Emma Exam - WordPress.com
advertisement

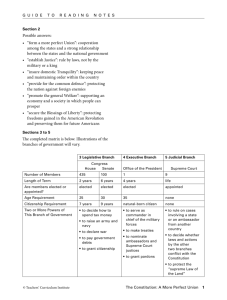
Project- Create an AP Test Emma Feyler SECTION I c. The ability to impeach the President, provide welfare within the states, and establish and maintain schools. d. The ability to establish circuit courts, convene a joint session of Congress, and coin money. e. The ability to negotiate foreign treaties, to issue drivers’ licenses, and convene a joint session of Congress. 4) Which of the following is the best definition of federalism? a. A political system in which power is divided in three branches in the federal government in order to limit the power of the government. b. A political system in which power is divided and shared between the central government and the states in order to limit the power of government. c. The belief that all powers reserved for the federal government should be removed and given to the states. d. A political system in which a weak central government is established in order to preserve the rights of the people. e. The belief that the writing of the Constitution should be abandoned and the Articles of Confederation should be maintained with little to no alterations. 5) Which of the following is true about Dual Federalism and Cooperative Federalism? I. Dual Federalism is characterized by tension. II. In Cooperative Federalism power is shared between all levels of government. III. Today, the United States political system operates under Dual Federalism. IV. In Cooperative Federalism, the central, state, and local governments work together to solve common problems. a. Only I and III are true. Constitutional Underpinnings & Federalism (6 Questions) 1) Under the Articles of Confederation a. The federal government could not levy taxes, while under the Constitution the federal government was given that power. b. The army was raised by Congress, while under the Constitution the army is raised solely by the judicial branch. c. There were federal and circuit courts that were regulated by the states. d. A majority vote was needed to pass laws, while under the Constitution 9 out of 13 states need to approve. e. The president was granted a 4 year term with no limit to the number of terms he or she may serve. 2) One way in which the different branches of government are able to check each other is a. The Supreme Court nominates judges for circuit courts which the President approves. b. The President can veto congressional legislation and the veto cannot be overturned. c. The Senate has the power to impeach the President and the House of Representatives has the power to remove him or her from office. d. The House of Representatives has the power to impeach the President and the Senate has the power to remove him or her from office. e. The Executive branch controls the budget. 3) A few examples of enumerated powers are: a. The ability to establish circuit courts, to issue drivers’ licenses, and to set up a national bank. b. The ability to regulate both interstate and intrastate trade, conduct elections, and negotiate foreign treaties. 1 b. Only II, III and IV are true. c. I, II, III and IV are true. d. Only I, II and IV are true. e. Only III is true. 6) Categorical grants a. Are preferred by states as they allow for much freedom in using the money. b. Are competitive grants issued for a specific project. c. Are based on a formula and given to states and localities for broad purposes. d. Are the same as unfunded mandates in that in order to be eligible for grants, states and localities have to enforce federal laws and regulations. e. Are no longer practiced due to the Supreme Court case The People vs. Categorical Grants in 1903 which ruled Categorical Grants unconstitutional based on Article I, section 8 of the Constitution. e. 9) 10) Political Beliefs and Behaviors (9 Questions) 7) In regards to voter turnout, the presidential election a. Lower than non-presidential elections. b. About the same as non-presidential elections. c. Higher than non-presidential elections. d. Only election in which people vote. e. The only election that Cubans have a voter turnout of over 50%. 8) Which of the following is true of the MotorVoter Law (1993)? a. It allowed people to register to vote when they were issued their license. b. It restricted voting to only owners of an automobile. c. It was a widespread belief 1970s the Civil Rights Movement that the government purposefully placed polls in remote places so that only people who owned a car would be able to get to them and vote. d. It was a movement during the 1990s that organized car-pooling to voting sites. 11) 12) 2 It overturned a previous law that stated that only people who owned cars were allowed to vote in closed primaries. All of the following contribute to low voter turnout EXCEPT: a. The difficulty of absentee voting. b. Voter fatigue. c. Weak political parties. d. Weekday, non-holiday voting. e. Sickness. Which of the following is the best definition of political socialization? a. A process during the ages of 5-15 by which people form their ideas about politics and acquire political values. b. A lifelong process by which people form their ideas about politics and acquire political values. c. A period during early adulthood that people’s political efficacy is at its highest. d. The process by which the government conveys information to the people. e. A process by which a person’s ideas about politics are shaped by their family. All of the following a factors that contribute to political socialization, EXCEPT: a. Family b. Education