File
advertisement

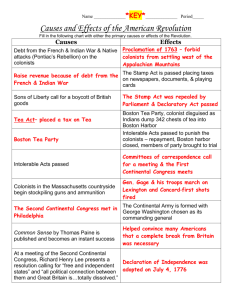
1754-1763 French and Indian War 1763 Proclamation of 1763 1764 Sugar Act 1765 Stamp Act 1765 Sons of Liberty (in response to Stamp Act) 1765 Stamp Act Congress 1766 Boycott of British goods 1766 Repeal of Stamp Act 1766 Declaratory Act 1767 Townshend Acts 1770 Boston Massacre 1773 Tea Act 1773 Boston Tea Party 1774 Committees of Correspondence 1774 Intolerable Acts 1774 First Continental Congress 1775 Lexington and Concord 1775 Second Continental Congress 1775 Bunker Hill 1775 Olive Branch Petition 1776 Declaration of Independence Jigsaw: assign 5th: 27: 9 groups of 3 7th: 28: 8 groups of 3, one group of 4 9th: 19: 5 groups of 3, 1 group of 4 A Using your book, put the following events in order on your timeline. These events will fall on spaces 1-7 on your timeline. Make sure to list the date, what the event was about, and the significance of the event on the road to revolution. You will then work with classmates with “B” and “C” assignments to get the rest of your timeline filled out. Stamp Act Congress Proclamation of 1763 Boycott of British goods Sugar Act French and Indian War Stamp Act Sons of Liberty B Using your book, put the following events in order on your timeline. These events will fall on spaces 8-14 on your timeline. Make sure to list the date, what the event was about, and the significance of the event on the road to revolution. You will then work with classmates with “A” and “C” assignments to get the rest of your timeline filled out. Tea Act Repeal of Stamp Act Boston Tea Party Declaratory Act Boston Massacre Townshend Acts Committees of Correspondence C Using your book, put the following events in order on your timeline. These events will fall on spaces 15-21 on your timeline. Make sure to list the date, what the event was about, and the significance of the event on the road to revolution. You will then work with classmates with “A” and “B” assignments to get the rest of your timeline filled out. Olive Branch Petition Intolerable Acts Declaration of Independence First Continental Congress Second Continental Congress Bunker Hill Lexington and Concord Road to Revolution Timeline Year Event Description of Event 1 17541763 French and Indian War War between England and its colonies against the French and Native Americans (although there were Native Americans that supported the British as well). 2 1763 Proclamation of 1763 3 1764 Sugar Act 4 1765 Stamp Act 5 1765 Sons of Liberty (In response to Stamp Act) 6 1765 Stamp Act Congress 7 1766 Boycott of British Goods 8 1766 Repeal of Stamp Act 9 1766 Declaratory Act 10 1767 Townshend Acts Significance of Event Removed France from much of North America. Damaged relationship between colonists and Great Britain. British government stations troops in the colonies and leads to increased taxes on colonies to pay for the war. Undermined British authority – they could not enforce the law effectively. Banned colonies from moving west of the Appalachian mountains (to limit conflict with Native Americans) 1) Halves tax on foreign-made molasses Colonists complain it will reduce 2) Taxes imports that weren’t profits and claim the British are before violating their rights. Introduces 3) Changes prosecutors of idea of “No taxation without smuggling court cases from a representation” “sympathetic jury of However, almost exclusively colonists” to a single alleffects merchants. powerful judge First tax that effects colonists, Colonists must purchase special rich and poor, directly (as stamped paper for every legal opposed to just merchants like document, license, newspaper, the Sugar Act). Violators also pamphlet, and almanac and pay tried against single judge in stamp duties on playing cards and vice-admiralty court. (& Sons of dice. Liberty) Secret group of colonists unite in Stamp agents all over the protest against Great Britain, led by colonies resign and push back Sam Adams. the beginning of stamp sales 9 colonies create Stamp Act Congress and issue Declaration of Colonies are beginning to act as Rights and Grievances stating one and further pushes idea of Parliament cannot impose taxes on “No taxation without the colonies without representation representation.” in Parliament. Colonists boycott British made goods Parliament repeals the Stamp in order to repeal the stamp act Act in March of 1766 (Britain relies on their commerce) Victory for colonists, but Parliament Repeals Stamp Act Parliament will assert its power through Declaratory Act Parliament states it has the full right to make laws “to bind the colonies Parliament reinforces and and people in America.. in all cases emphasizes its power. whatsoever.” Colonists are enraged and resist. Protest “taxation without Indirect taxes on imports to colonies representation.” Another from Great Britain and a 3 cent tax boycott on British goods. British on Tea (popular in colonies) send troops to Boston to curb violence. 11 1770 Boston Massacre Fight that broke out in Boston that left 5 dead. Gave The British East India Co. the right to sell Tea Act tea to colonies free of taxes that the colonial tea distributors had to pay. Boston rebels disguise themselves as Boston Tea Native Americans, snuck on British Party ships, and dumped 15,000 lbs of tea into the harbor. Committees of Network of communication between Correspondence colonial leaders. Laws that Colonists deemed intolerable (ie: Quartering act – Intolerable Acts allowed British soldiers to live in private homes and buildings) Sold to colonists as a British attack on defenseless citizens – angers colonists. Angers colonists due to cost on colonial tea. 12 1773 13 1773 14 1772-4 15 1774 16 1774 First Continental Congress 56 colonial delegates meet to discuss colonial rights. 17 1775 Lexington and Concord Battle between British Soldiers and Massachusetts militiamen. Colonists defeat the British. Long period of discussion between colonial leaders. Debates over the future of colonies and British rule. Appoint the militiamen as Continental Army, with George Washington as the head. Authorized printing paper money. Organized a committee to deal with foreign nations. Battle between Militiamen camped outside of Boston and British Army at Breed’s Hill. 311 Colonists died, 1,000 casualties for British. 18 1775 Second Continental Congress 19 1775 Bunker Hill 20 21 King George III is angry and results in the passage of the Intolerable Acts as punishment. Will lead to first continental congress. Angers the colonists, will lead to committees of correspondence creating the first continental congress. Create a declaration of colonial rights, support protests in Massachusetts, and threaten to fight back against British force. 1775 Olive Branch Petition Petition to return to former peace between Britain and the Colonies King George rejects the petition and issues a proclamation stating that the colonies were in rebellion urges a naval blockage of the American Coast. 1776 Declaration of Independence Document declaring independence from Great Britain drawing on philosophical principles of John Locke. Independence for the Colonies, and clear step toward war.