Topic 11.2 Muscles Review Questions
advertisement

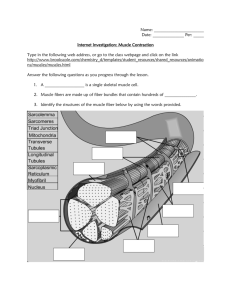
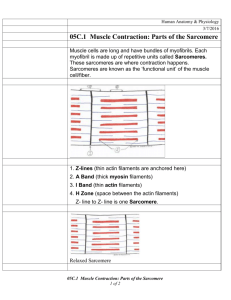
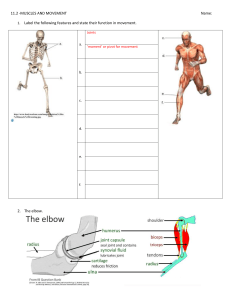
Topic 11.2 Muscles Review Questions 1. Identify the structures labelled I and II on the diagram of the elbow joint below. [2] [Source: R Allen and T Greenwood, (2001) Advanced Biology 2, Student Resource and Activity Manual, 3rd edition, Biozone International Limited, page 98 ] 2. Compare the action of the hip and knee joints. Hip (similar to shoulder) Knee Type of joint Ball and socket Range of movement Bones Lever Flex/ effort Extend/ effort Image Femur [10] 3. Label these structures of a muscle cell. [10] a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. 4. Outline the need for large numbers of mitochondria in muscle cells. [2] _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 5. Label the structures of the sarcomere: [5] a. _____________________ b. _____________________ c. _____________________ d. _____________________ e. _____________________ 6. Identify the number of complete number of sarcomeres in this EM image: Number of sarcomeres = ________________ [1] 7. Compare these two electron micrographs of a skeletal muscle sarcomere. [6] Contracted or relaxed? Sarcomere length Shorter Z-bands Closer H-bands No change Light bands Dark bands No change 8. From below, choose the description matching the relative roles of actin and myosin fibres from the image: [1] A. Myosin fibres move, actin fibres remain in position. B. Actin fibres move, myosin fibres remain in position. C. Both actin and myosin fibres move. D. Neither actin nor myosin fibres move. 9. Explain how a muscle fibre contracts, following depolarisation of its plasma membrane. [7] Include: sarcolemma, sarcoplasmic reticulum, Ca2+, actin binding sites, cross bridges, myosin heads, ATP. Action potential (AP) reaches terminal end of motor neuron. ACh is released into synapse. Action potential is initiated in the muscle cell membrane. Sarcoplasmic reticulum… Muscles Practice Questions 1. Which is the sequence of events in muscle contraction? I. Use of ATP II. Formation of cross bridges III. Release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum IV. Actin filament moves towards the centre of the sarcomere A. I → II → III → IV B. III → II → IV → I C. IV → I → II → III D. II → IV → I → III (Total 1 mark) 2. What is indicated by the letters X, Y and Z? X Y Z A. sarcomere myosin filaments actin filaments B. sarcomere actin filaments myosin filaments C. dark band myosin filaments actin filaments D. dark band actin filaments myosin filaments (Total 1 mark) 3. What does label X indicate? A. Sarcolemma B. Sarcomere C. Sarcoplasmic reticulum D. Endoplasmic reticulum (Total 1 mark) 4. What structure within muscle tissue is surround by membrane and has multiple nuclei? A. Muscle bundle B. Muscle fibre C. Myofibril D. Sarcomere (Total 1 mark) 5. What happens during muscle contraction? A. The number of light bands is reduced. B. The width of the dark bands is reduced. C. The lengths of the sarcomeres are reduced. D. Actin and myosin filaments coil up. (Total 1 mark) 6. The diagram below shows the side view of the arm joint. Which letter is pointing to the ulna? A. W B. X C. Y D. Z (Total 1 mark) 7. What are the names of the two structures labelled I and II in the arm joint diagram below? I II A. biceps radius B. biceps humerus C. triceps humerus D. triceps ulna (Total 1 mark) 8. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers. (2) (a) Draw a labelled diagram showing the structure of a motor neurone. (4) (b) Outline how heartbeat is controlled as the body goes from rest to hard exercise. (6) (c) Explain how skeletal muscle contracts. (8) (Total 20 marks)