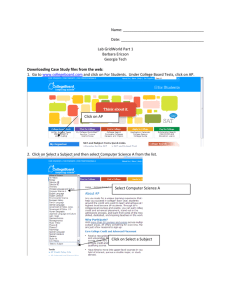
GridWorld Case Study - tjapcomputerscience
advertisement

GridWorld Case Study
Part 2
Bug Variations
Pages 10 to 12
Methods of the Bug Class
• 3 methods that specify how bugs move and
turn.
– 1. public boolean canMove()
• Tests whether the bug can move forward into a location
that is empty or contains a flower.
– 2. public void move()
• Moves the bug forward putting a flower into the location it
previously occupied.
– 3. public void turn()
• Turns the bug 45 degrees to the right() without changing its
location.
Act Method
• Bug’s act method uses all 3 methods
public void act()
{
if(canMove())
move();
else
turn();
}
Bug’s Behavior
1. Bug moves forward when it can
2. Bug can’t move if a rock or grid edge is in front of it,
so it turns.
3. Bug can step on a flower (which removes the flower
from the grid)
4. When the bug moves, it leaves a flower in its previous
location.
The above behavior is determined by the act method and
the 3 methods that the act method calls.
Extending the Bug Class
1.You can create a new type of bug with different
behaviors by extending the Bug class and
overriding the act method.
2. No new methods need to be added since you
extended the Bug which allows you to use the 3
methods (canMove(), move(), and turn()).
BoxBug Class
1.A BoxBug moves in a square pattern.
2.In order to keep track of its movement, the
BoxBug class has two instance variables (object
variables), sideLength and step.
Do You Know Set 2
Page 12
1-7