c. Media d. Dietary habits e. Peer Groups Which of the following describes a push poll? a. An unofficial vote which is taken to discover what people think about an idea or problem or how they intend to vote in an election. b. An official poll that contains a randomized set of representative participants. c. A purposefully inaccurate poll designed to get voters to think in a certain way by offering suggestive wording of questions. d. A poll conducted outside of a voting location, in which Pollsters as voters who they chose. e. A type of poll in which people are bribed to answer a certain way. 13) Who is most likely to vote liberal? a. A Roman Catholic who lives in the city. b. A Cuban who lives just outside of Chicago and has been recently naturalized. c. A lower class African American woman who lives in the city. d. A rich, white, male college graduate who hails from South Carolina. e. A Jewish woman who had a very poor childhood but is now a very successful lawyer. 14) All of the following are true of someone with high political efficacy, EXCEPT: a. Someone with high political efficacy holds the belief that he/she can influence the government. b. Is more likely to be politically active. c. Is more likely to participate in a rally and contribute to a political campaign. d. Is more likely to vote in a low profile election. e. Supports everything the government does no matter what. 15) Which of the following is an example of a crosscutting cleavage? a. An African American in the South. b. A rich, white man. c. A Jewish, urban-dweller. d. A poor Hispanic. e. A rich Mormon. of political parties, interest groups, and the media. c. There are three linkage institutions: political parties, interest groups, and the media. d. A linkage institution is a contraption that links two otherwise separate objects together, such as a staple or the clasp on a necklace. e. Linkage institutions consist mainly of interest groups, which are further broken down into six types. 17) Which of the following is true of political parties? a. The regulation of political parties is established in the Constitution as an enumerated power in Article I, Section 8. b. The number of dominant political parties varies from election to election, but typically stays somewhere within the range of 2-4. c. They were the cause of the Great Depression due to an inability to work together to establish a budget. d. Though the names of the dominant political parties have changed, there are usually two powerful parties: one liberal and one conservative. e. Third parties, such as the Green Party, play a vital role in policy making in the federal government. 18) All of the following are true of congressional elections EXCEPT: a. Congressional elections are regional; Senate by state and the House by district. b. House elections are less competitive than Senate due mainly to incumbency advantage. c. Every two years one third of the Senate and the entire House is up for reelection. d. The coattail effect, the consequence of the popularity of the President effecting Congressional elections in midterm years, is outdated and no longer an issue in modern day politics. Political Parties, Interest Groups & Media (9 Questions) 16) Which of the following is the best explanation of linkage institutions? a. Linkage institutions, used mainly during President Lincoln’s era, were the means by which important information was shared between the North and the South. b. Linkage institutions are the channels through which people’s concerns become political issues on the government’s policy agenda, consisting 3 e. Only about 36% of people vote in a midterm, or “off,” year. 19) One criticism of “horse race politics” is that a. It perpetuates the gambling epidemic spreading throughout the country. b. It favors underdogs too highly and therefore hardly gives incumbents a fair chance of winning. c. It becomes a gossipy, unreliable source of news. d. It places too much emphasis on the candidate and not parties and elections thus become less about ideals and more like popularity contests. e. Only jockeys have access to it. 20) Which of the following includes the five tools that interest groups use to influence policy making? a. Lobbying the government, mobilizing the public, litigation, electioneering, and educational reform. b. Lobbying the government, educating the public, litigation, impeaching the President, and the revolving door. c. Electioneering, litigation, blackmail, mobilizing the public, lobbying the government, and educating the public. d. Litigation, mobilizing the public, educating the public, electioneering, and lobbying the government. e. The revolving door, impeaching the President, blackmail, electioneering, and mobilizing the public. 21) In politics, the “revolving door,” a. Is the movement of high-level employees from public sector jobs to private sector jobs and vice versa. b. Is the 1998 legislation that states that politicians who have held their seat for over 7 years must not run in the next election in order to minimize the effects of incumbency advantage. c. Is the back door of the White House that only the President and his family are authorized to use. d. Refers to the constant flow of new Congress people. e. Is a term coined by President Hoover that refers to the uncertainty of politics. 