The Integumentary System
advertisement
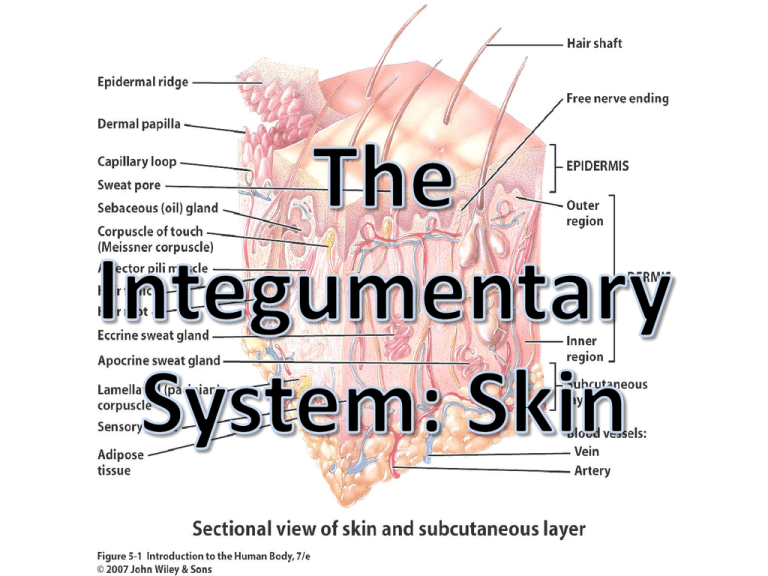
• • • • The Body Covering (Fun Fact! Largest organ of the body) Includes: Skin, Nails & Hairs Skin A.K.A. Cutaneous Membrane Functions: – Body Temperature Regulation: Sweating at surface and adjusting blood flow in dermis. – Protection: Keratin protects from microbes, abrasions, heat and chemicals, lipids slow evaporation of water, melanin protects from UV rays. – Cutaneous Sensations: Sensory input/output – Excretion and Absorption: Eliminates substances, passage of materials into body cells (drugs) – Synthesis of Vitamin D: UV light activates creation of Vit D • Skin is divided into two main parts: – Epidermis (epi = above) Surface epithelial layer – Dermis: Deeper connective tissue layer • Subcutaneous Layer Deep dermis not part of the skin. – Fibers from dermis anchor skin to this layer which then allows for attachment to other tissue and/or organs. • Made of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium • Capable of regeneration (new cells ~ q4 weeks) • 4 cell types: – Keratinocytes: 90% of epidermal cells, 4 – 5 layers, produces keratin (rough fibrous protein that protects skin), waterproofs skin. – Melanocytes: 8% of epidermal cells, produce the pigment melanin, transfer melanin to keratinocytes, susceptible to UV light damage. – Langerhans cells: Produce immune response against pathogens entering skin. – Merkel cells: Detect touch/sensory sensations. • Consists of two distinct regions: – The superficial part is composed of areolar connective tissue. – The deeper part is composed of dense irregular connective tissue. • Attaches to the subcutaneous layer. • The outer layer contains nerve endings for touch, thermal sensations, pain, tickling, and itching. • Skin color is due to the melanin in the epidermis, carotene in the dermis, and hemoglobin in the capillaries of the dermis. – Melanin (Brown-Black pigment) • Darkness depends on amount of melanin produced. • Gives some protection against UV – MALIGNANT MELANOMA, (cancer of the melanocytes), is a particularly serious skin cancer. Liver or age spots, are non-cancerous clusters of melanin. – Carotene (Yellow-Orange pigment) • In deeper skin and adipose layers – Hemoglobin (Pink-Red pigment) • Found in blood • Depends on blood flow 1. What are the 5 functions of skin? 2. What are the two main parts of skin called? 3. What 4 cells make up the superficial/thinner part of the skin? 4. What is the function of the subcutaneous layer? 5. What specific type of epithelial cells make up the epidermis? 6. Which skin layer contains nerve endings? 7. Which pigments contribute to which skin color? 8. The shade of your skin depends on which factors? 9. What are the characteristics and functions of keratinocytes? 1. What are the 5 functions of skin? • Body Temperature Regulation • Protection • Cutaneous Sensations • Excretion and Absorption • Synthesis of Vitamin D 2. What are the two main parts of skin called? • Epidermis and Dermis 3. What 4 cells make up the superficial/thinner part of the skin? • Keratinocytes • Melanocytes • Langerhans cells • Merkel cells 4. What is the function of the subcutaneous layer? • Allows for skin to attach to other tissue and/or organs. • Storage site for fat • Supplies skin with blood (remember epithelial cells are avascular) 5. What specific type of epithelial cells make up the epidermis? • Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium 6. Which skin layer contains nerve endings? • Dermis 7. Which pigments contribute to which skin color? • Melanin (black-brown), Carotene (yellow-orange), Hemoglobin (red) 8. The shade of your skin depends on which factors? • Mainly depends