File
advertisement

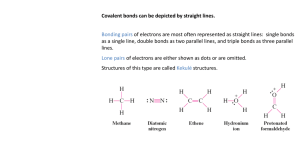
Chapter 8 ppt. 2 Bond Energy, Resonance and Formal Charges Breaking Vs. Forming Bonds To break bonds, energy must be added (required, endothermic, energy is positive) To form bonds, energy must be removed (given off, exothermic, energy is negative) Change in enthalpy: DH = sum of the energies required to break old bonds (positive signs) plus sum of energies released in formation of new bonds (negative signs) Bond Energies Energy stored in bonds can be used to determine energy accompanying various chemical reactions. Bond dissociation energies = energy required to break bonds (positive kJ/mol, endothermic)… reverse for forming bonds. Table 8.4 in book DH = all bonds broken – all bonds formed Must use a balanced equation! EXAMPLE data 8.4 in your book to determine DH for the following reaction. CH4(g) + 4F2(g) CF4(g) + 4HF(g) Use Answer: -1932 kJ Localized Electron Bonding Model…Highlights Defined: A molecule is composed of atoms that are bound together by sharing pairs of electrons using the atomic orbitals of the bonded atoms Localized to one of the atoms (LONE PAIR) Localized to the space between atoms (BONDING PAIR) LE Model Parts 1. Description of the valence electron arrangement in the molecule using Lewis structures 2. Prediction of the geometry of the molecule using the valence shell electron-pair repulsion (VSEPR) model 3. Description of the type of atomic orbitals used by the atoms to share electrons or hold lone pairs Exceptions to Octet Rule If valence electron total is odd, the octet rule doesn’t work Some atoms do not require all 8 valence electrons (or have more than 8) These molecules can exist in stable form Boron: forms compounds where boron has less than 8 electrons (ex: BF3) More than 8 only happens with elements in period 3 and beyond ex: SF6 See pg. 371 purple box for rules if needed Resonance Molecules with more than one possible electron dot structure Do not switch back and forth Molecules exist as a mixture (hybrid) of the resonance forms Use double headed arrow to signify Formal Charges Can’t use oxidation numbers because electrons are not shared evenly between atoms (electronegativities) Atoms can be assigned formal charges using the following: Formal Charge = (# valence e- on atom) – (# valence eassigned to the atom in the molecule) # valence e- assigned = (# lone pair e-) + (½ # shared e-) Atoms want to have formal charges close to zero Negative formal charges should be on the most electronegative atom ***ESTIMATES of charges (not exact charges) Resonance Example Draw the Lewis dot (Localized Electron Model) structure(s) of CO32- Example Assign formal charges to each atom in CO2 Which is more likely? Answer: two double bonds b/c all formal charges are zero Draw all resonance structures and show the most stable one for SCN Answer: two double bonds b/c N more electronegative than S