acid_base_review_sheet_CP answers
advertisement
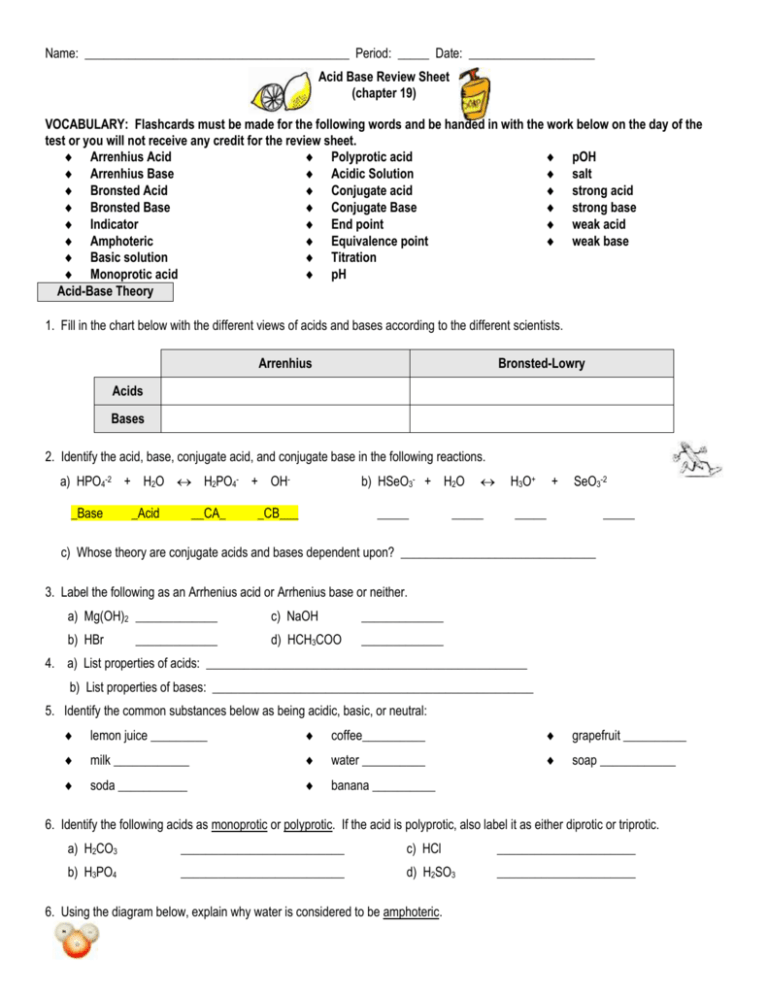
Name: __________________________________________ Period: _____ Date: ____________________ Acid Base Review Sheet (chapter 19) VOCABULARY: Flashcards must be made for the following words and be handed in with the work below on the day of the test or you will not receive any credit for the review sheet. Arrenhius Acid Polyprotic acid pOH Arrenhius Base Acidic Solution salt Bronsted Acid Conjugate acid strong acid Bronsted Base Conjugate Base strong base Indicator End point weak acid Amphoteric Equivalence point weak base Basic solution Titration Monoprotic acid pH Acid-Base Theory 1. Fill in the chart below with the different views of acids and bases according to the different scientists. Arrenhius Bronsted-Lowry Acids Bases 2. Identify the acid, base, conjugate acid, and conjugate base in the following reactions. a) HPO4-2 + H2O H2PO4- + OH_Base _Acid __CA_ b) HSeO3- + H2O _CB___ _____ _____ H3O+ + SeO3-2 _____ _____ c) Whose theory are conjugate acids and bases dependent upon? _______________________________ 3. Label the following as an Arrhenius acid or Arrhenius base or neither. a) Mg(OH)2 _____________ c) NaOH _____________ b) HBr d) HCH3COO _____________ _____________ 4. a) List properties of acids: ___________________________________________________ b) List properties of bases: ___________________________________________________ 5. Identify the common substances below as being acidic, basic, or neutral: lemon juice _________ coffee__________ grapefruit __________ milk ____________ water __________ soap ____________ soda ___________ banana __________ 6. Identify the following acids as monoprotic or polyprotic. If the acid is polyprotic, also label it as either diprotic or triprotic. a) H2CO3 __________________________ c) HCl ______________________ b) H3PO4 __________________________ d) H2SO3 ______________________ 6. Using the diagram below, explain why water is considered to be amphoteric. Acid-Base Properties 10. What is an indicator? 11. List three types of indicators that we have learned about: a) ______________________ b) ______________________ c) ______________________ 14. With which of the following will HNO3 react? Circle all that apply. a) KOH c) Zn b) CaCO3 d) Cu 15. With which of the following would NaOH react? Circle all that apply. a) HCN c) CaCO3 b) KOH d) H2S 16. Examine the data in the table. Fill in the blank spaces to the right with the appropriate term. Substance Red Litmus Blue Litmus Reaction with Phenolphthalein Acid, Base, 0r Neutral? Unknown A stays red turns red stays clear acid Unknown B No change No change No change neutral Unknown C turns blue stays blue turns pink base a) Which of the unknowns above would have more hydrogen ions? _unknown A__________ b) Which of the unknowns above would have a pH above 7? ____unknown C______ pH and pOH 17. a) How is pH mathematically defined? ___________________ c) _____ + _____ = 14 b) How is pOH mathematically defined? _________________ 18. a) [H+] = [OH-] describes a substance with a pH of ____7 (neutral)___. b) [H+] > [OH-] describes a substance with a pH of ____0-6.9 (acid)_____. c) [H+] < [OH-] describes a substance with a pH of ____7.1-14 (base)________. 19. Fill in the blanks in the following chart, and then answer the questions below. Substance Acidic, Alkaline, or Neutral? [H+] [OH-] pH Unknown A Acid 1.0 x 10-6 M 1.0 x 10-8 M 6 Unknown B Base 2.50 x 10-8 M 3.9 x 10-7 7.6 Unknown C --- --- Unknown D --- 1.3 x 10-10 M Unknown E 1.0 x 10-7 M 1.0 x 10-7 M a) Which substance is the most acidic? _______________ b) Which substance is the most basic? _______________ pOH 8 6.4 4 7 7 Strong vs. Weak Acids and Bases 20. a) What determines the strength of an acid or base? _________________________________________ b) Is it correct to state that a strong acid is a concentrated acid and that a weak acid is a dilute acid? ____ Explain. 21. Acid A and acid B are tested with a conductivity apparatus. When the conductivity apparatus is placed in acid A, the bulb glows dimly. When it is placed in acid B, the bulb glows more brightly. Which acid is stronger, and how do you know? 22. a) Write the complete ionization reaction for nitric acid. 23. List the 4 strong acids. above acids _____________ 24. What elements make the strongest bases? _______________________________ Acid Nomenclature and Formula Writing 24. Fill in the blanks in the following chart by either giving the acid formula or acid name. Acid Formula a) HNO2 b) H2S c) HClO3 d) HI Acid Name Nitrous acid e) Hydrosulfuric Acid Hydroiodic acid Sulfuric Acid Neutralization Reactions 25. When an acid reacts with a base a _______neutralization_________________________ reaction takes place. This means _____salt___________ and ______water____________ are produced. 26. Explain how a salt is formed. 27. Write and balance each of the following neutralization reactions. a) hydroiodic acid and ammonium hydroxide HI + NH4OH NH4I + H2O (Acid + base salt + water) b) phosphorous acid and calcium hydroxide c) hydrocyanic acid and lithium hydroxide HCN + LiOH LiCN + H2O c) Which acid and base would form cesium selenide and water? H2Se + CsOH CsSe + H2O