The New Imperialism
advertisement

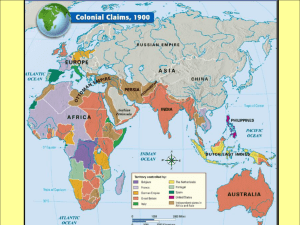
1800-1900 Note: This power point presentation is based on reading selections from Students’ Friend. Ideas and topics highlighted in red indicate new information not included in the Students’ Friend reading. New Imperialism-What is it? The physical, economic, or political domination or control of another nation What causes or influences Imperialism? *Nationalism (national pride) *Social Darwinism (racist attitudes) *Money (Industrial Revolution & colonies) Imperialism in India British East India Company gained control of most of India British government took over after the Sepoy Rebellion that resulted over religious & cultural differences Advantages: postal service, telegraph, roads, railroad network, schools, kept peace Disadvantages: destroyed Indian textile industry, high taxes, pushed cotton growing instead of food=famines Imperialism in China British demand for tea and other products drained silver from Britain (trade imbalance). British pushed opium trade in order to balance trade Chinese objected, resulted in Opium War in 1839. Opium War With superior ships and technology the British won an easy victory. Chinese under the Qing emperor were forced to pay cost of war and to open new ports to Western ships. Continued Foreign Pressure in China Spheres of influenceareas where only one foreign country had the right to trade with the Chinese Open Door PolicyUnited States forced all countries to share equal rights to trade in China in 1899 Chinese Reaction to Foreign Pressure Boxer Rebellion (1900)-A secret society, the Boxers, swore to destroy foreigners and began killing foreigners across China, especially Christian missionaries. Trapped foreigners in Beijing were rescued by French, German, British, Japanese, Russian, and American troops. Qing Dynasty forced to give up more ports and pay for huge losses. The dynasty was finally overthrown in 1911. Imperialism in Japan Tokugawa shogunate attempted to keep out foreign influences. Americans sent warships and threatened attack unless Japan open its ports to trade with the United States Tokugawa Shogunate Falls The Tokugawa shogunate (& feudalism) was overthrown and replaced with a modern centralized government. Japanese citizens given equal rights. Emperor (Meiji) restored to god-like power and devotion. Japan embraces Industrial Revolution & becomes powerful. Imperialism in Africa King Leopold II of Belgium hired Henry Stanley to explore Congo River basin and make treaties with African leaders. This set off a “Scramble for Africa” by European countries which led to the division of Africa without any input from Africans. Boers & Zulus Boers, descendants of Dutch farmers, came into contact and conflict with the Zulus. Boer guns eventually overcame Zulu spears Africa was carved into countries with boundaries that had nothing to do with cultural groups living there. Europeans built railroads to remove African resources. Nearly destroyed African culture and development. Imperialism in Latin American The Monroe Doctrine was issued by the United States in 1823. Closed Americas to any future European colonization The United States in Latin America The United States took about half of Mexico’s territory in the Mexican war in 1846. Latin American countries would gain independence but a white upper class usually kept control. New wealth from trade and industrialization benefited the elites. American Imperialism Spanish-American War U. S. supported Cuban rebels against Spain Battleship Maine blew up in Havana harbor & Spain was blamed (mistakenly). U. S. declared war on Spain. Theodore Roosevelt & Rough Riders U. S. won war and acquired Puerto Rico, Guam, Philippines. American Attitude The United States took control of Hawaii. Theodore Roosevelt declared the U.S. would take control of any Latin American country that didn’t run it’s government the way the U.S. wanted it to. Caused resentment Westernization Western nations: Industrialized Wealthy Powerful Aggressive How could nonWestern nations respond? Isolation (China & Japan) Fight (Zulus) Adopt Western ideas, (industrialize, modernize) Problems Education was one route to Westernization but there were problems: Western countries already had factories, workers, and controlled world markets.