Photosynthesis
advertisement

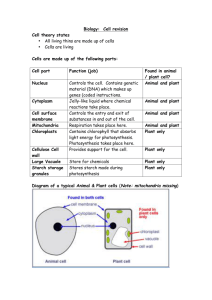
Biodiversity and Interdependence Photosynthesis (d) Learning Intention • To be able to give the word equation for photosynthesis. • To be able to describe the role of chlorophyll in photosynthesis. Photosynthesis • Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants make food using light energy. Carbon Dioxide + Water Glucose + Oxygen Chlorophyll • Photosynthesis happens in the chloroplasts of a plant cell. • Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll which absorbs the light energy needed to power photosynthesis and changes it to chemical energy. Chlorophyll Testing For Starch • If a leaf has been carrying out photosynthesis, it will have starch present. • This is because the plant stores food as starch. • Iodine solution is used to test for starch. Learning Intention • To be able to describe the photolysis stage of photosynthesis. Photolysis • Photosynthesis happens as a series of enzyme controlled reactions. • The first stage of photosynthesis is called photolysis. Photolysis • The light energy is used to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. • The oxygen is released as a byproduct. Photolysis • The hydrogen that is produced in photolysis is needed for the next stage of photosynthesis. • It joins with a hydrogen carrier which ‘carries’ it on to the next stage. H H H H H Learning Intention • To be able to describe the carbon fixation stage of photosynthesis. Carbon Fixation • The second stage of photosynthesis is called Carbon Fixation. • The raw material needed for this stage is carbon dioxide. Carbon Fixation • Carbon Fixation is an enzyme controlled cycle. • The hydrogen from photolysis combines with the CO2 to form glucose. Used in photolysis Released during photolysis Chlorophyll and light Carbon dioxide + Water Used in carbon fixation Used in photolysis Glucose + Oxygen Produced during carbon fixation Learning Intention • To be able to state the different fates of carbon dioxide in photosynthesis. Fates of CO2 • The CO2 that is taken in during photosynthesis is used to make glucose, which the plant can use as a source of energy. • The glucose can then be turned into: – Starch for storage – Cellulose to build the cell wall Learning Intention • To be able to name the limiting factors for photosynthesis Photosynthetic Rate • What factors might affect the rate of photosynthesis? 1. Light Intensity 2.CO2 concentration 3.Temperature Limiting Factors • If any of these are in short supple then the rate of photosynthesis will be slowed down or limited. • Therefore if one factor is in short supply we call this a limiting factor. Examples of Limiting Factors 1. If there is a lack of carbon dioxide in the air, the rate of photosynthesis is reduced. 2. If there is a lack of light the rate of photosynthesis will also be reduced. 3. Finally low temperature also affects the rate of photosynthesis. Investigating the Effect of Varying Light Intensity Results Results Results Light is a limiting factor at low light intensities. There comes a point that extra light will not increase the rate of the reaction. At this point light is no longer a limiting factor. There is a point at which further addition of CO2 will not increase the rate of photosynthesis. Carbon dioxide is not the limiting factor. When the concentration of carbon dioxide is low the rate of photosynthesis is also low. When you’re asked what the limiting factor is at a point where the graph is rising, you look DOWN and whatever the factor on the x axis is ,this is your limiting factor LIGHT 50 Rate of Photosynthesis 40 30 20 A 10 0 10 20 Light Intensity 30 40 50 When you are asked what the limiting factor is at a point where the graph is level, you look up and see what the difference is between the two lines this is your limiting factor. Temperature 50 Rate of Photosynthesis 20oC 40 B 30 15oC 20 10 0 10 20 Light Intensity 30 40 50 TEMPERATURE 30oC 50 Rate of Photosynthesis C 40 20oC 15oC 30 20 10 0 10 20 Light Intensity 30 40 50