Sanitation and Food Safety
advertisement

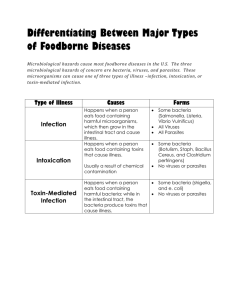
Sanitation and Food Safety By: Samantha Hughes Food Poisoning What is it? What causes it? What will it do to you? How can it be prevented? Every year, 100 million people get ill from food that has spoiled because of improper handling and storage. Foodborne Illness A disease transmitted by food is called a foodborne illness Many cases go unreported because people mistake their symptoms for the “flu” Hazards in Foods A contaminant is a substance that may be harmful that has accidentally gotten into food. Physical- hard or soft objects in food that can cause injury (broken glass, jewelry, bandage, and staples) Chemical- poisonous substances that occur naturally or are added during food handling (Ex. Cleaning agents, pesticides, and certain metals) Biological/microorganism- germs that cannot be seen without a microscope (Ex. Parasites, bacteria, and viruses) How to prevent? Potentially Hazardous Food Animal products: meat, fish, poultry, raw eggs, seafood, and dairy products Cooked starches: rice, beans, pasta, and potatoes Fruits and vegetables: cooked veggies, tofu, sprouts, cut melons, and garlic or herbs bottled in oil FAT-TOM FAT-TOM needed for foodborne illness to grow Food Acidity Temperature Time (past 4 hrs.) Oxygen Moisture Highly Susceptible Populations Younger than 5 years old Older than 65 years old Pregnant Immune-compromised (due to cancer, aids, diabetes, certain medications, or other conditions Bacterial Illnesses Campylobacteriosis E. Coli infection Listeriosis Perfringens poisoning Salmonellosis Shigellosis Vibrio infection Illness from toxins produced by bacteria: Botulism Staphylococcal poisoning Symptoms for Bacterial Illness Can appear 30 minutes to 30 days after eating Abdominal cramps Diarrhea Fatigue Headache Fever Vomiting Illness from Parasites Hogs and other sources of red meat are often affected with the parasite Toxoplasma gondii This parasite causes the infection Toxoplasmosis Which can damage the central nervous system Keep Foods Safe Sanitation starts with keeping yourself clean, your kitchen clean and using proper procedures Keep out of danger zone (41 to 140 degree Fahrenheit) Do not work with food when your ill Wash hands Use barriers with ready to eat foods Wash, rinse, and sanitize Top 3 Food Safety Defenses Hygiene: be clean Temps: Hot foods Hot and Cold foods Cold (DZ- no longer than 2hrs.) Limit cross-contamination Fire Safety http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Em5f R1KwOmM http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m3Kx XukWrpg&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PlzS3 HVmcGU&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1glh1 eN5Lbc&feature=related