Chapter 13
The Blood System
Copyright © 2008, 2005 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
In this chapter you will
• Identify terms related to the composition,
formation, and function of blood.
• Differentiate between the different blood
groups.
• Build words and recognize combining forms
used in the blood system.
• Apply new terminology in their proper
1
Introduction – page 504
Blood: Transports foods, gases, and wastes to
and from the cells of the body.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CRh_dAzXuoU
• Other transported items:
• chemical messengers (Hormones)
• blood proteins, white blood cells, and platelets
2
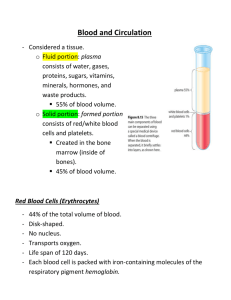
Composition of Blood
•
•
•
•
Cells (45%)
plasma
water
proteins
•
•
•
•
sugar
salts
hormones
vitamins
3
Cell Types and Function
Erythrocytes: red blood cells transport
nutrients and oxygen
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Iv_PRnaVjjo
Leukocytes: white blood cells
Thrombocytes: platelets; clot blood
4
RBC facts
• Immature red blood cell is called a erythroblast
• Erythrocytes originate In bone marrow
• Production stimulated by a the renal system,
erythropoietin
• https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xpsGsfuffEM
• spleen, liver, and bone marrow destroy worn-out
erythrocytes with macrophages
5
White Blood Cells
6
Leukocytes: or white blood
cells
basophils: contain heparin (prevents clotting) and
histamine (involved in allergic responses)
eosinophils: phagocytic cells involved in allergic
responses and parasitic infections
neutrophils: phagocytic cells that accumulate at
sites of infection
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0TvTyj5FAaQ
7
Leukocytes
monocytes: phagocytic cells that become
macrophage and digest bacteria and
tissue debris
lymphocytes: control the immune
response; make antibodies to antigens
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tDTLC
2swhlQ
8
9
STAGES IN BLOOD DEVELOPMENT
(HEMATOPOIESIS) – page 505
10
Review: Composition of Blood- 509
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lnKbx_s6PUM
11
Plasma Protiens
• albumin - maintains proper concentration of
water in blood
• globulins: immunoglobulins
(IgG,IgA, IgM, IgD, IgE) - Antibodies
• Fibrinogen – clotting protein
• Prothrombin – clotting protein
12
Blood Types – page 490
Type A: A antigen and anti-B antibody
Type B: B antigen and anti-A antibody
Type AB: A and B antigens and no antibodies
(universal recipient)
13
Blood Types
Type O: no A or B antigens and both
anti-A and anti-B antibodies (universal
donor)
Rh factor (positive and negative)
Coombs Test:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ooPz
oYR2a0s
14
Blood Clotting – page 510
Coagulation: fibrin clot
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_yQD0
U3ZtCs
Anti-coagulants: heparin, warfarin
(Coumadin)
15
QUICK QUIZ:
1. The blood contains the following
to transport oxygen:
A. white blood cells
B. plasma
C. platelets
D. red blood cells
16
QUICK QUIZ:
2. Blood contains these clotting
cells:
A. erythrocytes
B. plasma
C. thrombocytes
D. leukocytes
17
Vocabulary – page 512
• Albumin – protein in blood; maintains proper
amt of water in blood.
• Bilirubin – orange-yellow pigment in bile formed
from breakdown of hemoglobin when RBC die.
• Coagulation – blood clotting
• Erythropoietin (EPO) – Hormone secreted by
kidneys that stimulates the formation of RBC
18
Vocabulary
• Fibrinogen – plasma protein converted to fibrin
• Hemoglobin – blood protein containing iron,
carries oxygen
• Heparin – Anticoagulant found in blood and
tissue cells
19
Vocabulary – page 513
• Plasmapheresis – removal of plasma from
withdrawn blood. Donor cells and new plasma
are returned back to donor.
