. 16 Acids and Bases Review 16.1 Name:__________________________________________ Pd: _____
advertisement

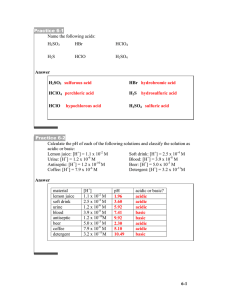
Ch. 16 Acids and Bases Review Name:__________________________________________ Pd: _____ 16.1 1. According to the Arrhenius model, acids are substance that dissociate and produce ___________, and bases are substances that dissociate and produce _______________. Arrhenius developed his model because he observed that acidic and basic solutions ____________________________________________________________. 2. According to the Brownsted-Lowry model, acids are substance that ___________________________, and bases are substances that ____________________________________. 3. What is a conjugate acid? What is a conjugate base? 4. What is the conjugate base of HF? What is the conjugate acid of H2O and what is its name? 5. Write a balanced equation for a. how HCl acts as an acid (assume the Bronsted-Lowry model is more correct) and connect with lines the conjugate acid-base pairs. b. Repeat part a. with NH4+ instead of HCl. 6. [H3O+] often written as simply ________________ 7. If the [OH-] of a solution increases then then the [H+] _______________________ 8. A strong acid has a weak _________. A weak acid has a ____________________________. 9. XOH is definitely a strong base if X represents an element that is a ___________________ metal. 10a. What is the [OH-] of a solution if [H+] = 2.54 x 10-4 M (at 25 degrees Celsius)? b. Is the solution acidic, basic, or neutral? c. What is the pH and pOH of this solution? 11. If .111 mol of HNO3 are dissolved in 120 mL of water, calculate [H+], [OH-], the pH, and the pOH. (HNO3 is a strong acid.) 12. A strong acid differs from a weak acid in that a strong acid _____________________________________ and a weak acid __________________________________________________. 13. An acid where the acid H is bonded to an O is called _______________________. An acid with a carbon backbone and a carboxyl group (COOH) is called ________________. H2SO4 is called diprotic because __________ ___________________________________________________________________________. 16.2 14. If the pOH of a solution is 8.94, what is [H+]? 15. What is the pH of HNO3 (a strong acid) with a molarity of .010 M? Why is the pH of a .010 M weak acid not the same? 16. What is the pH of a solution of 10-3 M LiOH? 17. A substance that can act as an acid or as a base is called ________________________. 18. A solution is acidic if it has more ____________ than ___________, or if the pH is __________________. 19. What is the hydroxide ion concentration if the pH= 4.80? What is the hydronium ion concentration? 16.3 20. When an acid and a base are mixed a _______________________________ reaction occurs, which always produces ____________________ and a ____________. 21. An indicator is a substance that changes _____________ in an acidic and/or basic solution. For example, litmus paper turns _________ in an acid and _________ in a basic solution. Phenolphthalein is ____________ in an acidic solution and ____________ in a basic solution. 22. The point at which exactly enough of the titrant has been added to react with the solution being analyzed is called the __________________________________________. 23. A ___________________ is a solution that resists a change in pH even when a strong acid or base is added to it. It is formed by the presence of a ____________________________ and _____________________________. 24. How much .500 M HCl is needed to completely titrate 43.0 mL of .300 M NaOH? 25. If 153 mL of Ca(OH)2 is completely titrated by 62.0 mL of 1.11 M HNO3, what is the molarity of the Ca(OH)2?