Meiosis
advertisement

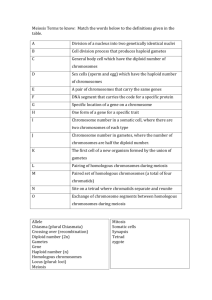
FROM MOM FROM DAD ** Mitosis is asexual reproduction & occurs ONLY in regular old body cells called SOMATIC CELLS (skin, nails, your pancreas, etc..) NOT sperm and eggs ** These cells contain autosomal chromosomes that are nonsex chromosomes ** 22 from Mom autosomal chromosomes from mom and 22 from dad Diploid (2n) number of chromosomes you have 44 or 22 pair of autosomal chromosomes (2n=44) **Haploid means 1 (n). You receive a haploid number of chromosomes from mom and a haploid number from Dad that makes YOU diploid!! ( **46 in all; 22 autosomal, an X from mom and an X or Y from dad **SO there are half as many chromosomes in gametes (sperm and eggs) Replicates Same types if genes on each chromosome, just different variations from each parent Required for Sexual Reproduction Similar to Mitosis but there are two sets of phases and the end result are haploid cells (gametes) **Produces gametes in the ovaries (females) and testes (male) **Results in 4 NON-IDENTICAL haploid (n) cells Either sperm or egg **Diploid to haploid cells **Genetic Recombination Occurs From Dad From Mom A Tetrad of Homologous Chromosomes They Replicate Prior to Meiosis to form a tedtrad……… Four Haploid gametes are produced!! Look On Page 264 #1-4 **After interphase (DNA replication phase) **Meiosis I Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, telophase I and cytokenisis. **2 cells **Meiosis II Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, Telophase II and cytokinesis **4 cells, the gametes!! ** A reassortment of chromosomes and genetic information they carry **crossing over between non-sister chromatids during Prophase 1 **independent segregation of homologous chromosomes **Pink is from your mom, blue from your dad **Non-sister chromatids exchange genetic information **Nondisjunction BOTH chromosomes of a homologous pair (tetrad) fail to separate and move to the same pole of the cell. **Occur in all living organisms, but they are especially common in plants. **Few harmful gene mutations are passed on to the next generation because the zygote usually dies. If it lives, the offspring may have birth defects. A B C D E F G H A B C E Deletion F G H A B C D E F G H A B C B C D E F G H Insertion **When part of a chromatid breaks off and attaches to its sister chromatid ABCDE FGH AD CBE FGH Inversion **When part of a chromosome breaks off and reattaches backwards onto the same chromosome AB C D E F G H W X AB C DE F G H WX Y Z Y Z Translocation **When part of one chromosome breaks off and is added to a different chromosome, a translocation occurs. **Cut them out and paste them in the correct order !!! Mitosis •Occurs in 1 stage Meiosis •Occurs in 2 stages • It is Asexual Reproduction • For Sexual Reproduction • Produces “clones” with no genetic variability • Produces genetically variability due to recombination • Occurs in body cells (autosomal) and creates two diploid cells • Occurs in sex cells called gametes or germ cells and four haploid cells (sperm and egg) • 2n=46 22 pair of autosomal chromosomes and 1 pair sex chromosomes • n=23 22 autosomal chromosomes and 1 sex chromosome •Forms a tetrad Meiosis Mitosis