22) All of the following are types of interest groups EXCEPT: a. Trade associations b. Peak organizations c. Unions d. Corporations e. The media 23) Superdelegates a. Include governors, members of Congress, and members of the Democratic/Republican National Committee whom are free to vote for any candidate they wish at the National Convention. b. Are the “superheroes” of politics, taking over in states of emergency. c. Are members of the Electoral College who vote for the President. d. May cast a vote, but it is worth only 1/3 of what a “regular” vote is worth. e. Are candidates on “standby,” ready to step in in case their Presidential candidate dies suddenly or becomes extremely sick. 24) What types of candidates do interest groups typically target and why? a. Those running for office for the first time because the public is always looking for fresh blood. b. Incumbents because they already have the job and are more likely to win the election. c. Those running for office for the first time because it is widely known that interest groups are perpetually unsatisfied with the state of the government. d. Incumbents because they are many times good friends of people in the interest group. e. Interest groups do not typically target one type of candidate, it depends completely on the election and who the candidates are. Institutions: Congress, President, Courts, Bureaucracy (24 Questions) 4 25) What is the order of leadership in the House of Representatives? a. Speaker of the House, majority whip, President Pro Tempore b. President of the Senate, majority leader, majority whip, Speaker of the House c. Speaker of the House, majority leader, Majority whip d. Vice President, Minority leader, minority whip, majority whip e. Speaker of the House, majority whip, majority leader 26) Which of the following perpetuates incumbency advantage in the House of Representatives? I. Franking II. Name recognition III. The revolving door IV. A proven track record. b. I and II only. c. I, III and IV only. d. I only. e. I, II and IV only. f. I, II, III and IV. 27) The President has which of the following powers pertaining to bills: a. To approve and sign or veto a bill. b. To approve only certain parts of a bill. c. To override Congress’ veto of a bill. d. To assign bills to committees. e. To veto only certain parts of a bill. 28) A Conference Committees a. Consist of only House Representatives or Senators and handle bills in specific policy areas. b. Consist of both House and Senate members and are temporary committees meant to draw attention to specific issues. c. Are exactly the same as Select committees except that they consist of both House and Senate members. d. Are long-standing, well established committees with the most influence in Congress. e. Consist of both members from the House and Senate and are formed to hammer out differences between House and Senate versions of similar bills. 29) All of the following are criticisms of Congress EXCEPT: a. Pork-barrel legislation. b. Blue-slipping. c. Logrolling. d. Christmas Tree Bills. e. Franking. 30) Senators who do not want to see a bill voted on may delay the vote by means of filibuster, a. A protracted, one-sided argument against a bill designed to derail the legislative process by consuming the time and patience of the Senate. b. A protracted, one-sided argument against a bill designed to derail the legislative process by consuming the time and patience of the House. c. The process by which a Joint Committee goes through each point of a bill and explains why it should not be passed. d. Or “bust-a-filler,” which is when someone takes over speaking indefinitely and eventually the full room empties, or is “busted.” e. Which, similar to Amicus Curiae, is something an interest group can present to sway the court. 31) Which of the following are methods of gerrymandering? I. Malapportionment II. Logrolling III. Packing IV. Cracking a. I only. b. II, III and IV only. c. II and IV only. d. III and IV only. e. I, III and IV only. 32) What is senatorial courtesy? a. Holding the door for the Senator behind you. b. A custom of interest groups “courting” a senator and wining and dining him or her. c. A custom of the United States Senate of refusing to confirm a presidential appointment of an official in or from a 5 state when the appointment is opposed by the senators from that state. d. Manipulating district boundaries to benefit a party or group. e. Groupings of Senators pushing for similar interests. 33) Which of the following is the correct order of superiority of the courts, from lowest to highest? a. District Courts, Courts of Appeals, Supreme Court. b. District Courts, Supreme Court, Court of Appeals. c. Supreme Court, Courts of Appeals, District Courts. d. Supreme Court, District Courts, Courts of Appeals. e. Courts of Appeals, District Courts, Supreme Court. 34) Which of the following is true of judicial review? a. It is a publication that rates Supreme Court justices on the quality of their decisions. b. It is expressly defined in Article III of the Constitution as “A constitution, is, in fact, and must be regarded by the judges, as a fundamental law. It therefore belongs to them to ascertain its meaning, as well as the meaning of any particular act proceeding from the legislative body.” c. It allows courts to rule on the constitutionality of laws, giving the court the power to strike down or reinforce policy. d. It was declared unconstitutional in the 1803 Marbury vs. Madison Supreme Court ruling. e. It was put into effect by the Judiciary Act of 1789. 