Causes of the Revolution
advertisement

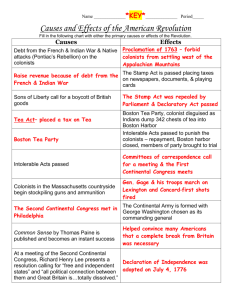
Jump Start – On Level Create a KWL chart in your notebook about the Boston Tea Party and complete it. What you KNOW What you want to LEARN What you LEARNED (to be completed after) Jump Start – Pre AP In your notebook…Civil disobedience is a refusal to follow a law we think is unjust. Create an example of civil disobedience in school, at home, and in an extra curricular activity. What punishment would fit those examples? Causes of the Revolution Causes of the Revolution Things we have seen so far… Mercantlism Economic theory that says a nations wealth depends on the amount of gold it has Raw materials were exported from colonies in order for Britain to make a profit – Cash crops such as lumber, grain, tobacco, etc. Colonies were established to benefit the mother country (Britain)…not for the colonists’ benefit French and Indian War England vs. France – Colonists fought for the British, Native Americans fought for the French. Both were competing for the Ohio River Valley. England won received all lands east of the Mississippi River, except new Orleans. BUT the war left England in huge debt…causing taxes. Proclamation of 1763 King George III said colonists could not settle west of the line because it was too costly to defend against the natives. Causes of the Revolution New Taxes Increase Conflict New Taxes Increase Conflict Conflict with Indians was not the only problem Britain was dealing with How were they going to pay off the debt from the French and Indian War? – Citizens in England were already overtaxed The government decided that the colonists should start paying their fair share Taxation Without Representation: SUGAR ACT (1764) SUMMARY Parliament passes the Sugar Act – Taxed sugar, molasses, and other products SIGNIFICANCE Colonists considered this Act tyranny – Unjust use of power They were not opposed to taxes, but this tax was passed by Parliament – They had no representation Taxation Without Representation: STAMP ACT (1765) SUMMARY The British government passed a new law called the Stamp Act – required colonists to buy a stamp for every piece of paper used (included newspapers, legal documents, and books) SIGNIFICANCE New kind of tax – – Colonists boycotted British goods – Applied within the colonies; not just imports Effected many more people Boycott – refusal to buy After months of protest, it was repealed in 1766 Taxation Without Representation: QUARTERING AND TOWNSHEND ACTS (1765) Quartering Act SUMMARY Required colonists to provide shelter and supplies to British troops stationed in their towns SIGNIFICANCE Providing these things cost the colonists $$$ – They saw this as the same thing as a tax Townshend Acts SUMMARY Taxed popular goods that the colonists imported from Britain – glass, lead, paint, paper, and tea SIGNIFICANCE Colonists felt that they were being taxed for necessities Samuel Adams led colonists in another boycott of British goods following the tax British government repealed all of the taxes except one… the Tea tax… Boston Massacre March 5, 1770 British troops vs. citizens of Boston A mob of Patriots antagonized British troops, who were quartered (stationed) in Boston British troops panicked and fired – 5 people killed, 10 injured Samuel Adams deemed this a “horrid massacre” – Contributed to colonial anger The Tea Act of 1773 On the same day as the Boston Massacre, Parliament proposed a repeal of the Townshend Act except on Tea. The act made British tea cheaper than foreign tea and gave a monopoly to the British East India Tea Company. Colonists felt that Britain was forcing them to pay another unjust tax, leading to more boycotts. Boston Tea Party A protest against the Tea Act of 1773 Made British tea cheaper than the foreign tea the colonists were smuggling – On Dec. 16, 1773, the Sons of Liberty dressed as Indians and dumped British tea into Boston harbor – Sons of Liberty- secret society, led by Samuel Adams, that were opposed to British policies 342 packages=45 tons=$12 million today Intolerable Acts Passed to punish the Massachusetts for the Boston Tea Party – – – – Closed the port of Boston until they paid for the destroyed tea Placed the government of Massachusetts under British control British soldiers accused of murder would now stand trial in England, not the colonies Sent even more troops to enforce the new law Instead of giving in, the colonists banded even closer together Virginia called for a Congress to discuss a solution to the conflict with Britain Wrap Up Civil disobedience is a refusal to follow a law we think is unjust. In what was the Boston Tea Party an example? Do you think it was justified? Explain your reasoning. First Continental Congress In September of 1774, delegates met from all of the colonies – – – Carpenter’s Hall, Philadelphia Agreed to send a message to King George urging him to consider their complaints Called for a boycott of British goods until Intolerable Acts were repealed Planned to meet again in seven months