on the amount of melanin produced by melanocytes, but it is the interaction of all in #7 that determines the shade of skin. 9. What are the characteristics and functions of keratinocytes? • Makes up most of the epidermis • Produces keratin (rough fibrous protein ) which protects skin • Waterproofs skin #10 • Function: Protection – Injury – UV light – Foreign Particles • Found: On most skin surfaces – – – – Scalp Brows External genitalia Not on palmar surfaces of hand and fingers or plantar surfaces of feet Supatra is one of only 50 sufferers of Ambras Syndrome documented since the Middle Ages. It is caused by a faulty chromosome. Yu was born in the city of Anshan in the Chinese province of Anshan in 1979 and began growing hair at the age of two that eventually covered approximately 96% of his body. • Composition: – Keratinized cells – Shaft: mostly above ground – Root: below surface • Surrounded by hair follicle – Bulb: base of hair follicle includes matrix producing cells and blood vessels. – Nerves: hair root plexuses • Sensitive to touch – Muscle (Smooth): Arrector pili • Contraction causes goose bumps Hair Shaft Hair Root Hair Root Plexus Bulb Arrector pili muscle • • • Function: Secrete substances Composition: Epithelial cells Types: Sebaceous Gland – Sebaceous Glands: secrete oily sebum • Protects skin from drying out and Hair Root Plexus bacteria Bulb • Connected to hair follicles – Sudoriferous (soo-dor-IF-er-us) Glands: secrete sweat • Eccrine are widely distributed; aid in thermoregulation • Apocrine are found in the axilla, groin, areolae, beard – Ceruminous (se-ROO-mi-nus) Glands: secrete wax • External auditory canal • Combine with sebum to produce earwax • Provide barrier against foreign bodies • Function: Help us grasp, manipulate objects, protect ends of digits, scratching • Composition: Plates of packed keratinized cells of the epidermis. – Nail body: Visible portion – Free edge: Part extending past digit – Root: Part not visible • Growth: 1 mm per WEEK! Slows within 2nd / 3rd decade – Becomes brittle with age Free Edge Nail Body Root 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. What are the functions of hair? What protein is hair composed of? What 5 structures make up hair within skin? What causes goose bumps? What is sebum? Which gland secretes sebum? Which gland aids in thermoregulation? How? Which glad’s secretions combine with sebum to produce earwax? Why is this important? 8. What are the functions of nails? 9. What specifically are nails made of? 10.Of the 5 nail parts, name the 3 you need to know? 1. What are the functions of hair? • To protect from injury, UV light, and foreign particles 2. What protein is hair composed of? • Keratin 3. What 5 structures make up hair within skin? • Hair shaft • Hair root • Hair root plexus • Blub • Arrector pili muscle 4. What is sebum? Which gland secretes sebum? • An oily substance produced by the sebaceous glands 5. What causes goose bumps? • When the hair root plexus stimulates the arrector pili muscle it contracts causing the skin around the hair shaft to elevate. 6. Which gland aids in thermoregulation? How? • Eccrine sweat glands produce sweat; when the sweat evaporates it cools your skin. 7. Which gland’s secretions combine with sebum to produce earwax? Why is this important? • Ceruminous glands’ secretions provide a sticky barrier against foreign bodies 8. What are the functions of nails? • Grasp, manipulate objects, protection to the ends of fingers, scratching 9. What specifically are nails made of? • Plates of tightly packed hard keratinized cells of the epidermis 10.Of the 5 nail parts, name the 3 you need to know? 1. Free Edge 2. Nail Body 3. Nail Root








