Document
advertisement

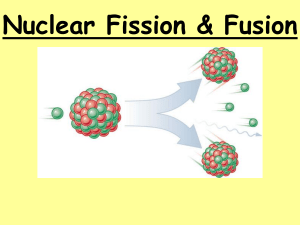
Nuclear Chemistry Fusion and Fission Nuclear Fission • The splitting of a nucleus into smaller fragments is called nuclear fission. • Heavy atoms (mass number>60) tend to break into smaller atoms, thereby increasing their stability. • Nuclear fission releases a large amount of energy. Nuclear Fission The Fission Process A neutron travels at high speed towards a uranium-235 nucleus. 1 0 n 235 92 U The Fission Process A neutron travels at high speed towards a uranium-235 nucleus. 1 0 n 235 92 U The Fission Process A neutron travels at high speed towards a uranium-235 nucleus. 1 0 n 235 92 U The Fission Process The neutron strikes the nucleus which then captures the neutron. 1 0 n 235 92 U The Fission Process The nucleus changes from being uranium-235 to uranium-236 as it has captured a neutron. 236 92 U The Fission Process The uranium-236 nucleus formed is very unstable. It transforms into an elongated shape for a short time. The Fission Process The uranium-236 nucleus formed is very unstable. It transforms into an elongated shape for a short time. The Fission Process The uranium-236 nucleus formed is very unstable. It transforms into an elongated shape for a short time. The Fission Process It then splits into 2 fission fragments and releases neutrons. 1 0 n 1 0 n 1 0 n 141 56 Ba 92 36 Kr The Fission Process It then splits into 2 fission fragments and releases neutrons. 1 0 n 1 0 n 1 0 n 141 56 Ba 92 36 Kr The Fission Process It then splits into 2 fission fragments and releases neutrons. 1 0 n 1 0 n 1 0 n 141 56 Ba 92 36 Kr The Fission Process It then splits into 2 fission fragments and releases 1 neutrons. 0n 141 56 Ba 1 0 92 36 Kr 1 n Energy Nuclear Fission Examples 235 1 141 92 1 235 1 138 96 1 U n + 92 0 U n + 92 0 Ba Kr n 3 + + 56 36 0 Cs Rb n 2 + + 55 37 0 Review: Balancing Nuclear Equations • Mass numbers and Atomic numbers must add up on both sides of the reaction arrow. 256 140 112 46 1 Pd • 100Fm 54Xe + ____ + 4 0n For Atomic numbers 100 = 54 + X X = 46 For Mass Numbers: 256 = 140 + X + 4 X = 112 White Boards Supply the missing atomic symbol to complete the equation for the following nuclear fission reaction. 1n 0 + 235U 92 137Te 52 + ?X + 2 1n + energy ? 0 18 Solution 1n 0 + 235U 92 137Te 52 + 97Zr + 2 1n + energy 40 0 19 Fission Chain Reactions • One fission reaction can lead to more fission reactions in a process called a chain reaction. • Example - The fission of Uranium-235 Chain Reaction of Uranium-235 • A chain reaction can only occur if the starting material has enough mass to sustain a chain reaction. This amount is called the critical mass. • Nuclear Fission is what occurs in Nuclear Reactors and Atomic Bombs. • The Nuclear reactor is a controlled fission reaction, the bomb is not. • The chain reaction releases a large amount heat and energy that produces an atomic explosion. Nuclear Fusion • The combining of atomic nuclei to form a larger atom is called fusion • Nuclear fusion occurs in the sun when two nuclei with low mass numbers combine to produce a single nucleus with a higher mass number. • Fusion releases large amounts of energy. • Example: 1 4 1H + 2 0e -1 4 2 He + energy Energy Nuclear Fusion The Fusion Process 2 1H 3 1H The Fusion Process 2 1H 3 1H The Fusion Process 2 1H 3 1H The Fusion Process 2 1H 3 1H The Fusion Process The Fusion Process The Fusion Process The Fusion Process The Fusion Process 1 0 4 2 He n The Fusion Process 1 0 4 2 He n The Fusion Process 1 0 4 2 He n The Fusion Process 1 0 4 2 He n Nuclear fusion is what powers our sun - and all stars. And also - Hydrogen Bombs Fusion • Fusion reactions also release very large amount of energy but require extremely high temperatures to start. • Nuclear fusion also occurs in new stars and is how all of our elements were made. 4 2 4 2 He + He + 4 2 He 8 4 Be 8 4 Be + energy 12 6 C + energy Other Fusion Reactions • Hydrogen Bomb or possible Fusion nuclear reactor reaction • 3H 1 + 12H 4He + 10n 2 • New elements discovered: • 20Ca + 95Am 115Uup • 115Uup 113Uut 4 + 2He Remember: Nuclear fission and fusion both occur with an incredible release of energy. Energy Learning Check Indicate if each of the following describes 1) nuclear fission or 2) nuclear fusion. ___ A. a nucleus splits. ___ B. large amounts of energy are released ___ C. small nuclei form larger nuclei. ___ D. hydrogen nuclei react. ___ E. several neutrons are released. Solution Indicate if each of the following is 1) nuclear fission or 2) nuclear fusion. 1 A. a nucleus splits. 1, 2 B. large amounts of energy are released. 2 C. small nuclei form larger nuclei. 2 D. hydrogen nuclei react. 1 E. several neutrons are released. 44 Chemical Reactions • Involve changes in electrons – Acids & Bases, combustion, displacement Nuclear Reactions • Involve changes in the nucleus – Nuclear fusion, nuclear fission • The same atoms appear on both sides of the reaction. • New atoms appear as products of the reaction. • Small amount of energy generated • Large amount of energy generated – Burning fossil fuels – 1 million times more than chemical reactions – Nuclear fusion on the sun – Nuclear fission for reactors Decay vs. Nuclear Reactions • Alpha, beta, and gamma • Nuclear reactions involve decay occur as ONE more than just getting rid of atom tries to increase a few protons or neutrons. The new atoms produced it’s stability by getting rid of a few neutrons, or are VERY different protons & neutrons. elements than the reactant. • The product is an alpha, • Nuclear reactions must be beta, or gamma particle started, so there are 2 and ONE new atom. things on the left hand side. There is only ONE thing – Nuclear fission: makes 2 on the left hand side. or more much smaller atoms – Nuclear fusion: makes 1 much larger atom Nuclear Fission Alpha Decay What are the differences between the 2 above nuclear equations??