35) Which of the following is true of amicus curiae briefs? I. 3rd parties are permitted to file these briefs on behalf of either litigant. II. 3rd parties are often wellfunded interest groups, corporations or special interest groups. III. The Supreme Court does not need to consider these briefs but often do. IV. Amicus curiae briefs are an example of influencing the SCOTUS. a. I and II only. b. I, II, and III only. c. II and IV only. d. II and III only. e. I, II, III, and IV. 36) What is selective incorporation? a. The tradition that only a select number of corporations are invited to the State of the Union Address. b. When only parts of a bill are passed and the rest is vetoed. c. It is the process by which certain rights given to us in the Bill of Rights are applied at the state level by the Supreme Court through the 14th amendment Due Process clause. d. When power is given back to the states by the federal government. e. The process by which rights given to us in the Bill of Rights are applied at the federal level by the Supreme Court through the 14th amendment Due Process clause. 37) Which of the following are ways in which the power of the Supreme Court is checked? I. The President appoints all judges and Congress must approve them. II. Congress may alter the structure of the court system. III. Judges may be impeached if they have broken federal law. IV. Congress may amend the Constitution if the courts find a law unconstitutional. a. I only b. I and III only c. I, III and IV only. d. I, II and IV only. e. I, II, III and IV. 38) Which of the following best describes a writ of mandamus? 6 a. Something that a higher court issues and all lower courts must abide by the ruling. b. A law that retroactively changes the legal consequences before the enactment of the law. c. When a higher court approves a lower court’s ruling. d. Says that you must be charged with a crime to be put in jail. e. Means “according to the law.” 39) Which of the following is an example of de jure and de facto? a. De jure, apples are all red. De facto, some apples are green. b. De jure, the President must address Congress from “time to time.” De facto, it’s once a year. c. De jure, you are supposed to come to a complete stop at a stop sign for four seconds. De facto, most people roll through stop signs. d. De jure, there is something called executive privilege. De facto, Nixon had to give up his tapes anyway. e. De jure, this is a test. De facto, this is a standardized test. c. 42) 43) 40) Which of the following best describes a writ of 44) certiorari? a. Says that you must be charged with a crime to be put in jail. b. Means “according to the law.” c. When a higher court approves a lower court’s ruling. d. A writ that is issued by a higher court that requests a case be sent up for review. e. When 4 out of the 9 judges decide to hear a case. 41) Which of the following best describes the Rule of Four? a. All four Supreme Court justices must agree to hear a case. b. All four levels of the court system must rule in favor of capital punishment in order for someone to be put on death row. 45) 7 Four percent of the Senate and four percent of the House of Representatives must vote in favor of impeachment in order for a judge to be impeached. d. There must be four lawyers present in the court at all times. e. In order for the Supreme Court to take a case, four out of the nine judges must agree to hear it. What does it mean to be “borked?” a. A nickname for pork barrel legislation. b. To bring eat a meal during a meeting with the press. c. In the Senate, when someone takes control of the mic and does not stop talking until the bill up for debate is pulled. d. To be rejected based solely on your politics instead of your qualifications. e. To be impeached. All of the following are presidential duties EXCEPT: a. Commander in Chief of the armed forces. b. Approving legislation. c. Appointment of judges and bureaucrats. d. Budge approval. e. Diplomatic head of state. The primary reason why the popular vote and the electoral vote for president may differ is a. The prevalence of horse-trading and corruption in American politics. b. The candidates focus their campaigns only on a few swing states. c. Small states have more power in the Electoral College than their population would merit. d. Electors often switch votes to vote for the winning candidate to gain political influence and advance their careers. e. The winner-take-all system most states use in selecting electors. Which of the following actions of the president has no basis in the Constitution? a. Issuing executive orders. b. Serving as leader of his political party. c. Stationing U.S. troops at bases abroad. d. Negotiating free trade agreements with other countries. e. Proposing legislation to Congress. 46) An issue network occurs when a. Many competing interests (including the media) enter the debate, slowing the policy making process and derailing the iron triangle. b. Alliances form between legislators, regulators and interest groups to make or preserve policies that promote their common interests. c. Many different interest groups are working towards the same goal but there is too much competition among the groups for any unity so nothing gets done. d. Those in a political party’s beliefs are not all aligned with one another and alliances are made with the opposing party. e. Many competing interests (including the media) enter the debate, speeding up the policy making process and reinforcing the iron triangle. 