• https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DVg78KXKh
K4
20
COMBINING FORMS
- page 514-515
Combining Form
Meaning
• bas/o
base
• chrom/o
color
• coagul/o
clotting - anticoagulant
21
Combining Forms and meaning
• Combining Form
Meaning
• cyt/o
cell – cytology
• eosin/o
red, dawn, rosy
• erythr/o
red - erythrocytopenia
22
COMBINING FORMS
AND TERMINOLOGY
Combining Form
Meaning
• granul/o
granules – granulocyte
• hem/o
blood – hemolysis
• hemat/o
blood - hematocrit
23
Combining Forms
• Combining Form
Meaning
• hemoglobin/o
hemoglobin
• is/o
same, equal
• kary/o
nucleus
24
COMBINING FORMS
AND TERMINOLOGY
Combining Form
Meaning
• leuk/o
white – leukocytopenia
• mon/o
one, single
• morph/o
shape, form
25
Combining Formw
• Combining Form
Meaning
• myel/o
bone marrow
• neutr/o
neutral
• nucle/o
nucleus
26
COMBINING FORMS
AND TERMINOLOGY
Combining Form
Meaning
• phag/o
eat, swallow – phagocyte
• poikil/o
varied, irregular
• sider/o
iron
27
Combining Forms
• Combining Form
Meaning
• spher/o
globe, round
• thromb/o
clot - thrombocytopenia
28
Suffixes – page 515-516
• -apheresis – remove, carry away
• -blast – immature cell
• -cyte – cell
• -cytosis – abnormal condition of
29
Suffixes
• emia – blood condition – leukemia
• -globin – protein – hemoglobin
• -globulin – protein – immunoglobulin
• -lytic – destruction - thrombolytic
30
Suffixes
• -oid – derived from – myeloid
• -osis – abnormal condition – thrombosis
• -penia – deficiency – pancytopenia
• -phage – eat, swallow - macrophage
31
Suffixes
• philia – attraction for, increase in numbers
• -phoresis – carrying, transmission
• -poiesis – formation – hematopoiesis
• -stasis – stop, control - hemostasis
32
More Blood Terminology
33
anticoagulant
• anti- against
• coagul/o: clotting
• -ant: one who; a substance
•
• A substance that works against blood clotting
• Ex: Heparin, Coumadin
34
Coagulopathy
• Coagul/o: clotting process
• -pathy: disease
• Disease condition of the clotting process
• DIC is an example
• Disseminated intravascular coagulation
• https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I_Xs1X56QIQ
35
hematocrit
• hemat/o:
• -crit: to seperate
•
• Separation of blood
• percentage of red blood cells in a given volume of blood
36
myeloblast
• myel/o: bone marrow
• -blast: immature cell
• Immature bone marrow cell
37
myelogenous
• myel/o: bone marrow
• -genous: pertaining to produced in
• Pertaining to produced in the bone
marrow
38
neutropenia
• neutr/o: neutral
• -penia: deficiency
•
• Deficiency in neutrophils
• A granulocyte with neutral staining granules
39
thrombocytopenia
• thromb/o: clot
• cyt/o: cell
• -penia: deficiency
• Deficiency of clotting cells
40
plasmapheresis
• plasm/o: plasma
• -apheresis: removal, carry away
• Removal of plasma
• from the rest of the blood by mechanical
means (centrifuge)
41
42
hemoglobin
• hem/o: blood
• -globin: protein
•
• Blood protein
• in erythrocytes; enables the cell to carry
oxygen
• H&H
43
thrombolytic therapy
• thromb/o: blood clot
• -lytic: destroy
• Therapy: treatment
• Treatment to destroy blood clots
44
pancytopenia
• pan-: all
• cyt/o
• -penia
•
• Deficiency of all (blood) cells
45
hemostasis
• hem/o
• -stasis: stop, control
•
• Stoppage of blood
46
Diseases of Red Blood Cells- p. 517
Anemia: deficiency in erythrocytes or
hemoglobin
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VkN_JVQ
68Ms
• aplastic anemia – failure in production
• hemolytic anemia – excessive destruction
• pernicious anemia- lack of mature erythrocytes
caused by inability to absorb vitamin B12
47
Anemia
• Sickle cell anemia – inherited condition
characterized by abnormal sickle shape of
erythrocytes and hemolysis
• Thalassemia – Inherited defect in the ability to
produce hemoglobin, usually seen in persons of
Mediterranean background
48
hemochromatosis: Excess iron deposits
throughout the body.
polycythemia vera: General increase in red blood
cells.
