Key
advertisement

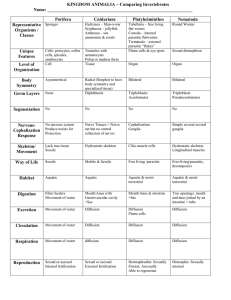
KINGDOM ANIMALIA – Comparing Invertebrates Name: ________________________________________________________________ Porifera Representative Organisms / Classes Unique Features Cnidarians Sponges jellyfish anemones corals Very simple with specialized cells for functions Cell Tentacles with nematocysts Polyp or medusa form Tissue Asymmetrical Platyhelminthes Flatworms turbuleria – aquatic trematode – flukes cestoda - tapeworms Flame cells & eye spots Nematoda Round Worms Sexual dimorphism Many Parasites Organ Organ Radial Bilateral Bilateral None Diploblastic Triploblastic Triploblastic None No None No Acoelomates No Pseudoceolomates No NONE Produce toxins for Protection NONE Nerve Tissues = Nerve net but no central collection of nerves YES Ganglia – grouping of nerve cells YES Simple several ganglia NONE – spicule cells make them hard Hydrostatic skeleton Calcarious endo or exo None Hydrostatic skeleton Way of Life Sessile Sessile No Muscles Mobile & Sessile Muscle Cells (not tissue) Free living /parasitic Longitudinal muscles Free-living/parasitic, decomposers Habitat Aquatic Aquatic Aquatic & moist terrestrial Aquatic & moist terrestrial Digestion NONE INCOMPLETE COMPLETE -Two openings: mouth and anus joined by an intestine = tube Excretion Filter feeders Movement of water Intracellular Movement of water INCOMPLETE Mouth/Anus with Gastrovascular cavity =Sac Intra & Extracellular Diffusion Circulation Movement of water Diffusion Diffusion Diffusion Respiration Movement of water diffusion Diffusion Diffusion Reproduction Sexual or asexual Internal fertilization Sexual or asexual External fertilization Hermaphrodite: Sexually Fission: Asexually Able to regenerate Dimorphic: Sexually internal Level of Organization Body Symmetry Germ Layers Coelom Segmentation NervousCephalization Response Skeleton/ Movement Mouth/Anus & intestine =Sac Extracellular all rest Diffusion aided by Flame cells NO SPECIALIZATION Diffusion Annelids Representative Segmented Worms Organisms / Classes Polychaeta – many chaeta Oligochaeta - earthworms Hirudinea - leeches Unique Features Segmentation Organization Body Symmetry Germ Layers Development Segmentation NervousCephalization Response Metemerism & Septa Organ Bilateral Triplo-ceolomates Protostomes yes Ventral nerve chord with specialized sensory organs in the head region Skeleton/ Hydrostatic Pressure Movement Muscles and cheatae Way of Life Free-living & Parasitic , decomposers Habitat Aquatic, terrestrial Digestion COMPLETE Some specialization pharynx & development of crop & gizzard in some species Mollusks Bivalves –Clam, scallop… Gastropods – snails, slugs Cephalopods – octopus, squid… Basic body plan = Foot Mantle and visceral mass Organ Bilateral Basic body plan = Foot Mantle and visceral mass Triplo-ceolomates Protostomes No Simple in Bivalvia and gastropoda Complex in Cephalopods -ventral nerve cords, -sensory organs Hydrostatic Pressure Secrete mucus – gastropoda -Jet propulsion – cephalopods & bivales Free living herbivores and carnivores, also some filter feeders Aquatic and terrestrial but generally moist COMPLETE regional specialization many, external fertilization & indirect development -Radula: a tongue-like organ bearing rows of teeth that is used in feeding (scraping, drilling, etc.) most have kidneys (metanephridia) -open circulatory system (in most classes) -closed system in cephalopods bc large & v. mobile mainly gills, however terrestrial species have evolved lungs monoecious and dioecious usually internal fertilization indirect development with the presence of a trochophore larva (link to mollusks) trochophore larva (link to annelids) Excretion nephridia Circulation Closed system *** Respiration Skin, gills, diffusion Reproduction Sexual, hermaphroditic in Arthropods Crustacea – crab, crayfish Arachnida – spiders – Insecta - insects Most diverse of all animal -Jointed appendages Organ Bilateral -3 parts-head, thorax, abdomen (fused head & thorax = cephalothorax) Triploblastic ceolomates Protostomes yes Well developed with brain and ganglia in head Echinoderms Starfish – Sea Urchins – Sea cucumbers Believed to be closest related to Chordates because early development of larva are the same & internal skeletons Spiny skin Water vascular system organ 5 part Radial Triplo-ceolomates Deuterostomes yes Simple nervous system and no brain & no head -ventral nerve chords -complex sensory organs Hard external skeleton made of chitin – molt/shed to grow Nerve ring Muscles Water vascular System All – free-living parasitic, herbivore, carnivore, detrivore, filter feeders All aquatic and All terrestrial COMPLETE regional specialization All aquatic!!! Herbivores Carnivores, detritus and filter feeders ALL aquatic None terrestrial COMPLETE without specialization Malpighiam tubules and green glands Open circulatory system with a more advanced heart and sinuses **limits arthropods size Internal Skeleton Carnivore starfish flip stomach inside out and digest prey with enzymes before ingesting Solid waste via anus Ammonia via tube feet Open Circ. System Tracheal Tubes(insects), book Gills(aquatic), Book lungs (spiders) Separate sexes Internal fertilization Through tube feet or gills Incomplete metamorphosis = egg– nymph-adult External fertilization Male and female or hermaphrodites Can regenerate Complete metamorphosis = egg, larva, pupa, adult