47) Which of the following is an independent regulatory commission? a. An organization under a cabinet department the sets health regulations. b. An organization that regulates a sector of the economy that is independent of both the president and larger departments. c. An agency that is not part of the cabinet, does not regulate the economy, does not report to the president but has a special function, like NASA. d. A for-profit business run by the government but has a large degree of freedom, like the post office. e. A department in the cabinet headed by a secretary like the State Department. 48) Which of the following are criticisms of the bureaucracy? I. Bureaucracies often have overwhelming rules and regulations that are difficult to navigate. II. Competing agencies often work toward opposite goals. a. b. c. d. e. III. Difficulty in firing an incompetent bureaucrat. IV. Several agencies that appear to do the same things. I only I and III only I, III and IV only. I, II and IV only. I, II, III and IV. Public Policy (6 Questions) 49) Which of the following is the largest source of federal government revenue? a. Sales tax. b. Corporate income tax. c. Personal income tax. d. Bank loans. e. Bond sales. 50) What is the main goal of the federal reserve? a. To set prices of precious metals. b. Keep the economy from overheating or bottoming out. c. To collect taxes and organize tax returns. d. To influence public policy. e. To print money. 51) Which of the following are actions that the Federal Reserve Board can take? I. Raising and lowering the interest rate. II. Increasing and decreasing the money supply. III. Increasing and lowering the reserve rate. IV. Disallowing the sale of bonds. a. I only b. I and III only c. I, III and IV only. d. I, II and III only. e. I, II, III and IV. 52) In the last 80 years, a. Spending on entitlement programs has been steadily increasing. b. Discretionary spending has become a much larger percentage of the budget than mandatory spending. c. Presidents and Congresses have become more reluctant to increase spending on 8 social programs and very slow to increase taxes. d. The United States government has passed a “Balanced Budget Amendment” that requires Congress to limit spending to tax revenues. e. Income tax has been trending steadily downward as the largest source of revenue for the federal government. 53) An African American female voter from Chicago would most likely favor, a. A decrease in federal program spending. b. A reduction of monetary regulation. c. Tax cuts to the wealthy. d. An increase in federal program spending. e. Stricter immigration laws. 54) The difference between mandatory and discretionary spending is that a. Discretionary spending is dictated by previous policy decisions and is composed of entitlements interest payments on bonds and loans, while mandatory spending is authorized by the current administration and may expire or be renewed. b. In the past few decades, discretionary spending has become a much larger percentage of the budget than mandatory spending. c. Discretionary spending applies only to state governments while mandatory spending applies to both federal and state governments. d. Mandatory spending is formulated by the president, the OMB, the IRS and Congress, while discretionary spending is formulated by Congress alone. e. Mandatory spending is dictated by previous policy decisions and is composed of entitlements interest payments on bonds and loans, while discretionary spending is authorized by the current administration and may expire or be renewed. 55) The primary effect of Furman v. Georgia was a. That it limited the use of the death penalty by ruling that the defendant’s character must be taken into account. b. Is set the precedent for evolving standards of decency. c. It held the constitutionality of the Defense of Marriage Act. d. It limited the use of the death penalty by ruling that capital punishment cannot be used on the mentally disabled. e. It overturned Brown v. Board of Education, ruling that segregation was unconstitutional. 56) The 13th Amendment did which of the following? a. It incorporated the Bill of Rights to the states. b. It banned involuntary servitude except as a form of punishment. c. It says that suffrage cannot be denied based on race or previous condition of servitude. d. It was adopted as a condition of the Southern state’s readmission to the Union after the Civil War. e. It provided a basis for the selective incorporation of the 6th Amendment right to a counsel. 57) Which of the following is true of civil liberties? a. They are constitutionally established guarantees against government interference. b. The term applies to both constitutionally established guarantees against government interference, and positive acts of government designed to protect individual liberties. c. They are positive acts of government designed to protect individual liberties. d. It is another term for the Bill of Rights. e. They are core American values established in the Declaration of Independence. 58) When dealing with the 14th Amendment’s relationship to the Bill of Rights, the Supreme Court has adopted a policy of a. Complete incorporation. b. Limited incorporation. Civil Rights and Liberties (6 Questions) 9 c. Partial incorporation. d. “Somewhat” incorporation. e. Selective incorporation. 59) Which of the following types of speech is generally protected under the Constitution? a. Commercial speech. b. Speech that presents a clear and present danger. c. “Eminent domain” speech. d. Obscenity. e. Slander and Libel. 60) All of the following are amendments that deal with protecting due process for the criminally accused, EXCEPT a. The Third Amendment. b. The Fourth Amendment. c. The Fifth Amendment. d. The Sixth Amendment. e. The Thirteenth Amendment. 10 11