49
QUICK QUIZ:
3. What is the most common type
of anemia?
A. hemolytic anemia
B. sickle cell anemia
C. iron deficiency anemia
D. aplastic anemia
50
Types of Anemia
51
Disorders of Blood Clotting – p. 519
hemophilia: Excessive bleeding caused by one of
the protein substances necessary for blood
clotting.
purpura: Multiple pinpoint hemorrhages and
accumulation of blood under the skin.
52
Diseases of White Blood Cells- 520
leukemia: An increase in cancerous white blood
cells.
•
•
•
•
acute myelogenous leukemia (AML)
acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL)
chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML)
chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
53
Acute Leukemia
• Acute
Myeloblastic Leukemia
• Acute Lymphoblastic
Leukemia
54
Diseases of White Blood Cells
(cont’d.)
granulocytosis: Abnormal increase in
granulocytes in the blood.
mononucleosis: An infectious disease
marked by increased numbers of
leukocytes and enlarged cervical lymph
nodes.
55
Disease of Bone Marrow Cells p. 522
multiple myeloma: Malignant neoplasm
of bone marrow. Malignant cells destroy
bone tissue and cause overproduction of
immunoglobulins.
56
Laboratory Blood Tests – p. 522
• antiglobulin test
• bleeding time
• coagulation time
• complete blood count (CBC)
• erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) – rate at which
RBCs settle out of plasma. Elevated ESR is a sign of
infection, joint inflammation, and tumor
57
Laboratory Blood Tests – p. 523
• hematocrit (Hct) - % of RBCs in a volume of blood.
Low levels indicate bleeding or increased
destruction of RBCs.
• hemoglobin test (H, Hg, HGB)- Low levels effect the
bodies ability to carry oxygen to the tissues.
• partial thromboplastin time (PTT) – ability of blood
to clot
58
Laboratory Blood Tests (cont’d.)
• platelet count
• prothrombin time (PT)
• red blood cell count (RBC)
• red blood cell morphology
• white blood cell count (WBC)
• white blood cell differential
59
Clinical Procedures p. 524
apheresis: Separation of blood into
component parts and removal of a
select part from the blood.
blood transfusion: Whole blood or
cells are taken from a donor and
infused into a patient.
60
61
Clinical Procedures
bone marrow biopsy: Microscopic examination of
a core of bone marrow removed with a needle.
hematopoietic stem cell transplant: Peripheral
stem cells from a compatible donor are
administered into a recipient’s vein. (Bone
Marrow Transplant)
62
Stem Cell Research
• Stem Cells are crucial to develop organisms.
They are nonspecialized cells which have the
potential to create other types of specific cells,
such as blood-, brain-, tissue- or muscle-cells.
• Some types of stem cells may be able to create
all other cells in the body. Others have the
potential to repair or replace damaged tissue or
cells.
63
•
64
Stem Cell Transplant
65
Abbreviations – See page 525-526
66
REVIEW SHEET
COMBINING FORMS
Combining Form
•
•
•
•
•
•
bas/o
chrom/o
coagul/o
cyt/o
eosin/o
erythr/o
Meaning
base
color
clotting
cell
red, dawn, rosy
red
67
REVIEW SHEET
COMBINING FORMS
Combining Form
•
•
•
•
•
•
Meaning
granul/o
hem/o
hemat/o
hemoglobin/o
is/o
kary/o
granules
blood
blood
hemoglobin
same, equal
nucleus
68
REVIEW SHEET
COMBINING FORMS
Combining Form
•
•
•
•
•
•
leuk/o
mon/o
morph/o
myel/o
neutr/o
nucle/o
Meaning
white
one, single
shape, form
bone marrow
neutral
nucleus
69
REVIEW SHEET
COMBINING
FORMS
Combining Form
Meaning
•
•
•
•
•
phag/o
poikil/o
sider/o
spher/o
thromb/o
eat, swallow
varied, irregular
iron
globe, round
clot
70