Units of Measurements and Uncertainty
advertisement

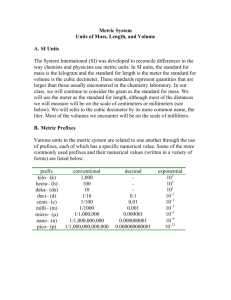
Units of Measurements and Uncertainty Objectives: • 1. Identify the metric units of measurement for length, mass, and volume. • 2. List the common metric prefixes and demonstrate how metric prefixes can be used to change units • 3. Explain why measuring always involves estimation. • 4. Describe two causes of uncertainty in measurements. • 5. Explain the difference between accuracy and precision. Key Terms: metric system, International System of Units (SI), base unit, mass, derived unit, volume, metric prefix, precision, accepted value, accuracy • Measurements are required for scientific inquiry. In order to have meaning a unit must be attached to the measurement. Throughout the different scientific disciplines you will find the use of the metric system. Becoming familiar with the standard prefixes will make solving equations and converting units easier. Metric Prefixes Prefix exa- Prefix Symbol E Meaning Scientific Notation 1,000,000,000,000,000,000 1018 peta- P 1,000,000,000,000,000 1015 teragigamegakilohectodekameter decicentimillimicronanopicofemtoatto- T G M k h da 1,000,000,000,000 1,000,000,000 1,000,000 1,000 100 10 1 0.1 0.01 0.001 0.000001 0.000000001 0.000000000001 0.000000000000001 0.000000000000000001 1012 109 106 103 102 101 100 10-1 10-2 10-3 10-6 10-9 10-12 10-15 10-18 d c m m n p f a SI Units The units used in science are those primarily used throughout the world. The International System of Units (SI) is a system based on the metric system. There are 7 fundamental units of measure Name Symbol length (distance) l (d) mass m time t electric charge Q temperature T amount of a n substance Unit of Measure meter kilogram second coulomb Kelvin mole Unit Symbol m kg s C K mol Unit Dimensions m kg s C K mol English to Metric Conversions: Distance 1km = 0.62 mi Mass 1kg = 2.2lbs Volume 3.744L = 1 gal 1m = 39.37in 907.185kg = 1ton 1 L = 1.06qt 1m = 1.0963yd 28.3g = 1oz 250ml = 1c 1cm = 0.39370in 453.59g = 1lb Pressure / Energy Temperature oC = 5/9 (oF-32) 101,325Pa = 1atm oK = oC + 273 4.184J = 1cal Other SI units derived from the base units Name acceleration Symbol a area capacitance density A C D electric current I electric field E intensity electric resistance R Unit of Measure Unit Symbol meter per second m/s2 squared square meter m2 Farad F kilogram per cubic kg/m3 meter Ampere A Newton per N/C coulomb Ohm d Unit Dimensions m/s2 Volt V Joule J Newton N hertz Hz Joule J lumens per square lx meter Henry H lumen lm Weber Wb Tesla (weber per T square meter) Volt V kg*m2/C*s2 kg*m2/s2 kg*m/s2 s-1 kg*m2/s2 cd/m2 m2 C2*s2/kg*m2 kg/m3 C/s kg*m/C*s2 kg*m2/C2*s emf energy force frequency heat illuminance x E F f Q E inductance luminous flux magnetic flux magnetic flux density potential difference power pressure L F f B P p Watt W Pascal (Newton Pa per square meter) kg*m2/s3 kg/m*s2 velocity v meters per secondm/s m/s volume work V W cubic meter Joule V m3 J kg*m2/C2 cd kg*m2/C*s kg/C*s kg*m2/C*s2 m3 kg*m2/s2 Some commonly used values in science. Speed of light in a vacuum Speed of sound Acceleration due to Gravity Average Earth - Sun distance (1 AU) Average Earth - moon distance Average radius of the Sun Average radius of Jupiter Average radius of Earth Average radius of the moon Average radius of the hydrogen atom Mass of the Sun Mass of Jupiter Mass of Earth Mass of the moon Proton mass Neutron mass Electron mass Atomic mass unit (amu) Electron charge Avogadro's number Planck's constant (h) Gas constant (R) Molar volume of gas 2.9979 x 108 m/s 330 - 350 m/s (depending on temperature) 9.8 m/s2 1.50 x 1011 m 3.84 x 108 m 6.96 x 108 m 6.99 x 107 m 6.37 x 106 m 1.74 x 106 m ~5 x 10-11 m 1.99 x 1030 kg 1.90 x 1027 kg 5.98 x 1024 kg 7.35 x 1022 kg 1.6726 x 10-27 kg 1.6749 x 10-27 kg 9.11 x 10-31 kg 1.66054 x 10-27 kg 1.6 x 10-19 C 6.02 x 1023 6.6262 x 10-34 J-s 0.08206 atm-L/mol-K 22.4L